 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Palabras clave: Heart failure, survival, ethnic groups
Introduction
In western countries, it is estimated that one to two people per 100 adults have heart failure. In Latin America, and particularly in Ecuador, few studies have assessed survival in this disease. For this reason, this study aimed to determine survival and prognostic factors based on clinical and socio-demographic characteristics.
Methods
We did a single-center study of survival analysis in 228 patients with heart failure between 2015 and 2019. Survival analysis was done by the actuarial method and a multivariate Cox regression analysis.
Results
Overall survival at the first year was 86% and at five years was 46%. Heart failure etiology (hazard ratio, 1.162: 95% confidence interval, 1.001 to 1.349; P = 0.049), ethnicity (1.415; 10.1 to 199; P = 0.043), age (1.035; 1.011 to 1.06; P = 0.04) and altered values of basal creatinine (1.21; 1.002 to 1.461; P = 0.048) were associated with worse prognosis.
Conclusions
Global survival time was similar to other international studies. Etiology, ethnicity, creatinine values, and age were factors associated with a worse vital prognosis.
Main messages
|
Globally, there are 26 million people with heart failure, and in western countries, one to two people per 100 adults have the disease [1][2].
During the last few years, there have been important treatment breakthroughs. However, mortality is still higher than several commonly diagnosed types of cancer [1][2].
To date, few studies have evaluated survival from heart failure in Latin America. Most data comes from first-world countries where economic and social conditions differ from our population [3][4]. In Ecuador, there is a lack of research in survival analysis for this disease.
In this context, this study aimed to determine the survival of patients diagnosed with heart failure based on their clinical and socio-demographic characteristics.
Study design
A single-center survival study was conducted on patients diagnosed with heart failure between January 2015 and July 2019 at San Vicente de Paúl General Hospital in Ibarra, Ecuador.
Population
The universe of patients consisted of 228 cases. Using patient's medical history records, diagnoses were defined through the international classification of diseases (ICD-10) with codes: I-50, I-51, I-52, I-23, and I-42. This coding corresponded to congestive heart failure, complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart failure, other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, and certain current complications following acute myocardial infarction, and cardiomyopathy, respectively.
Socio-demographic variables included sex, age, ethnic group (patients self-determination), and alcohol and cigarette consumption. Clinical variables assessment involved hospitalizations, NYHA (New York Heart Association) functional class, arterial hypertension, acute myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and ischemic cerebrovascular events. Data were based on the medical history records.
Survival was studied from January 2015 to July 2019. Patients with congenital diseases or incomplete clinical histories were excluded.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were carried out for both quantitative and qualitative variables, and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test assessed the distribution of variables. Chi-square and the Fisher's Exact Test were used to measure significance and Cramer's V to measure association. Additionally, a survival analysis was performed using the actuarial method, and for the analysis of factors associated with survival, a Cox proportional risk multivariate regression analysis was used. The hazard ratio was calculated with a significance level of P = 0.05 and a 95% confidence interval. The statistical package IBM SPSS 25 was used to process the cases.
Ethics
The Institutional Ethics Committee of the Hospital General San Vicente de Paúl Ibarra, Ecuador, approved this study in an official letter issued on August 31, 2018. The study was based on data obtained from secondary sources (medical records). The privacy and confidentiality of the data were maintained as indicated by the Helsinki declaration of principles of Ethics for Human Medical Research.
Baseline characteristics
According to the last Ecuadorian Census of 2010, 26% of the inhabitants of the province of Imbabura – whose reference hospital is the San Vicente de Paúl General Hospital – defined themselves as Indigenous, 6% as Afro-Ecuadorian, and the remaining 68% as mixed-raced (in the following text called "Mestizo") [5].
