 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Adding rituximab to the treatment with corticosteroids has been proposed as a therapeutic alternative for inducing remission in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, especially when fertility is a concern, or when there is contraindication or intolerance to cyclophosphamide.
Searching in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening 30 databases, we identified only one systematic review including three pertinent randomized controlled trials. We combined the evidence using meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings following the GRADE approach. We concluded rituximab may slightly increase induction of remission rate, but it may also increase the risk of infection. It is not clear whether it increases the risk of cancer, or whether increases or decreases mortality because the certainty of the evidence is very low.
Immunosuppression with cyclophosphamide and corticosteroids has constituted the standard treatment for induction of remission in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis for years. Given the multiple adverse effects of cyclophosphamide, alternatives have been searched, such as the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab.
Clinical guidelines recommend it as a therapeutic alternative, especially in patients concerned about fertility preservation that maintain disease activity after standard treatment, or those that have contraindication or do not tolerate it.
We used Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening more than 30 databases, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. With this information we generated a structured summary using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We found one systematic review [1] including 37 primary studies reported in 42 references Three studies correspond to randomized controlled trials, reported in eight references [2],[3],[11],[13],[20],[21],[37],[43]. This table and the summary in general are based on the latter. |
|
What types of patients were included |
All studies included patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. All studies included patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis or microscopic polyangiitis, and two studies also included renal limited vasculitis [2],[11],[37],[43]. Average age was 52 years [3],[13],[20],[21], 68 years [37],[43] and it was not reported in one study [2],[11]. Two studies reported the percentage of patients with new disease: 66% [3],[13],[20],[21] and 100% [37],[43]. The degree of disease activity measured with BVAS was 8.4 [3],[13],[19],[20],[21],[37],[43], and it was not reported in one study [2],[11]. |
|
What types of interventions were included |
All studies considered rituximab as the intervention. Two studies [3],[13],[20],[21],[37],[43] administered 375 mg/m2/week during four weeks. One study [2],[11] administered an infusion of 500 mg per day at days 1 and 15, then at 5.5 months and when completing 18 months. One study [37],[43] added cyclophosphamide 15 mg/kg during the first and third rituximab infusion. Two studies [3],[13],[20],[21],[37],[43] used cyclophosphamide as comparison. One of them [3],[13],[20],[21] employed a dose of 2 mg/kg/day and the other [37],[43] used 15 mg/kg every 2 weeks for the first three doses, then every 3 weeks until achieving remission. Both studies switched cyclophosphamide to azathioprine after achieving remission. The third study [2],[11] used azathioprine as comparison in an initial dose of 2 mg/kg/day during 22 months. |
|
What types of outcomes |
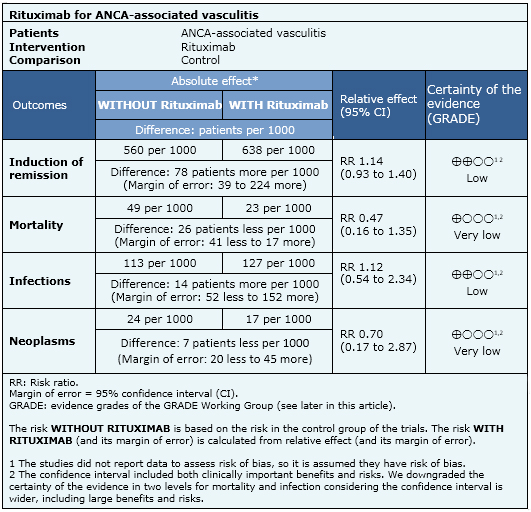
Induction and maintenance of remission, serious adverse events, defined as hospitalizations, cancer or mortality; other adverse effects as infections or hematological events. |
The information on the effects of rituximab is based on three randomized trials including 350 patients. All studies reported mortality and adverse effects. Only two studies reported remission [3],[13],[20],[21],[37],[43].

