 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Loop diuretics are widely used in acute heart failure. However, there is controversy about the superiority of continuous infusion over bolus administration. Searching in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening 30 databases, we identified four systematic reviews including 11 pertinent randomized controlled trials overall. We combined the evidence using meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings following the GRADE approach. We concluded continuous administration of loop diuretics probably reduces mortality and length of stay compared to intermittent administration in patients with acute heart failure.
The management of patients with acute heart failure is largely based on the use of loop diuretics. However, they may be administered as intermittent bolus or continuous infusion.
While bolus administration of furosemide is associated with lower costs, it could increase adverse effects as a consequence of changes in volume which would increase plasma concentration of the drug. Moreover, high doses administered intermittently may produce acute tolerance to diuretics by compensatory renal retention after their effect has subsided. Continuous administration of furosemide has been proposed as a solution to these problems but there is controversy about the clinical effects of both approaches.
We used Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening more than 30 databases, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. With this information we generated a structured summary using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We found four systematic reviews [1],[2],[3],[4], including 11 randomized controlled trials reported in 12 articles [5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10],[11],[12],[13],[14],[15],[16]. |
|
What types of patients were included |
All studies included adults with acute heart failure with an average age ranging from 53 to 74 years. Four studies included patients with functional capacity between III and IV [8],[11],[15], two studies included patients with functional capacity between II and III [5],[10] while the remaining studies did not describe functional capacity. Regarding renal function, all studies included patients with creatinine ≤2 mg/dL. |
|
What types of interventions were included |
Regarding continuous infusion of loop diuretics, one study used torsemide [10] and the remaining ten used furosemide; of these, four [7],[11],[14],[15] used a loading dose of 40 mg followed by continuous infusion at variable rate. One study did not report doses and only reported it was determined by the attending physician. All studies compared against bolus injection. Two studies [8],[10] administered bolus injection once a day, seven [5],[6],[7],[9],[11],[14],[15] twice a day and one used three boluses per day. Daily doses of furosemide ranged from 120 mg/day to 2000 mg/day in the continuous infusion group and from 90 mg/day to 2000 mg/day in the bolus injection group. |
|
What types of outcomes |
All-cause mortality, cardiac death, length of stay, electrolyte disturbances, changes in serum creatinine, adverse effects (hair loss and tinnitus), body weight, urine output, and urinary sodium excretion. |
|
We found three systematic reviews [5], [6], [7], including 14 studies reported in 21 references [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25], [26], [27], [28]. Eight studies correspond to randomized controlled trials (15 references [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [16], [17], [19], [21], [22], [23], [24], [26], [27]). This table and the summary in general are based on the latter. One study [15] did not contribute data to any of the outcomes of interest. |
Information on the effects of continuous loop diuretics compared to bolus injection for congestive heart failure is based on 11 randomized trials including 622 patients. Four studies reported overall mortality and four studies reported length of stay.


|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
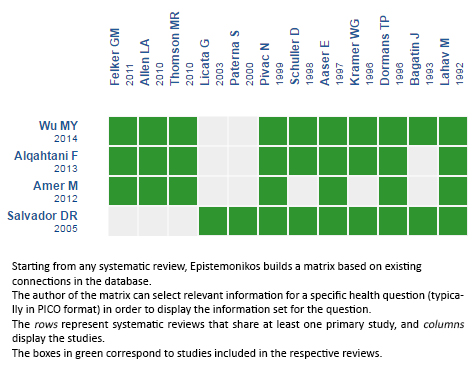
Follow the link to access the interactive version Continuous infusion versus bolus injection
of loop diuretics for heart failure
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier. After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
The details about the methods used to produce these summaries are described here http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
These summaries follow a rigorous process of internal peer review.
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Loop diuretics are widely used in acute heart failure. However, there is controversy about the superiority of continuous infusion over bolus administration. Searching in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening 30 databases, we identified four systematic reviews including 11 pertinent randomized controlled trials overall. We combined the evidence using meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings following the GRADE approach. We concluded continuous administration of loop diuretics probably reduces mortality and length of stay compared to intermittent administration in patients with acute heart failure.