The average age of the patients was 75.88 years (standard deviation: 13 years), and according to the stages of the life cycle, the highest percentage of patients corresponded to the old age group (Table 1).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of subjects. N = 228
The distribution according to sex was similar for both men and women. The accumulated incidence of this disease was 7.7 per 10,000 inhabitants for Afro-Ecuadorian, 2.62 per 10,000 inhabitants for Indigenous people, and 5.69 per 10,000 inhabitants for Mestizo. Concerning mortality rates, it was observed that by 2019 these were 7.4, 2.5, and 6.5 per 10,000 inhabitants for the Afro-Ecuadorian, Indigenous, and Mestizo populations, respectively.
The leading cause of heart failure was hypertension (Table 1), while alcohol and tobacco consumption was 18% and 25%, respectively.
At the time of the evaluation, most patients were diagnosed in NYHA functional class III (36.5%) followed by class II (33%) (Table 1). The mean value of the body mass index was 26 kg/m2 (standard deviation, 7 kg/m2) and the glomerular filtrate rate was 53.57 ml/minute/1.73m2 (standard deviation, 28 ml/minute/1.73m2) with an average creatinine value of 1.41 mg/dl (standard deviation, 1.33 mg/dl). The most prevalent comorbidities were arterial hypertension (76%) and atrial fibrillation (38.5%). In one-third of cases, patients had ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation.
Treatment was mainly based on loop diuretics, followed by aldosterone receptor antagonists, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers (ACE inhibitors/ARBs), and beta-blockers.
Survival according to socio-demographic characteristics
Overall survival at the first year of diagnosis was 86% and at five years was 46%. Assessing survival by sex, it was found that it was 87% in women, while in men, it was 85%. After five years, survival was 44% and 48% in men and women, respectively (P = 0.690) (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to sex.
Regarding age, patients between 65 and 74 years old (later adulthood) had an 87% survival at one year, while in patients over 75 years (senescence), survival was 85%. When evaluating survival after five years, it was shown that survival was 62% in later adulthood and 40% in senescence (P = 0.455).
We found that the Mestizo, Afro-Ecuadorian and Indigenous population had an 89%, 82%, and 76% survival during the first year, respectively; while after five years, survival in the Mestizo population was 49%, in the Afro-Ecuadorian population, 34%, and in the Indigenous population 51% (P = 0.323) (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to ethnic groups.
Among alcohol consumers, it was shown that the first-year survival rate was 65% in later adulthood, while in non-consumers, it was 93%. After five years, survival was 54% and 63% in consumers and non-consumers, respectively (P = 0.011) (Figure 3). When this variable was analyzed in the senescence stage, survival at the first year was 76% in consumers and 87% in non-consumers. In contrast, after five years survival rate was 33%, both in consumers and non-consumers (P = 0.542).
Figure 3. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to alcohol con-sumption.
Smokers had an 82% survival rate, while in those without such habit, it was 87%. Moreover, survival after five years was 43% and 47% in smokers and non-smokers, respectively (P = 0.203) (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to cigarette smoking.
Survival according to clinical characteristics
We identified that mortality was 100% in those who had five or more hospitalizations during their illness. In contrast, those who had between one and four hospitalizations had 43% mortality. On the other hand, mortality was 6% in those who had no hospitalizations (Cramer's V = 0.315, P = 0.001).
Concerning body mass index, 1.8% of patients diagnosed with heart failure had a low body mass index, 33.8% were average weight, 39.9% were overweight, and 24.6% were obese. No statistically significant difference in survival was found between these groups (P = 0.193).
In terms of functional class, it was found that functional classes III and IV predominated in a higher proportion of the Mestizo population, followed by the Indigenous and Afro-Ecuadorian populations (P = 0.714). Patients with functional class III had a survival at one year of 81% and 22% at five years, while in patients with functional class IV, survival at one year was 85% and at five years 31% (P = 0.201) (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to NYHA func-tional class.
Hypertension was more frequent among Afro-Ecuadorian descents (87%), followed by the Mestizos (75.3%) and Indigenous (66.7%) (P =0.185). Regarding survival of hypertensive patients, during the first year, it was 89%, while after five years, it was 29% (P = 0.040). We found a better prognosis in women than in men (P = 0.08) (Figure 6).