|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
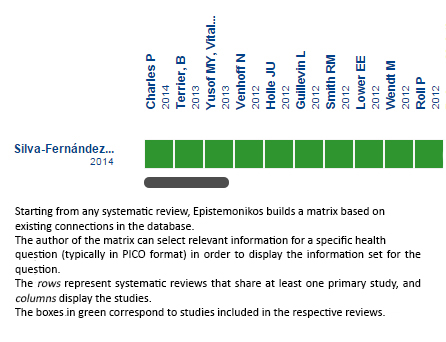
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
Matrix of evidence (static version).
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Rituximab in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier. After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
The details about the methods used to produce these summaries are described here http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
These summaries follow a rigorous process of internal peer review.
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

 Matrix of evidence (static version).
Matrix of evidence (static version).
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Adding rituximab to the treatment with corticosteroids has been proposed as a therapeutic alternative for inducing remission in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, especially when fertility is a concern, or when there is contraindication or intolerance to cyclophosphamide.
Searching in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening 30 databases, we identified only one systematic review including three pertinent randomized controlled trials. We combined the evidence using meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings following the GRADE approach. We concluded rituximab may slightly increase induction of remission rate, but it may also increase the risk of infection. It is not clear whether it increases the risk of cancer, or whether increases or decreases mortality because the certainty of the evidence is very low.
 Autores:
Carmen Rain[1], Tatiana Yáñez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[1,2,3,4,5]
Autores:
Carmen Rain[1], Tatiana Yáñez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[1,2,3,4,5]

Citación: Rain C, Yáñez T, Rada G. Is rituximab effective for induction of remission in ANCA-associated vasculitis?. Medwave 2015;15(Suppl 2):e6209 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2015.6209
Fecha de publicación: 13/8/2015

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Silva-Fernández L, Loza E, Martínez-Taboada VM, Blanco R, Rúa-Figueroa I, Pego-Reigosa JM, et al. Biological therapy for systemic vasculitis: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014 Feb;43(4):542-57. | CrossRef | PMC |
Silva-Fernández L, Loza E, Martínez-Taboada VM, Blanco R, Rúa-Figueroa I, Pego-Reigosa JM, et al. Biological therapy for systemic vasculitis: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014 Feb;43(4):542-57. | CrossRef | PMC | Terrier B, Pagnoux C, Karras A, Khouatra C, Aumaitre O, Cohen P, et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (MAINRITSAN): Follow-up at 34 months. La Presse Médicale. 2013;42(4P2): 778-779. | Link |
Terrier B, Pagnoux C, Karras A, Khouatra C, Aumaitre O, Cohen P, et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (MAINRITSAN): Follow-up at 34 months. La Presse Médicale. 2013;42(4P2): 778-779. | Link | Specks U, Merkel PA, Seo P, Spiera RF, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Immunoglobulin Concentrations and Infection Risk Among Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Treated with Rituximab or Cyclophosphamide. ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting, 2011. [online]. | Link |
Specks U, Merkel PA, Seo P, Spiera RF, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Immunoglobulin Concentrations and Infection Risk Among Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Treated with Rituximab or Cyclophosphamide. ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting, 2011. [online]. | Link | Azar L. Long-term outcome of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener) treated with rituximab. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link |
Azar L. Long-term outcome of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener) treated with rituximab. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link | Seo P, Specks U, Keogh KA. Efficacy42( of rituximab in limited Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. J Rheumatol. 2008 Oct;35(10):2017-23. Epub 2008 Aug 1. | PMC |
Seo P, Specks U, Keogh KA. Efficacy42( of rituximab in limited Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. J Rheumatol. 2008 Oct;35(10):2017-23. Epub 2008 Aug 1. | PMC | Smith RM, Jones RB, Guerry MJ, Laurino S, Catapano F, Chaudhry A, et al. Rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3760-9. | CrossRef | PMC |
