 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Palabras clave: Ranolazine, stable coronary artery disease, CAD, Epistemonikos, GRADE.
INTRODUCTION
There are several effective therapeutic alternatives for stable coronary artery, in terms of prevention of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, the best way to achieve symptomatic control is a matter of debate, particularly in those who do not respond to first-line therapy. This summary aims to evaluate the role of ranolazine as an additional therapy to standard antianginal treatment in patients with persistent symptoms.
METHODS
To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified four systematic reviews including 16 studies overall, all of which were randomized trials. We concluded additional treatment with ranolazine might decrease the frequency of anginal episodes but increase adverse effects. It probably has no effect on the risk of death or acute myocardial infarction.
Coronary artery disease includes a wide range of clinical manifestations, from acute presentations, such as myocardial infarction, to chronic conditions, such as stable coronary artery disease. The latter has a significant impact on both mortality and quality of life. There are several pharmacological alternatives with proven effect on reducing mortality - both cardiovascular and total - and improving the quality of life through symptomatic relief. However, there is a subgroup of patients that does not respond adequately to such therapy.
Ranolazine is a drug that inhibits late sodium currents that are abnormally active in the ischemic myocardiocyte. Its effect prevents intracellular calcium overload (as it is exchanged for sodium) with the consequent diastolic dysfunction that underlies the angina. This is why it has been proposed as an effective therapeutic option in stable coronary disease with suboptimal response to conventional treatment.
To answer the question, we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a section of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We found four systematic reviews [1],[2],[3],[4] that included 16 primary studies reported in 19 references [5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10],[11],[12],[13],[14],[15],[16], However, five trials were conducted in patients without stable coronary disease (microvascular angina or acute coronary syndrome) [7],[9],[10],[11],[22]; five used ranolazine as monotherapy [12],[13],[14],[17],[23]; and two measured clinically irrelevant outcomes (time to ST segment depression and mild adverse effects) [6],[16]. This table and the summary in general are based on four randomized trials that used ranolazine as an additional therapy in patients with stable coronary artery disease and reported outcomes critical for decision-making [5],[8],[18],[20]. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
All trials included symptomatic adults with coronary artery disease confirmed by angiography. One trial [20] included patients with ejection fraction less than 40%, while the remaining three excluded patients with severe heart failure (defined as NYHA functional class III or IV) [5],[18],[21]. All trials excluded patients with decompensated cardiac comorbidities (hypertension, pericarditis, among others) or systemic diseases (such as liver damage, chronic renal failure, diabetes). Likewise, three of the trials [5],[18],[21] excluded patients with a history of arrhythmia or comedication with proarrhythmic drugs. The average age of the participants ranged from 61 to 72 years in the different trials. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
All trials used ranolazine 1 g every 12 hours. Additionally, one trial [20] used standard medical therapy with ranolazine 500 mg every 12 hours; while another trial [21] also used standard medical therapy associated with ranolazine 750 mg every 12 hours. All trials compared against placebo associated with standard treatment. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The outcomes were grouped by the systematic reviews as follows:
The average follow-up of the trials was 5.75 months with a range from 9 weeks to 14 months. |
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
The information on the effects of ranolazine on symptomatic stable coronary artery disease is based on four randomized trials involving 2364 patients.
Three trials measured all cause mortality (2053 patients) [5],[8],[18], three measured quality of life (1533 patients) [8],[18],[20], two reported acute myocardial infarction (1509 patients) [5],[18] and three reported the frequency of anginal episodes (2004 patients) [5],[8],[18].