In terms of ethnicity, none Afro-Ecuadorian patients with hypertension and heart failure survived after five years, compared to 51% of the Mestizos and 42% of the Indigenous people during the same period (P = 0.028).
In patients with a history of acute myocardial infarction, survival at one year was 93%, while at five years, it dropped to 31%, compared with those who did not have this history (P = 0.087) (Figure 7). On the other hand, in patients with a history of heart attack and smoking, the mortality at five years was 100% compared to those who did not consume cigarettes, in which the mortality was 68% (P = 0.035).
As for a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, there was no difference in survival compared to non-diabetic patients at five years after diagnosis (P = 0.115) (Figure 8).
For patients with a history of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, survival at the first year was 50%, with no patients alive at five years, while those who did not present these arrhythmias, survival was 85% and 47% at the first and fifth years, respectively (P = 0.022).
Chronic pulmonary obstructive disease was present in 20.5% of the cases, and survival at the first year was 79% versus 88% in those without this history. Likewise, survival at five years was 33.5% in patients with this condition, compared to 50% who did not have this disease (P = 0.056) (Figure 9).
Patients with a history of stroke had 80% survival at the first year compared to 87% of those who did not present this event. Moreover, at five years, survival in the group with this history was 17% compared with 51% without this comorbidity (P = 0.012).
Comparing patients with a history of stroke with those without, we found that survival was 80% versus 87% at the first year and 17% versus 51% at five years, respectively (P = 0.012) (Figure 10).
Figure 10. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to history of stroke.
Finally, the Cox proportional risks multivariable regression, showed that age (hazard ratio, 1.035, 95% confidence interval, 1.011 to 1.06; P = 0.04), ethnicity (1.415; 10.1 to 199; P = 0.043), etiology (1. 162; 1.001 to 1.349; P = 0.049) and serum creatinine (1.21; 1.002 to 1.461; P = 0.048) were risk factors associated with lower heart failure survival.
This study demonstrated that the overall survival of heart failure patients at the first and fifth years was similar to other previous studies [4][6][7][8][9][10][11][12].
When beta-blockers were not available, heart failure survival analysis in Latin America showed that mortality reached up to 42% during the first 13 months of follow-up. Today, we see a 15% reduction in mortality compared with this previous era. Current reported statistics are similar to our findings [13].
Regarding prognosis according to sex, Sarría-Santamera et al. and Frigola-Capell et al. found no difference in survival between both sexes [10][11]; however, other studies showed that mortality was higher among women [1][8][14][15]. In our case, there were no significant differences in survival between men and women.
In terms of age, most of our population belonged to old age and senescence stages of life, which is similar to previous studies [4][11][14][16][17]. However, other works – especially in Latin American or African populations – reported lower average ages [3][4][9][10][13]. In our study, there were no differences in survival between age groups, and this result was similar to Gerber Y et al. findings [16].
Regarding ethnicity, we found evidence that Afro-Ecuadorian patients with a history of hypertension had a worse vital prognosis than other ethnic groups. This finding is similar to what was reported by Loehr LR et al., who showed a lower survival rate in Afro-descendant patients compared to other ethnic groups stratified by age and sex [18].
Given the low representation of Indigenous in Latin American studies, there is little evidence of how heart failure behaves in this population. Only one study published by Woods et al. in the Australian indigenous population showed that this ethnic group had a high prevalence of risk factors such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and coronary disease. However, there was no difference in survival due to heart failure compared to other population groups [19].
Our work showed that alcohol consumption had a more significant impact on survival during old age and senescence stages of life. Regarding this finding, Larsson SC et al. determined that the cardiotoxic effect of alcohol was directly proportional to the amount consumed and was more deleterious in people with associated cardiovascular risk factors [20].
Regarding cigarette consumption, it is known that maintaining the smoking habit increases mortality in patients with a history of heart failure [21]. However, contrary to this premise, our work found no difference in survival compared to non-cigarette users. This finding could be explained by under-recording or because of a tacit refusal of the patients to admit this habit.