Smith RM, Jones RB, Guerry MJ, Laurino S, Catapano F, Chaudhry A, et al. Rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Nov;64(11):3760-9. | CrossRef | PMC | Roccatello D, Baldovino S, Alpa M, Rossi D, Napoli F, Naretto C, et al. Effects of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody as a rescue treatment for ANCA-associated idiopathic systemic vasculitis with or without overt renal involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008 May-Jun;26(3 Suppl 49):S67-71. | PMC |
Roccatello D, Baldovino S, Alpa M, Rossi D, Napoli F, Naretto C, et al. Effects of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody as a rescue treatment for ANCA-associated idiopathic systemic vasculitis with or without overt renal involvement. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008 May-Jun;26(3 Suppl 49):S67-71. | PMC | Stasi R, Stipa E, Del Poeta G, Amadori S, Newland AC, Provan D. Long-term observation of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Nov;45(11):1432-6. | PMC |
Stasi R, Stipa E, Del Poeta G, Amadori S, Newland AC, Provan D. Long-term observation of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Nov;45(11):1432-6. | PMC | Venhoff N, Effelsberg NM, Salzer U, Warnatz K, Peter HH, Lebrecht D, et al. Impact of rituximab on immunoglobulin concentrations and B cell numbers after cyclophosphamide treatment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37626. | CrossRef | PMC |
Venhoff N, Effelsberg NM, Salzer U, Warnatz K, Peter HH, Lebrecht D, et al. Impact of rituximab on immunoglobulin concentrations and B cell numbers after cyclophosphamide treatment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37626. | CrossRef | PMC | Sánchez-Cano D, Callejas-Rubio JL, Ortego-Centeno N. Effect of rituximab on refractory Wegener granulomatosis with predominant granulomatous disease. J Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;14(2):92-3. | CrossRef | PMC |
Sánchez-Cano D, Callejas-Rubio JL, Ortego-Centeno N. Effect of rituximab on refractory Wegener granulomatosis with predominant granulomatous disease. J Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;14(2):92-3. | CrossRef | PMC | Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Karras A, Khoutra C, Aumaitre O, Cohen P. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link |
Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Karras A, Khoutra C, Aumaitre O, Cohen P. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link | Rees F, Yazdani R, Lanyon P. Long-term follow-up of different refractory systemic vasculitides treated with rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Sep;30(9):1241-5. | CrossRef | PMC |
Rees F, Yazdani R, Lanyon P. Long-term follow-up of different refractory systemic vasculitides treated with rituximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Sep;30(9):1241-5. | CrossRef | PMC | Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Rituximab versus | CrossRef | PMC | Link |
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, et al. Rituximab versus | CrossRef | PMC | Link | Keogh KA, Wylam ME, Stone JH, Specks U. Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Jan;52(1):262-8. | PMC |
Keogh KA, Wylam ME, Stone JH, Specks U. Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Jan;52(1):262-8. | PMC | Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Rossi D, Alpa M, Naretto C, Russo A, et al. Long-term effects of rituximab added to cyclophosphamide in refractory patients with vasculitis. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34(2):175-80. | CrossRef |
Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Rossi D, Alpa M, Naretto C, Russo A, et al. Long-term effects of rituximab added to cyclophosphamide in refractory patients with vasculitis. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34(2):175-80. | CrossRef | Tony HP, Burmester G, Schulze-Koops H, Grunke M, Henes J, Kötter I, et al. Safety and clinical outcomes of rituximab therapy in patients with different autoimmune diseases: experience from a national registry (GRAID). Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 13;13(3):R75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/ar3337 | PMC |