The summary of findings is as follows:
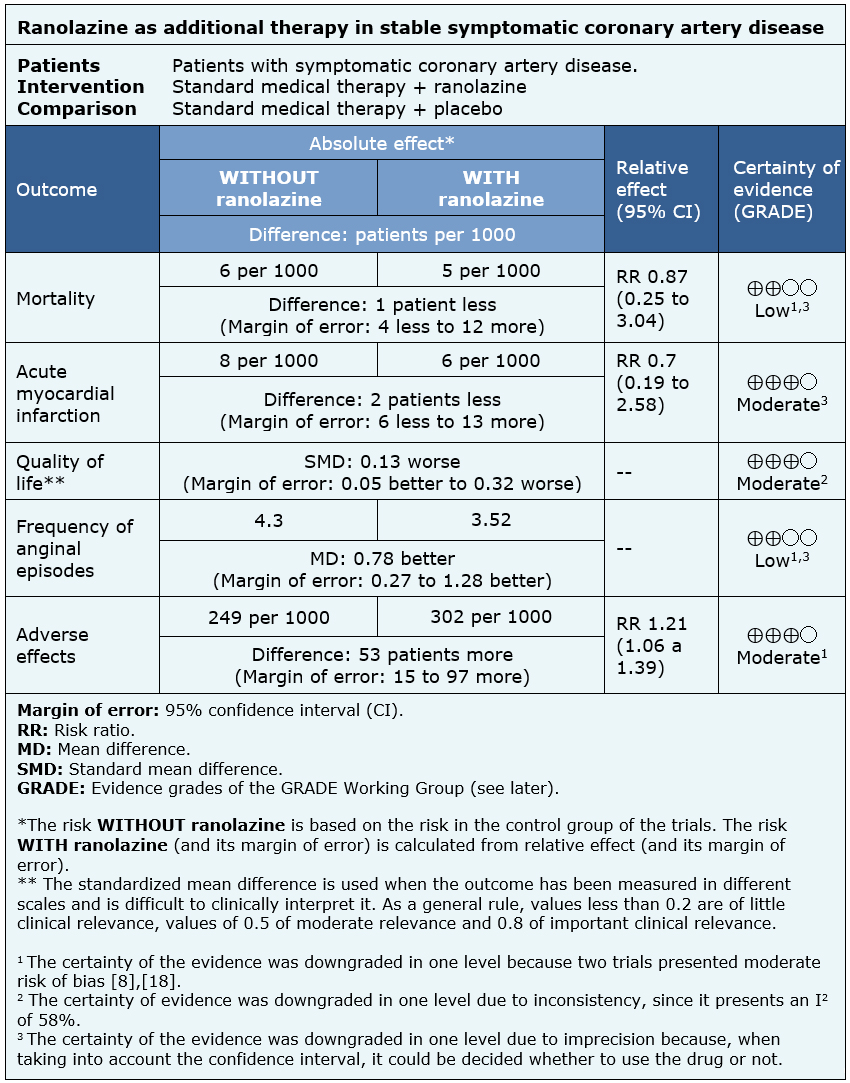
| Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings - iSoF) |
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
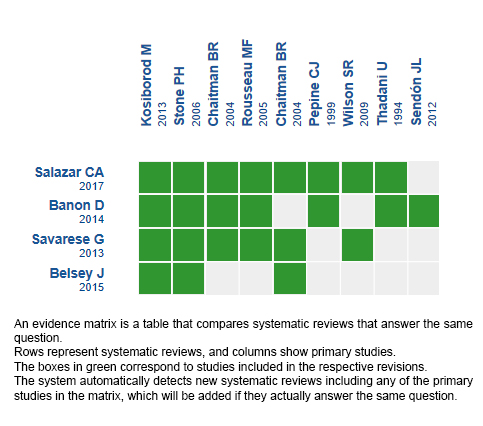
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Ranolazine for ischemic heart disease.
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

INTRODUCTION
There are several effective therapeutic alternatives for stable coronary artery, in terms of prevention of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. However, the best way to achieve symptomatic control is a matter of debate, particularly in those who do not respond to first-line therapy. This summary aims to evaluate the role of ranolazine as an additional therapy to standard antianginal treatment in patients with persistent symptoms.
METHODS
To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified four systematic reviews including 16 studies overall, all of which were randomized trials. We concluded additional treatment with ranolazine might decrease the frequency of anginal episodes but increase adverse effects. It probably has no effect on the risk of death or acute myocardial infarction.
 Autores:
Benjamín Sanfuentes[1,2], Juan Francisco Bulnes[2,3]
Autores:
Benjamín Sanfuentes[1,2], Juan Francisco Bulnes[2,3]

Citación: Sanfuentes B, Bulnes J. Ranolazine as an additional antianginal therapy in patients with stable symptomatic coronary artery disease. Medwave 2018;18(7):e7331 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2018.07.7331
Fecha de envío: 8/10/2018
Fecha de aceptación: 5/11/2018
Fecha de publicación: 12/11/2018
Origen: Este artículo es producto del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project de la Fundación Epistemonikos, en colaboración con Medwave para su publicación.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares sin ciego por parte del equipo metodológico del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project.