When evaluating the clinical variables, there was no significant difference in survival for body mass index. This finding contrasts with Crespo-Leiro et al. and Dokainish et al., who showed that weight was an independent factor in mortality [2][4]. One reason that could explain this finding is the low prevalence of underweight in our population.
In terms of functional class, most of our patients were diagnosed in functional classes III and IV. This result is similar to previously published findings, which showed that an advanced functional class is linked to a worse vital prognosis [4][7][13][16].
In this study, the prevalence of hypertension among the different ethnic groups was similar to previous studies [4][9][13][16]; and its presence was associated with a worse prognosis comparing with non-hypertensive patients regardless of age and sex [8].
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in our population was 18.5%; this finding was similar to previous studies [3][4][9][13]. The coexistence of these two diseases is associated with higher mortality [10][11]. However, our work found no difference in survival comparing with non-diabetic patients.
Heart failure patients have a prevalence of 20% to 80% of VT/VF, and 30% to 50% of deaths are associated with these arrhythmias [22]. In our case, the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation was associated with high mortality, and we found no survivors within five years of its diagnosis.
Other comorbidities such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and ischemic cerebrovascular events were also associated with a worse vital prognosis than those who did not have these diseases. These findings are similar to other previous studies [11][23].
Regarding the multivariate Cox regression, it was determined that age, etiology, ethnicity, and altered baseline creatinine values were independent markers of poor prognosis. Our study showed that the leading cause of heart failure was hypertensive. This result differs from other works in first-world countries where the primary etiology was ischemic [13]. Moreover, the presence of renal insufficiency was associated with a worse vital prognosis, similar to that reported by Park C et al., who showed that a reduced glomerular filtration rate was a strong predictor of mortality [24].
Among the limitations of this study, we can mention that the mono-centric study design could have limited the representativeness of the most complex cases, especially in those patients that required more complex diagnostic tests. Also, it is worth mentioning that the initial diagnosis of heart failure was based on the clinical records. Therefore, the actual onset of the disease could have been underestimated in many cases.
Finally, and although our work included an Indigenous population, the number of participants was limited, so it is not possible to draw reliable conclusions regarding the behavior of heart failure in this particular ethnic group.
The global survival of heart failure patients was similar to other international studies. Factors such as etiology, ethnicity, age, and creatinine were associated with increased heart failure mortality.
Patients with heart failure and a history of high blood pressure, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, ischemic cerebrovascular event, or alcohol consumption had shorter survival than those who did not have these comorbidities.
Notes
Contributor roles
AFGG-J: Conceptualization, investigation, project administration, validation and writing. RBA: Formal analysis, methodology, software and validation.
Competing interests
No conflicts of interest.
Funding
There was no funding for this work.
Ethics
The Institutional Ethics Committee of the Hospital General San Vicente de Paúl Ibarra, Ecuador, approved the elaboration of this study. The execution of this study was exempted from ethical responsibilities since the information was obtained from secondary sources (medical records).
During the writing of this article, the authors maintained the privacy and confidentiality of the data obtained, as stated in the Helsinki declaration regarding ethical principles for medical research on human beings.
Data sharing statement
We declare that results and the supplementary material published in this article could be available for delivery or for deposit in data repositories at the request of whoever needed this information.
Language of submission
English.