 Autores:
Patricio Zepeda[1,3], Carmen Rain[1,3], Paola Sepúlveda[1,2,3]
Autores:
Patricio Zepeda[1,3], Carmen Rain[1,3], Paola Sepúlveda[1,2,3]

Citación: Zepeda P, Rain C, Sepúlveda P. Continuous infusion or bolus injection of loop diuretics for congestive heart failure?. Medwave 2016;16(suppl 2):e6426 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.6426
Fecha de publicación: 22/4/2016

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Susantitaphong P, Dahal K, Jaber BL. A meta-analysis of continuous vs intermittent infusion of loop diuretics in hospitalized patients. J Crit Care. 2014 Feb;29(1):10-7. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Susantitaphong P, Dahal K, Jaber BL. A meta-analysis of continuous vs intermittent infusion of loop diuretics in hospitalized patients. J Crit Care. 2014 Feb;29(1):10-7. | CrossRef | PubMed | Wu MY, Chang NC, Su CL, Hsu YH, Chen TW, Lin YF, et al. Loop diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Crit Care. 2014 Feb;29(1):2-9. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Wu MY, Chang NC, Su CL, Hsu YH, Chen TW, Lin YF, et al. Loop diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Crit Care. 2014 Feb;29(1):2-9. | CrossRef | PubMed | Salvador DR, Rey NR, Ramos GC, Punzalan FE. Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics in congestive heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003178. | PubMed |
Salvador DR, Rey NR, Ramos GC, Punzalan FE. Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics in congestive heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003178. | PubMed | Amer M, Adomaityte J, Qayyum R. Continuous infusion versus intermittent bolus furosemide in ADHF: an updated meta-analysis of randomized control trials. J Hosp Med. 2012 Mar;7(3):270-5. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Amer M, Adomaityte J, Qayyum R. Continuous infusion versus intermittent bolus furosemide in ADHF: an updated meta-analysis of randomized control trials. J Hosp Med. 2012 Mar;7(3):270-5. | CrossRef | PubMed | Aaser E, Gullestad L, Tølløfsrud S, Lundberg J, Hall C, Djøseland O, et al. Effect of bolus injection versus continuous infusion of furosemide on diuresis and neurohormonal activation in patients with severe congestive heart failure. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997 Jul;57(4):361-7 | PubMed |
Aaser E, Gullestad L, Tølløfsrud S, Lundberg J, Hall C, Djøseland O, et al. Effect of bolus injection versus continuous infusion of furosemide on diuresis and neurohormonal activation in patients with severe congestive heart failure. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997 Jul;57(4):361-7 | PubMed | Allen LA, Turer AT, Dewald T, Stough WG, Cotter G, O'Connor CM. Continuous versus bolus dosing of Furosemide for patients hospitalized for heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2010 Jun 15;105(12):1794- | CrossRef | PubMed |
Allen LA, Turer AT, Dewald T, Stough WG, Cotter G, O'Connor CM. Continuous versus bolus dosing of Furosemide for patients hospitalized for heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2010 Jun 15;105(12):1794- | CrossRef | PubMed | Bagatin J, Sardelic S, Gancevic I. Diuretic efficiency of furosemide in continuous intravenous infusion vs. bolus injection in congestive heart failure: results of a pilot study. Pharmaca. 1993;31:279–86.
Bagatin J, Sardelic S, Gancevic I. Diuretic efficiency of furosemide in continuous intravenous infusion vs. bolus injection in congestive heart failure: results of a pilot study. Pharmaca. 1993;31:279–86.  Dormans TP, van Meyel JJ, Gerlag PG, Tan Y, Russel FG, Smits P. Diuretic efficacy of high dose furosemide in severe heart failure: bolus injection versus continuous infusion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Aug;28(2):376-82. | PubMed |
Dormans TP, van Meyel JJ, Gerlag PG, Tan Y, Russel FG, Smits P. Diuretic efficacy of high dose furosemide in severe heart failure: bolus injection versus continuous infusion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Aug;28(2):376-82. | PubMed | Felker GM, Lee KL, Bull DA, Redfield MM, Stevenson LW, Goldsmith SR, et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2011 Mar 3;364(9):797-805. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Felker GM, Lee KL, Bull DA, Redfield MM, Stevenson LW, Goldsmith SR, et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2011 Mar 3;364(9):797-805. | CrossRef | PubMed | Kramer WG, Smith WB, Ferguson J, Serpas T, Grant AG 3rd, Black PK, et al. Pharmacodynamics of torsemide administered as an intravenous injection and as a continuous infusion to patients with congestive heart failure. J Clin Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;36(3):265-70. | PubMed |