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Banon D, Filion KB, Budlovsky T, Franck C, Eisenberg MJ. The usefulness of ranolazine for the treatment of refractory chronic stable angina pectoris as determined from a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 15;113(6):1075-82. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Banon D, Filion KB, Budlovsky T, Franck C, Eisenberg MJ. The usefulness of ranolazine for the treatment of refractory chronic stable angina pectoris as determined from a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 15;113(6):1075-82. | CrossRef | PubMed | Belsey J, Savelieva I, Mugelli A, Camm AJ. Relative efficacy of antianginal drugs used as add-on therapy in patients with stable angina: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015 Jul;22(7):837-48. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Belsey J, Savelieva I, Mugelli A, Camm AJ. Relative efficacy of antianginal drugs used as add-on therapy in patients with stable angina: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015 Jul;22(7):837-48. | CrossRef | PubMed | Salazar CA, Basilio Flores JE, Veramendi Espinoza LE, Mejia Dolores JW, Rey Rodriguez DE, Loza Munárriz C. Ranolazine for stable angina pectoris. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 8;2:CD011747. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Salazar CA, Basilio Flores JE, Veramendi Espinoza LE, Mejia Dolores JW, Rey Rodriguez DE, Loza Munárriz C. Ranolazine for stable angina pectoris. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 8;2:CD011747. | CrossRef | PubMed | Savarese G, Rosano G, D'Amore C, Musella F, Della Ratta GL, Pellegrino AM, Formisano T, Vitagliano A, Cirillo A, Cice G, Fimiani L, del Guercio L, Trimarco B, Perrone-Filardi P. Effects of ranolazine in symptomatic patients with stable coronary artery disease. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2013 Nov 15;169(4):262-70. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Savarese G, Rosano G, D'Amore C, Musella F, Della Ratta GL, Pellegrino AM, Formisano T, Vitagliano A, Cirillo A, Cice G, Fimiani L, del Guercio L, Trimarco B, Perrone-Filardi P. Effects of ranolazine in symptomatic patients with stable coronary artery disease. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2013 Nov 15;169(4):262-70. | CrossRef | PubMed | Kosiborod M, Arnold SV, Spertus JA, McGuire DK, Li Y, Yue P, Ben-Yehuda O, Katz A, Jones PG, Olmsted A, Belardinelli L, Chaitman BR. Evaluation of ranolazine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic stable angina: results from the TERISA randomized clinical trial (Type 2 Diabetes Evaluation of Ranolazine in Subjects With Chronic Stable Angina). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 May 21;61(20):2038-45. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kosiborod M, Arnold SV, Spertus JA, McGuire DK, Li Y, Yue P, Ben-Yehuda O, Katz A, Jones PG, Olmsted A, Belardinelli L, Chaitman BR. Evaluation of ranolazine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic stable angina: results from the TERISA randomized clinical trial (Type 2 Diabetes Evaluation of Ranolazine in Subjects With Chronic Stable Angina). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 May 21;61(20):2038-45. | CrossRef | PubMed | Pepine CJ, Wolff AA. A controlled trial with a novel anti-ischemic agent, ranolazine, in chronic stable angina pectoris that is responsive to conventional antianginal agents. Ranolazine Study Group. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Jul 1;84(1):46-50. | PubMed |
Pepine CJ, Wolff AA. A controlled trial with a novel anti-ischemic agent, ranolazine, in chronic stable angina pectoris that is responsive to conventional antianginal agents. Ranolazine Study Group. Am J Cardiol. 1999 Jul 1;84(1):46-50. | PubMed | Wilson SR, Scirica BM, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Buros JL, Chaitman BR, Morrow DA. Efficacy of ranolazine in patients with chronic angina observations from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled MERLIN-TIMI (Metabolic Efficiency With Ranolazine for Less Ischemia in Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes) 36 Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Apr 28;53(17):1510-6. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Wilson SR, Scirica BM, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Buros JL, Chaitman BR, Morrow DA. Efficacy of ranolazine in patients with chronic angina observations from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled MERLIN-TIMI (Metabolic Efficiency With Ranolazine for Less Ischemia in Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes) 36 Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Apr 28;53(17):1510-6. | CrossRef | PubMed | Sendón JL, Lee S, Cheng ML, Ben-Yehuda O; CARISA study investigators. Effects of ranolazine on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina receiving maximally-tolerated background therapy: analysis from the Combination Assessment of Ranolazine In Stable Angina (CARISA) randomized trial. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012 Oct;19(5):952-9. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sendón JL, Lee S, Cheng ML, Ben-Yehuda O; CARISA study investigators. Effects of ranolazine on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina receiving maximally-tolerated background therapy: analysis from the Combination Assessment of Ranolazine In Stable Angina (CARISA) randomized trial. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012 Oct;19(5):952-9. | CrossRef | PubMed | Mehta PK, Goykhman P, Thomson LE, Shufelt C, Wei J, Yang Y, Gill E, Minissian M, Shaw LJ, Slomka PJ, Slivka M, Berman DS, Bairey Merz CN. Ranolazine improves angina in women with evidence of myocardial ischemia but no obstructive coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 May;4(5):514-22. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Mehta PK, Goykhman P, Thomson LE, Shufelt C, Wei J, Yang Y, Gill E, Minissian M, Shaw LJ, Slomka PJ, Slivka M, Berman DS, Bairey Merz CN. Ranolazine improves angina in women with evidence of myocardial ischemia but no obstructive coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 May;4(5):514-22. | CrossRef | PubMed | Bairey Merz CN, Handberg EM, Shufelt CL, Mehta PK, Minissian MB, Wei J, Thomson LE, Berman DS, Shaw LJ, Petersen JW, Brown GH, Anderson RD, Shuster JJ, Cook-Wiens G, Rogatko A, Pepine CJ. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of late Na current inhibition (ranolazine) in coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD): impact on angina and myocardial perfusion reserve. Eur Heart J. 2016 May 14;37(19):1504-13. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Bairey Merz CN, Handberg EM, Shufelt CL, Mehta PK, Minissian MB, Wei J, Thomson LE, Berman DS, Shaw LJ, Petersen JW, Brown GH, Anderson RD, Shuster JJ, Cook-Wiens G, Rogatko A, Pepine CJ. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of late Na current inhibition (ranolazine) in coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD): impact on angina and myocardial perfusion reserve. Eur Heart J. 2016 May 14;37(19):1504-13. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Villano A, Di Franco A, Nerla R, Sestito A, Tarzia P, Lamendola P, Di Monaco A, Sarullo FM, Lanza GA, Crea F. Effects of ivabradine and ranolazine in patients with microvascular angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2013 Jul 1;112(1):8-13. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Villano A, Di Franco A, Nerla R, Sestito A, Tarzia P, Lamendola P, Di Monaco A, Sarullo FM, Lanza GA, Crea F. Effects of ivabradine and ranolazine in patients with microvascular angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2013 Jul 1;112(1):8-13. | CrossRef | PubMed | Alexander KP, Weisz G, Prather K, James S, Mark DB, Anstrom KJ, Davidson-Ray L, Witkowski A, Mulkay AJ, Osmukhina A, Farzaneh-Far R, Ben-Yehuda O, Stone GW, Ohman EM. Effects of Ranolazine on Angina and Quality of Life After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Incomplete Revascularization: Results From the Ranolazine for Incomplete Vessel Revascularization (RIVER-PCI) Trial. Circulation. 2016 Jan 5;133(1):39-47. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Alexander KP, Weisz G, Prather K, James S, Mark DB, Anstrom KJ, Davidson-Ray L, Witkowski A, Mulkay AJ, Osmukhina A, Farzaneh-Far R, Ben-Yehuda O, Stone GW, Ohman EM. Effects of Ranolazine on Angina and Quality of Life After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Incomplete Revascularization: Results From the Ranolazine for Incomplete Vessel Revascularization (RIVER-PCI) Trial. Circulation. 2016 Jan 5;133(1):39-47. | CrossRef | PubMed | Thadani U, Ezekowitz M, Fenney L, Chiang YK. Double-blind efficacy and safety study of a novel anti-ischemic agent, ranolazine, versus placebo in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris. Ranolazine Study Group. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):726-34. | PubMed |
Thadani U, Ezekowitz M, Fenney L, Chiang YK. Double-blind efficacy and safety study of a novel anti-ischemic agent, ranolazine, versus placebo in patients with chronic stable angina pectoris. Ranolazine Study Group. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):726-34. | PubMed | Chaitman BR, Skettino SL, Parker JO, Hanley P, Meluzin J, Kuch J, Pepine CJ, Wang W, Nelson JJ, Hebert DA, Wolff AA; MARISA Investigators. Anti-ischemic effects and long-term survival during ranolazine monotherapy in patients with chronic severe angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Apr 21;43(8):1375-82. | PubMed |