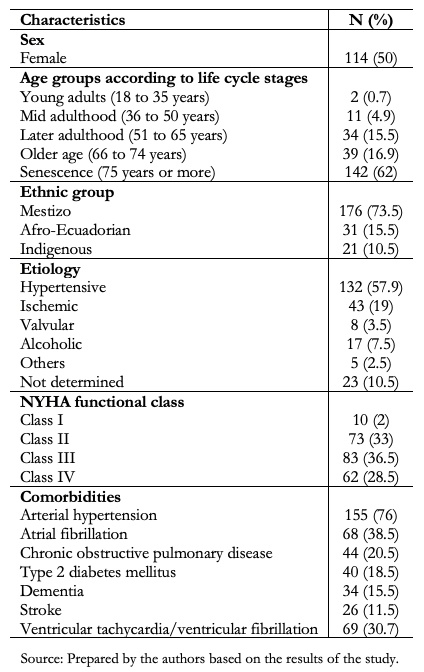 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of subjects. N = 228
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of subjects. N = 228

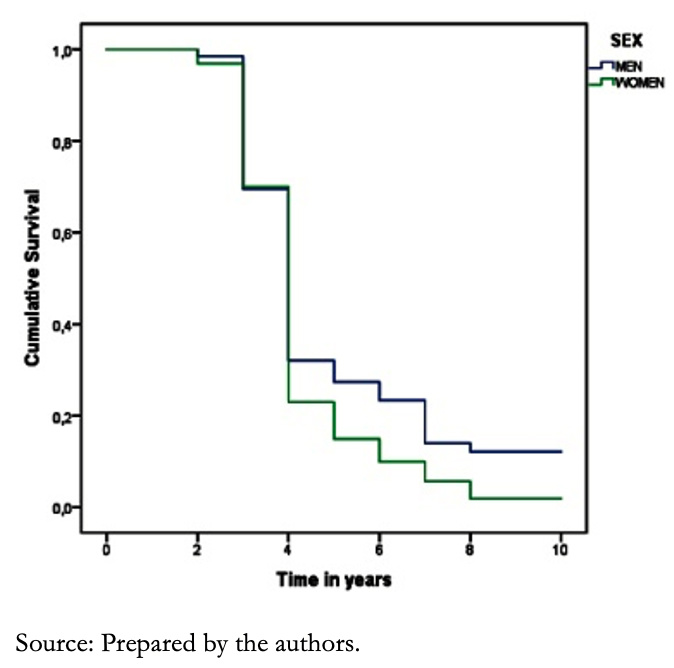 Figure 1. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to sex.
Figure 1. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to sex.

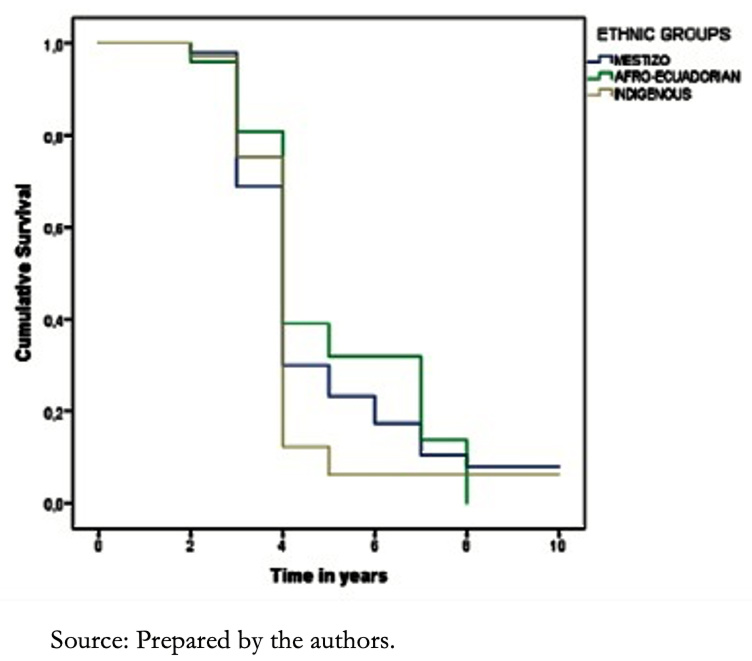 Figure 2. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to ethnic groups.
Figure 2. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to ethnic groups.