Tony HP, Burmester G, Schulze-Koops H, Grunke M, Henes J, Kötter I, et al. Safety and clinical outcomes of rituximab therapy in patients with different autoimmune diseases: experience from a national registry (GRAID). Arthritis Res Ther. 2011 May 13;13(3):R75. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/ar3337 | PMC | Keogh KA, Ytterberg SR, Fervenza FC, Carlson KA, Schroeder DR, Specks U. Rituximab for refractory Wegener's granulomatosis: report of a prospective, open-label pilot trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Jan 15;173(2):180-7. | PMC |
Keogh KA, Ytterberg SR, Fervenza FC, Carlson KA, Schroeder DR, Specks U. Rituximab for refractory Wegener's granulomatosis: report of a prospective, open-label pilot trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Jan 15;173(2):180-7. | PMC | Taylor SR, Salama AD, Joshi L, Pusey CD, Lightman SL. Rituximab is effective in the treatment of refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 May;60(5):1540-7. | CrossRef | PMC |
Taylor SR, Salama AD, Joshi L, Pusey CD, Lightman SL. Rituximab is effective in the treatment of refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 May;60(5):1540-7. | CrossRef | PMC | Jones RB, Ferraro AJ, Chaudhry AN, Brogan P, Salama AD, Smith KG, et al. A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jul;60(7):2156-68. | CrossRef | PMC |
Jones RB, Ferraro AJ, Chaudhry AN, Brogan P, Salama AD, Smith KG, et al. A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jul;60(7):2156-68. | CrossRef | PMC | Stone JH, Merkel PA, Seo P, Langford CA, HoffmanGS, KallenbergCGM, et al. Extended Follow-up of Treatment with Rituximab Versus Cyclophosphamide for Remission-Induction of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Which Subsets Are At Greatest Risk for Flare? | Immune Tolerance Network. American College of Rheumatology Chicago, IL, November 4-9. 2011. [on line] | Link |
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Seo P, Langford CA, HoffmanGS, KallenbergCGM, et al. Extended Follow-up of Treatment with Rituximab Versus Cyclophosphamide for Remission-Induction of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Which Subsets Are At Greatest Risk for Flare? | Immune Tolerance Network. American College of Rheumatology Chicago, IL, November 4-9. 2011. [on line] | Link | Geetha D, Fervenza FC. The Efficacy of Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for Treatment of Renal Disease in ANCA-associated Vasculitis: The RAVE Trial | Immune Tolerance Network. [on line]. | Link |
Geetha D, Fervenza FC. The Efficacy of Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for Treatment of Renal Disease in ANCA-associated Vasculitis: The RAVE Trial | Immune Tolerance Network. [on line]. | Link | Mansfield N, Hamour S, Habib AM, Tarzi R, Levy J, Griffith M, et al. Prolonged disease-free remission following rituximab and low-dose cyclophosphamide therapy for renal ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Oct;26(10):3280-6. | CrossRef | PMC |
Mansfield N, Hamour S, Habib AM, Tarzi R, Levy J, Griffith M, et al. Prolonged disease-free remission following rituximab and low-dose cyclophosphamide therapy for renal ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Oct;26(10):3280-6. | CrossRef | PMC | Charles P, Néel A, Tieulié N, Hot A, Pugnet G, Decaux O, et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitides: a multicentre retrospective study on 80 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Mar;53(3):532-9. | CrossRef | PMC |
Charles P, Néel A, Tieulié N, Hot A, Pugnet G, Decaux O, et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitides: a multicentre retrospective study on 80 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Mar;53(3):532-9. | CrossRef | PMC | Holle JU, Dubrau C, Herlyn K, Heller M, Ambrosch P, Noelle B, Ret al. Rituximab for refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis): comparison of efficacy in granulomatous versus vasculitic manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Mar;71(3):327-33. | CrossRef | PMC |
Holle JU, Dubrau C, Herlyn K, Heller M, Ambrosch P, Noelle B, Ret al. Rituximab for refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis): comparison of efficacy in granulomatous versus vasculitic manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012 Mar;71(3):327-33. | CrossRef | PMC | García Hernández FJ, Ocaña Medina C, González León R, Garrido Rasco R, Colorado Bonilla R, Castillo Palma MJ, et al. [Rituximab for treatment of patients with systemic autoimmune diseases]. Med Clin (Barc). 2007 Mar 31;128(12):458-62. Spanish. | PMC |