Chaitman BR, Skettino SL, Parker JO, Hanley P, Meluzin J, Kuch J, Pepine CJ, Wang W, Nelson JJ, Hebert DA, Wolff AA; MARISA Investigators. Anti-ischemic effects and long-term survival during ranolazine monotherapy in patients with chronic severe angina. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004 Apr 21;43(8):1375-82. | PubMed | Weisz G, Généreux P, Iñiguez A, Zurakowski A, Shechter M, Alexander KP, Dressler O, Osmukhina A, James S, Ohman EM, Ben-Yehuda O, Farzaneh-Far R, Stone GW; RIVER-PCI investigators. Ranolazine in patients with incomplete revascularisation after percutaneous coronary intervention (RIVER-PCI): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 Jan 9;387(10014):136-45. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Weisz G, Généreux P, Iñiguez A, Zurakowski A, Shechter M, Alexander KP, Dressler O, Osmukhina A, James S, Ohman EM, Ben-Yehuda O, Farzaneh-Far R, Stone GW; RIVER-PCI investigators. Ranolazine in patients with incomplete revascularisation after percutaneous coronary intervention (RIVER-PCI): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 Jan 9;387(10014):136-45. | CrossRef | PubMed | Babalis D, Tritakis V, Floros G, Mouzarou A, Kafkas N, Bampali K, Mertzanos G. Effects of ranolazine on left ventricular diastolic and systolic function in patients with chronic coronary disease and stable angina. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2015 May-Jun;56(3):237-41. | PubMed |
Babalis D, Tritakis V, Floros G, Mouzarou A, Kafkas N, Bampali K, Mertzanos G. Effects of ranolazine on left ventricular diastolic and systolic function in patients with chronic coronary disease and stable angina. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2015 May-Jun;56(3):237-41. | PubMed | Rousseau MF, Pouleur H, Cocco G, Wolff AA. Comparative efficacy of ranolazine versus atenolol for chronic angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2005 Feb 1;95(3):311-6. | PubMed |
Rousseau MF, Pouleur H, Cocco G, Wolff AA. Comparative efficacy of ranolazine versus atenolol for chronic angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2005 Feb 1;95(3):311-6. | PubMed | Stone PH, Gratsiansky NA, Blokhin A, Huang IZ, Meng L; ERICA Investigators. Antianginal efficacy of ranolazine when added to treatment with amlodipine: the ERICA (Efficacy of Ranolazine in Chronic Angina) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Aug 1;48(3):566-75. | PubMed |
Stone PH, Gratsiansky NA, Blokhin A, Huang IZ, Meng L; ERICA Investigators. Antianginal efficacy of ranolazine when added to treatment with amlodipine: the ERICA (Efficacy of Ranolazine in Chronic Angina) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Aug 1;48(3):566-75. | PubMed | Timmis AD, Chaitman BR, Crager M. Effects of ranolazine on exercise tolerance and HbA1c in patients with chronic angina and diabetes. Eur Heart J. 2006 Jan;27(1):42-8. | PubMed |
Timmis AD, Chaitman BR, Crager M. Effects of ranolazine on exercise tolerance and HbA1c in patients with chronic angina and diabetes. Eur Heart J. 2006 Jan;27(1):42-8. | PubMed | Shammas NW, Shammas GA, Keyes K, Duske S, Kelly R, Jerin M. Ranolazine versus placebo in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and persistent chest pain or dyspnea despite optimal medical and revascularization therapy: randomized, double-blind crossover pilot study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015 Mar 23;11:469-74. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Shammas NW, Shammas GA, Keyes K, Duske S, Kelly R, Jerin M. Ranolazine versus placebo in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and persistent chest pain or dyspnea despite optimal medical and revascularization therapy: randomized, double-blind crossover pilot study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015 Mar 23;11:469-74. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Chaitman BR, Pepine CJ, Parker JO, Skopal J, Chumakova G, Kuch J, Wang W, Skettino SL, Wolff AA; Combination Assessment of Ranolazine In Stable Angina (CARISA) Investigators. Effects of ranolazine with atenolol, amlodipine, or diltiazem on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004 Jan 21;291(3):309-16. | PubMed |