Kramer WG, Smith WB, Ferguson J, Serpas T, Grant AG 3rd, Black PK, et al. Pharmacodynamics of torsemide administered as an intravenous injection and as a continuous infusion to patients with congestive heart failure. J Clin Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;36(3):265-70. | PubMed | Lahav M, Regev A, Ra'anani P, Theodor E. Intermittent administration of furosemide vs continuous infusion preceded by a loading dose for congestive heart failure. Chest. 1992 Sep;102(3):725-31. | PubMed |
Lahav M, Regev A, Ra'anani P, Theodor E. Intermittent administration of furosemide vs continuous infusion preceded by a loading dose for congestive heart failure. Chest. 1992 Sep;102(3):725-31. | PubMed | Licata G, Di Pasquale P, Parrinello G, Cardinale A, Scandurra A, Follone G, et al. Effects of high-dose furosemide and small-volume hypertonic saline solution infusion in comparison with a high dose of furosemide as bolus in refractory congestive heart failure: long-term effects.Am Heart J. 2003 Mar;145(3):459-66. | PubMed |
Licata G, Di Pasquale P, Parrinello G, Cardinale A, Scandurra A, Follone G, et al. Effects of high-dose furosemide and small-volume hypertonic saline solution infusion in comparison with a high dose of furosemide as bolus in refractory congestive heart failure: long-term effects.Am Heart J. 2003 Mar;145(3):459-66. | PubMed | Paterna S, Di Pasquale P, Parrinello G, Amato P, Cardinale A, Follone G, et al. Effects of high-dose furosemide and small-volume hypertonic saline solution infusion in comparison with a high dose of furosemide as a bolus, in refractory congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2000 Sep;2(3):305-13. | PubMed |
Paterna S, Di Pasquale P, Parrinello G, Amato P, Cardinale A, Follone G, et al. Effects of high-dose furosemide and small-volume hypertonic saline solution infusion in comparison with a high dose of furosemide as a bolus, in refractory congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2000 Sep;2(3):305-13. | PubMed | Pivac N, Rumboldt Z, Sardelić S, Bagatin J, Polić S, Ljutić D, et al. Diuretic effects of furosemide infusion versus bolus injection in congestive heart failure. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1998;18(3):121-8. | PubMed |
Pivac N, Rumboldt Z, Sardelić S, Bagatin J, Polić S, Ljutić D, et al. Diuretic effects of furosemide infusion versus bolus injection in congestive heart failure. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1998;18(3):121-8. | PubMed | Schuller D, Lynch JP, Fine D. Protocol-guided diuretic management: comparison of furosemide by continuous infusion and intermittent bolus. Crit Care Med. 1997 Dec;25(12):1969-75. | PubMed |
Schuller D, Lynch JP, Fine D. Protocol-guided diuretic management: comparison of furosemide by continuous infusion and intermittent bolus. Crit Care Med. 1997 Dec;25(12):1969-75. | PubMed | Thomson MR, Nappi JM, Dunn SP, Hollis IB, Rodgers JE, Van Bakel AB. Continuous versus intermittent infusion of furosemide in acute decompensated heart failure. J Card Fail. 2010 Mar;16(3):188-93. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Thomson MR, Nappi JM, Dunn SP, Hollis IB, Rodgers JE, Van Bakel AB. Continuous versus intermittent infusion of furosemide in acute decompensated heart failure. J Card Fail. 2010 Mar;16(3):188-93. | CrossRef | PubMed | Heart Failure Society of America, Lindenfeld J, Albert NM, Boehmer JP, Collins SP, Ezekowitz JA, et al. HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Card Fail. 2010 Jun;16(6):e1-194. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Heart Failure Society of America, Lindenfeld J, Albert NM, Boehmer JP, Collins SP, Ezekowitz JA, et al. HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline. J Card Fail. 2010 Jun;16(6):e1-194. | CrossRef | PubMed | Moe GW, Ezekowitz JA, O'Meara E, Lepage S, Howlett JG, Fremes S, et al. The 2014 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Heart Failure Management Guidelines Focus Update: anemia, biomarkers, and recent therapeutic trial implications. Can J Cardiol. 2015 Jan;31(1):3-16. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Moe GW, Ezekowitz JA, O'Meara E, Lepage S, Howlett JG, Fremes S, et al. The 2014 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Heart Failure Management Guidelines Focus Update: anemia, biomarkers, and recent therapeutic trial implications. Can J Cardiol. 2015 Jan;31(1):3-16. | CrossRef | PubMed | McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012 Aug;14(8):803-69. | CrossRef | PubMed |
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012 Aug;14(8):803-69. | CrossRef | PubMed | Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):e147-239. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):e147-239. | CrossRef | PubMed |