 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Dear editor:
Scientometrics is an effective method to evaluate the scientific production of biomedical journals [1]. It provides an overview of the situation of scientific research of a journal and objectively measures its growth or decline [2].
It was a pleasure to read the manuscript of Gallardo-Sánchez et al [3], where they displayed the main scientometric indicators of Medwave through 2010-2015 that provides the “Publish or Perish” website.
We thought it would be also appropriate to identify the scientometric indicators that Scopus gives us [4] (Table 1)
Table 1. Scientometric indicators of Medwave according to Scopus.
Medwave belongs to journals in the fourth quartile, with an SJR index of 0.100, and an impact factor of 0.045. But it should be noted that this database only analyzes the contributions from 2014 onwards. The impact factor obtained from ResearchGate [5] is slightly higher with 0.07.
In recent years, successful editorial policies were launched that have undoubtedly improved Medwave indicators. We can mention the adoption of a continuous publication format that has speeded up the time between acceptance and publication of manuscripts, incorporating the Open Journal System (OJS), the referencing system CrossRef and the DOI system[6].
This has led to the incorporation and permanence of this journal in databases of high prestige as MEDLINE / PubMed, Scopus, Latindex, LILACS and DOAJ; in addition to the successful editorial decision of increasing its visibility in social networks like Facebook and ReseachGate.
Another interesting result is the contributions by country: Chile stands out with 49 manuscripts (Table 2). These results are provided by the database PubMed[7]. Despite having contributions from 38 countries, we don’t found items of international collaboration which is an important indicator to assess the quality of the journal
Table 2. Countries with major contributions to Medwave according to PubMed.
Finally, we agree with the authors when they raise that scientometric indicators "are especially useful when designing policies to visualize a journal and display its productivity"[3]. However, no recommendations that would be of special interest to the editorial team are proposed.
We therefore express the following recommendations for the sake of improving the quality and visibility of this journal:
It is a long and full of work way, but the future perspective must be to gain the preference of readers, and increase the quality and impact of the publication.
From the editor
The authors originally submitted this article in Spanish and English. The Journal has not copyedited this English version.
Declaration of conflicts of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Financing
The authors declare not having received any funding whatsoever for writing this letter

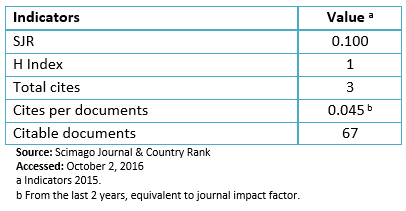 Table 1. Scientometric indicators of Medwave according to Scopus.
Table 1. Scientometric indicators of Medwave according to Scopus.

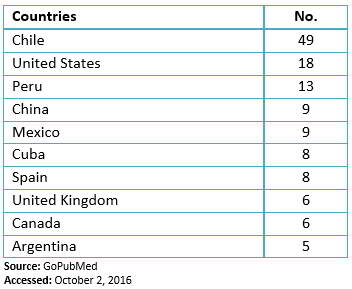 Table 2. Countries with major contributions to Medwave according to PubMed.
Table 2. Countries with major contributions to Medwave according to PubMed.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

 Autores:
Carlos Acosta-Batista[1], Rosali Mullings-Pérez[2]
Autores:
Carlos Acosta-Batista[1], Rosali Mullings-Pérez[2]

Citación: Acosta-Batista C, Mullings-Pérez R. Medwave scientometric indicators in Scopus and future challenges. Medwave 2016 Oct;16(9):e6575 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.09.6575
Fecha de publicación: 17/10/2016

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Clavera Vázquez TJ, Chaple Gil AM, Miranda Tarragó JD, Álvarez Rodríguez J. Algunos indicadores bibliométricos referidos a la endodoncia, presentes en revistas médicas cubanas. Rev Cubana Estomatol. 2015 Dic;52(4). | Link |
Clavera Vázquez TJ, Chaple Gil AM, Miranda Tarragó JD, Álvarez Rodríguez J. Algunos indicadores bibliométricos referidos a la endodoncia, presentes en revistas médicas cubanas. Rev Cubana Estomatol. 2015 Dic;52(4). | Link | Dávila Rodríguez M, Guzmán Sáenz R, Macareno Arroyo H, Piñeres Herera D, de la Rosa Barranco D, Caballero-Uribe CV. Bibliometría: conceptos y utilidades para el estudio médico y la formación profesional. Salud, Barranquilla. 2009 Dec;25(2):319-330. | Link |
Dávila Rodríguez M, Guzmán Sáenz R, Macareno Arroyo H, Piñeres Herera D, de la Rosa Barranco D, Caballero-Uribe CV. Bibliometría: conceptos y utilidades para el estudio médico y la formación profesional. Salud, Barranquilla. 2009 Dec;25(2):319-330. | Link | Gallardo Sánchez Y, Gallardo Arzuaga RL, Fonseca Arias M, Pérez Atencio ME. Scienciometric characterization of Medwave's scientific production 2010-2014: a descriptive study. Medwave 2016 Sep;16(8):6538. | CrossRef |
Gallardo Sánchez Y, Gallardo Arzuaga RL, Fonseca Arias M, Pérez Atencio ME. Scienciometric characterization of Medwave's scientific production 2010-2014: a descriptive study. Medwave 2016 Sep;16(8):6538. | CrossRef | Bachelet VC, Cardemil F. Medwave adopts continuous publication. Medwave 2013;13(3):e5649. | CrossRef |
Bachelet VC, Cardemil F. Medwave adopts continuous publication. Medwave 2013;13(3):e5649. | CrossRef |