Chaitman BR, Pepine CJ, Parker JO, Skopal J, Chumakova G, Kuch J, Wang W, Skettino SL, Wolff AA; Combination Assessment of Ranolazine In Stable Angina (CARISA) Investigators. Effects of ranolazine with atenolol, amlodipine, or diltiazem on exercise tolerance and angina frequency in patients with severe chronic angina: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004 Jan 21;291(3):309-16. | PubMed | Tagliamonte E, Rigo F, Cirillo T, Astarita C, Quaranta G, Marinelli U, Caruso A, Romano C, Capuano N. Effects of ranolazine on noninvasive coronary flow reserve in patients with myocardial ischemia but without obstructive coronary artery disease. Echocardiography. 2015 Mar;32(3):516-21. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tagliamonte E, Rigo F, Cirillo T, Astarita C, Quaranta G, Marinelli U, Caruso A, Romano C, Capuano N. Effects of ranolazine on noninvasive coronary flow reserve in patients with myocardial ischemia but without obstructive coronary artery disease. Echocardiography. 2015 Mar;32(3):516-21. | CrossRef | PubMed | Sandhiya S, Dkhar SA, Pillai AA, George M, Jayaraman B, Chandrasekaran A. Comparison of ranolazine and trimetazidine on glycemic status in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease - a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jan;9(1):OC01-5. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Sandhiya S, Dkhar SA, Pillai AA, George M, Jayaraman B, Chandrasekaran A. Comparison of ranolazine and trimetazidine on glycemic status in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease - a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jan;9(1):OC01-5. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Task Force Members, Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S, Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, Bugiardini R, Crea F, Cuisset T, Di Mario C. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. European heart journal. 2013 Aug 30;34(38):2949-3003. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2014 Sep
1;35(33):2260-1. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Task Force Members, Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S, Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, Bugiardini R, Crea F, Cuisset T, Di Mario C. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. European heart journal. 2013 Aug 30;34(38):2949-3003. Erratum in: Eur Heart J. 2014 Sep
1;35(33):2260-1. | CrossRef | PubMed | Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, Berra K, Blankenship JC, Dallas AP, Douglas PS, Foody JM, Gerber TC, Hinderliter AL, King SB 3rd, Kligfield PD, Krumholz HM, Kwong RY, Lim MJ, Linderbaum JA, Mack MJ, Munger MA, Prager RL, Sabik JF, Shaw LJ, Sikkema JD, Smith CR Jr, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Williams SV; American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines; American College of Physicians; American Association for Thoracic Surgery; Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Thoracic Surgeons. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS Guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Dec 18;60(24):e44-e164. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, Berra K, Blankenship JC, Dallas AP, Douglas PS, Foody JM, Gerber TC, Hinderliter AL, King SB 3rd, Kligfield PD, Krumholz HM, Kwong RY, Lim MJ, Linderbaum JA, Mack MJ, Munger MA, Prager RL, Sabik JF, Shaw LJ, Sikkema JD, Smith CR Jr, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Williams SV; American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines; American College of Physicians; American Association for Thoracic Surgery; Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Thoracic Surgeons. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS Guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Dec 18;60(24):e44-e164. | CrossRef | PubMed | Jones D, Weeraman D, Hussain M, Colicchia M, Mathur A, Baumbach A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of novel interventions for refractory angina. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018089748. | Link |
Jones D, Weeraman D, Hussain M, Colicchia M, Mathur A, Baumbach A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of novel interventions for refractory angina. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018089748. | Link | Shaukat F. Management of Ischemic Heart Disease With Angiwell-XR (Ranolazine). NCT03486561. | Link |
Shaukat F. Management of Ischemic Heart Disease With Angiwell-XR (Ranolazine). NCT03486561. | Link | Buch A. The Effectiveness of Ranolazine in Reducing Cardiac Ischaemia Induced by Chronic Total Occlusions of Coronary Arteries. NCT02423265. | Link |
Buch A. The Effectiveness of Ranolazine in Reducing Cardiac Ischaemia Induced by Chronic Total Occlusions of Coronary Arteries. NCT02423265. | Link | Buch A. The Effectiveness of Ranolazine in Reducing Cardiac Ischaemia Induced by Chronic Total Occlusions of Coronary Arteries. NCT02423265. | Link |
Buch A. The Effectiveness of Ranolazine in Reducing Cardiac Ischaemia Induced by Chronic Total Occlusions of Coronary Arteries. NCT02423265. | Link |