García Hernández FJ, Ocaña Medina C, González León R, Garrido Rasco R, Colorado Bonilla R, Castillo Palma MJ, et al. [Rituximab for treatment of patients with systemic autoimmune diseases]. Med Clin (Barc). 2007 Mar 31;128(12):458-62. Spanish. | PMC | Martinez Del Pero M, Chaudhry A, Jones RB, Sivasothy P, Jani P, Jayne D. B-cell depletion with rituximab for refractory head and neck Wegener's granulomatosis: a cohort study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2009 Aug;34(4):328-35. | CrossRef | PMC |
Martinez Del Pero M, Chaudhry A, Jones RB, Sivasothy P, Jani P, Jayne D. B-cell depletion with rituximab for refractory head and neck Wegener's granulomatosis: a cohort study. Clin Otolaryngol. 2009 Aug;34(4):328-35. | CrossRef | PMC | Wendt M, Gunnarsson I, Bratt J, Bruchfeld A. Rituximab in relapsing or refractory ANCA-associated vasculitis: a case series of 16 patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012 Mar;41(2):116-9. | CrossRef | PMC |
Wendt M, Gunnarsson I, Bratt J, Bruchfeld A. Rituximab in relapsing or refractory ANCA-associated vasculitis: a case series of 16 patients. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012 Mar;41(2):116-9. | CrossRef | PMC | Ramos-Casals M, García-Hernández FJ, de Ramón E, Callejas JL, Martínez-Berriotxoa A, Pallarés L, et al. Off-label use of rituximab in 196 patients with severe, refractory systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010 Jul-Aug;28(4):468-76. | PMC |
Ramos-Casals M, García-Hernández FJ, de Ramón E, Callejas JL, Martínez-Berriotxoa A, Pallarés L, et al. Off-label use of rituximab in 196 patients with severe, refractory systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010 Jul-Aug;28(4):468-76. | PMC | Lovric S, Erdbruegger U, Kümpers P, Woywodt A, Koenecke C, Wedemeyer H, et al. Rituximab as rescue therapy in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a single-centre experience with 15 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Jan;24(1):179-85. | CrossRef | PMC |
Lovric S, Erdbruegger U, Kümpers P, Woywodt A, Koenecke C, Wedemeyer H, et al. Rituximab as rescue therapy in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: a single-centre experience with 15 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Jan;24(1):179-85. | CrossRef | PMC | Henes JC, Fritz J, Koch S, Klein R, Horger M, Risler T, Kanz L, Koetter I. Rituximab for treatment-resistant extensive Wegener's granulomatosis--additive effects of a maintenance treatment with leflunomide. Clin Rheumatol. 2007 Oct;26(10):1711-5. | PMC |
Henes JC, Fritz J, Koch S, Klein R, Horger M, Risler T, Kanz L, Koetter I. Rituximab for treatment-resistant extensive Wegener's granulomatosis--additive effects of a maintenance treatment with leflunomide. Clin Rheumatol. 2007 Oct;26(10):1711-5. | PMC | Lower EE, Baughman RP, Kaufman AH. Rituximab for refractory granulomatous eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012;6:1613-8. | CrossRef | PMC |
Lower EE, Baughman RP, Kaufman AH. Rituximab for refractory granulomatous eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012;6:1613-8. | CrossRef | PMC | Aries PM, Hellmich B, Voswinkel J, Both M, Nölle B, Holl-Ulrich K, Let al. Lack of efficacy of rituximab in Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Jul;65(7):853-8. | PMC |
Aries PM, Hellmich B, Voswinkel J, Both M, Nölle B, Holl-Ulrich K, Let al. Lack of efficacy of rituximab in Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Jul;65(7):853-8. | PMC | Roll P, Ostermeier E, Haubitz M, Lovric S, Unger L, Holle J, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: results from a German registry (GRAID). J Rheumatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):2153-6. | CrossRef | PMC |
Roll P, Ostermeier E, Haubitz M, Lovric S, Unger L, Holle J, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: results from a German registry (GRAID). J Rheumatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):2153-6. | CrossRef | PMC | Pullerits R, Ljevak M, Vikgren J, Bokarewa M. Off-trial evaluation of the B cell-targeting treatment in the refractory cases of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: long-term follow-up from a single centre. Scand J Immunol. 2012 Oct;76(4):411-20. | CrossRef | PMC |
Pullerits R, Ljevak M, Vikgren J, Bokarewa M. Off-trial evaluation of the B cell-targeting treatment in the refractory cases of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: long-term follow-up from a single centre. Scand J Immunol. 2012 Oct;76(4):411-20. | CrossRef | PMC | Eriksson P. Nine patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive vasculitis successfully treated with rituximab. J Intern Med. 2005 Jun;257(6):540-8. | PMC |