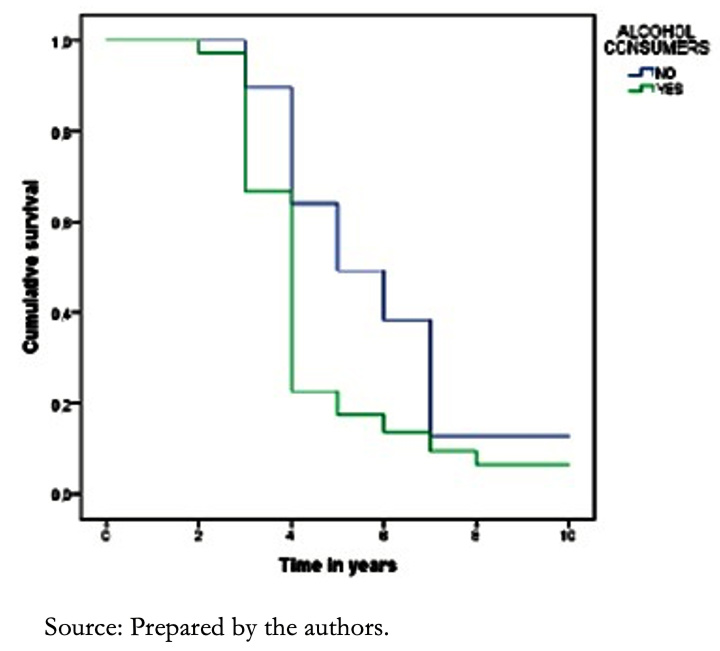 Figure 3. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to alcohol con-sumption.
Figure 3. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to alcohol con-sumption.

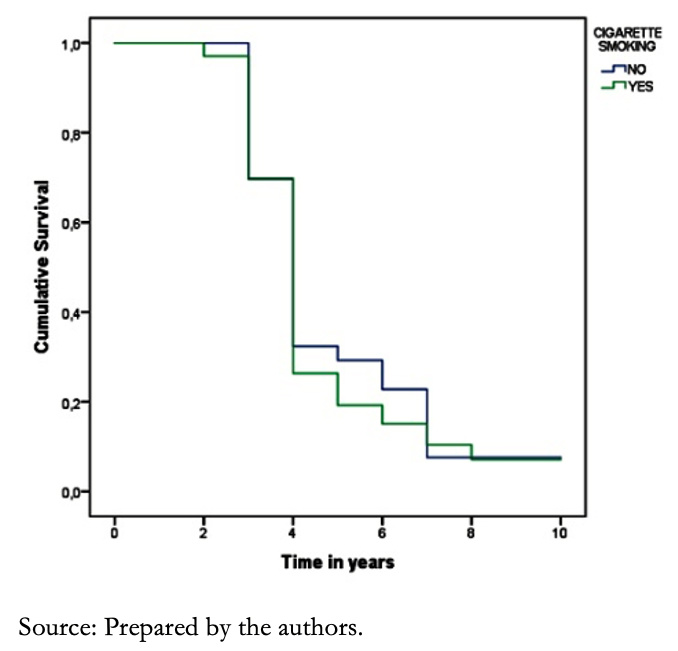 Figure 4. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to cigarette smoking.
Figure 4. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to cigarette smoking.

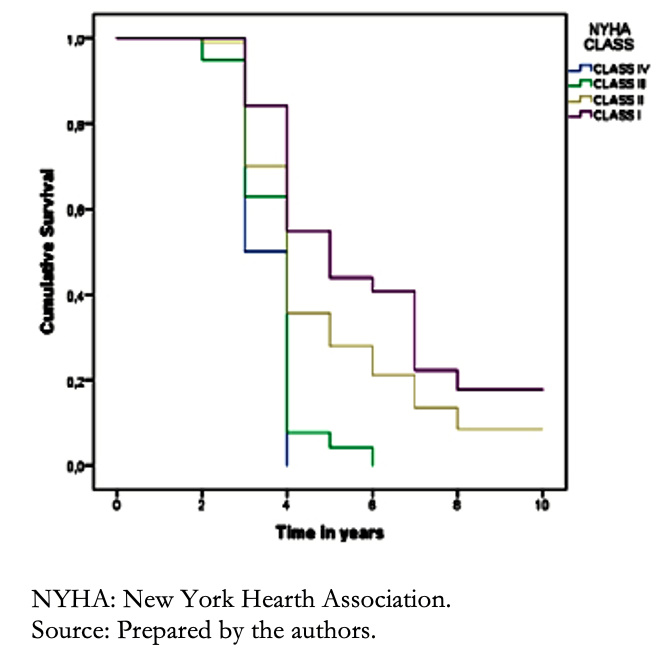 Figure 5. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to NYHA func-tional class.