Eriksson P. Nine patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive vasculitis successfully treated with rituximab. J Intern Med. 2005 Jun;257(6):540-8. | PMC | Roubaud-Baudron C, Pagnoux C, Méaux-Ruault N, Grasland A, Zoulim A, LE Guen J, et al. Rituximab maintenance therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. J Rheumatol. 2012 Jan;39(1):125-30. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Roubaud-Baudron C, Pagnoux C, Méaux-Ruault N, Grasland A, Zoulim A, LE Guen J, et al. Rituximab maintenance therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. J Rheumatol. 2012 Jan;39(1):125-30. | CrossRef | PubMed | Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):211-20. | CrossRef | PMC |
Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):211-20. | CrossRef | PMC | Brihaye B, Aouba A, Pagnoux C, Cohen P, Lacassin F, Guillevin L. Adjunction of rituximab to steroids and immunosuppressants for refractory/relapsing Wegener's granulomatosis: a study on 8 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007 Jan-Feb;25(1 Suppl 44):S23-7. | PMC |
Brihaye B, Aouba A, Pagnoux C, Cohen P, Lacassin F, Guillevin L. Adjunction of rituximab to steroids and immunosuppressants for refractory/relapsing Wegener's granulomatosis: a study on 8 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007 Jan-Feb;25(1 Suppl 44):S23-7. | PMC | Joshi L, Lightman SL, Salama AD, Shirodkar AL, Pusey CD, Taylor SR. Rituximab in refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis: PR3 titers may predict relapse, but repeat treatment can be effective. Ophthalmology. 2011 Dec;118(12):2498-503. | CrossRef | PMC |
Joshi L, Lightman SL, Salama AD, Shirodkar AL, Pusey CD, Taylor SR. Rituximab in refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis: PR3 titers may predict relapse, but repeat treatment can be effective. Ophthalmology. 2011 Dec;118(12):2498-503. | CrossRef | PMC | Lutalo PM, Scott IC, Sangle S, D’Cruz DP. Rituximab in relapsing granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis): a case series. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link |
Lutalo PM, Scott IC, Sangle S, D’Cruz DP. Rituximab in relapsing granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis): a case series. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link | Dubrau C, Arndt F, Gross WL, Moosig F. Successful treatment of churg-strauss syndrome with rituximab. Abstr Am Coll Rheumatol Rheumatol Heal Prof Annu Sci Meet. 2012 [on line]. | Link |
Dubrau C, Arndt F, Gross WL, Moosig F. Successful treatment of churg-strauss syndrome with rituximab. Abstr Am Coll Rheumatol Rheumatol Heal Prof Annu Sci Meet. 2012 [on line]. | Link | Yusof MY, Vital EM, Dass S. Safety of rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing ANCA-associated vasculitis: repeat cycles on clinical relapse are associated with low rates of hypogammaglobulinemia. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link |
Yusof MY, Vital EM, Dass S. Safety of rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing ANCA-associated vasculitis: repeat cycles on clinical relapse are associated with low rates of hypogammaglobulinemia. New Evidence in Rheumatology. 2013 Jan;(9):52. | Link | Jones RB, Tervaert JWC, Hauser T, Luqmani RS, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Two year follow-up results from a randomised trial of rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for generalized’ anca-associated vasculitis: rituxvas. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 [on line] | Link |
Jones RB, Tervaert JWC, Hauser T, Luqmani RS, Morgan MD, Peh CA, et al. Two year follow-up results from a randomised trial of rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for generalized’ anca-associated vasculitis: rituxvas. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 [on line] | Link | Nice. Rituximab in combination with glucocorticoids for treating anti- neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody- associated vasculitis. NICE Technol Apprais Guid 308. March, 2014. [on line]. | Link |
Nice. Rituximab in combination with glucocorticoids for treating anti- neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody- associated vasculitis. NICE Technol Apprais Guid 308. March, 2014. [on line]. | Link |