Figure 5. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to NYHA func-tional class.

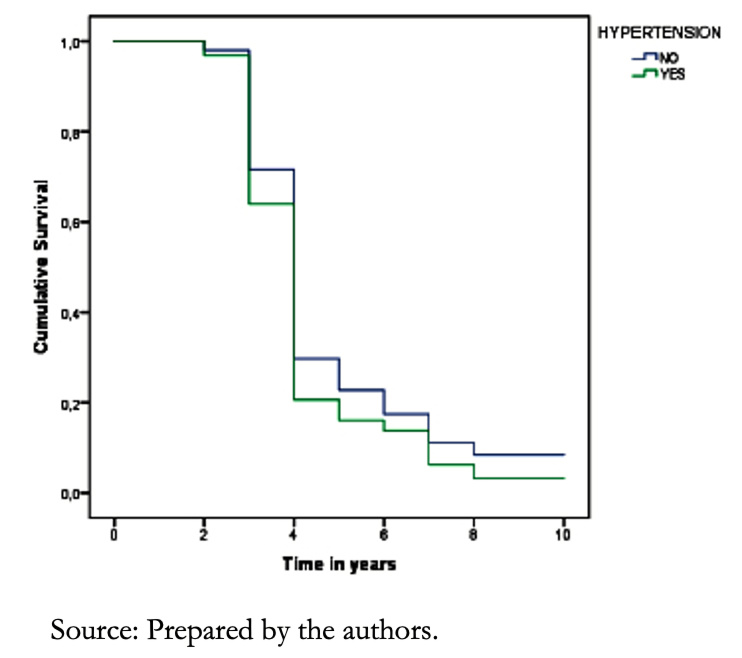 Figure 6. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence of arterial hypertension.
Figure 6. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence of arterial hypertension.

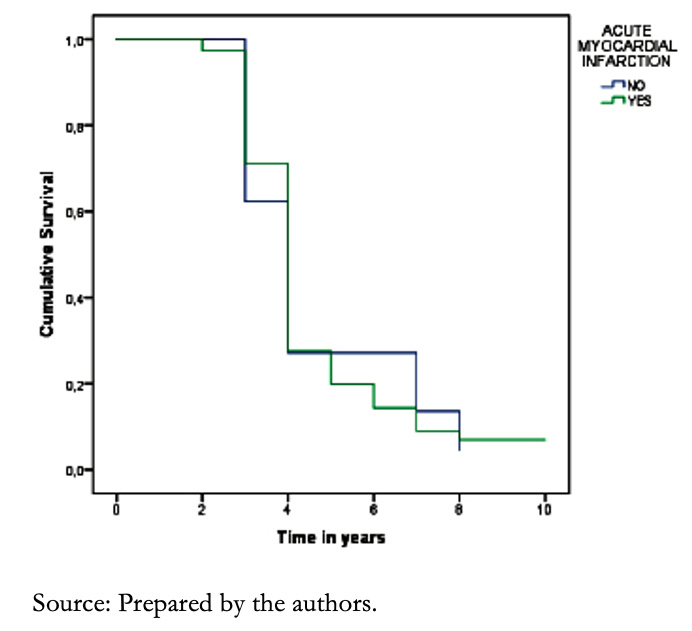 Figure 7. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to history of acute myocardial infection.
Figure 7. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to history of acute myocardial infection.

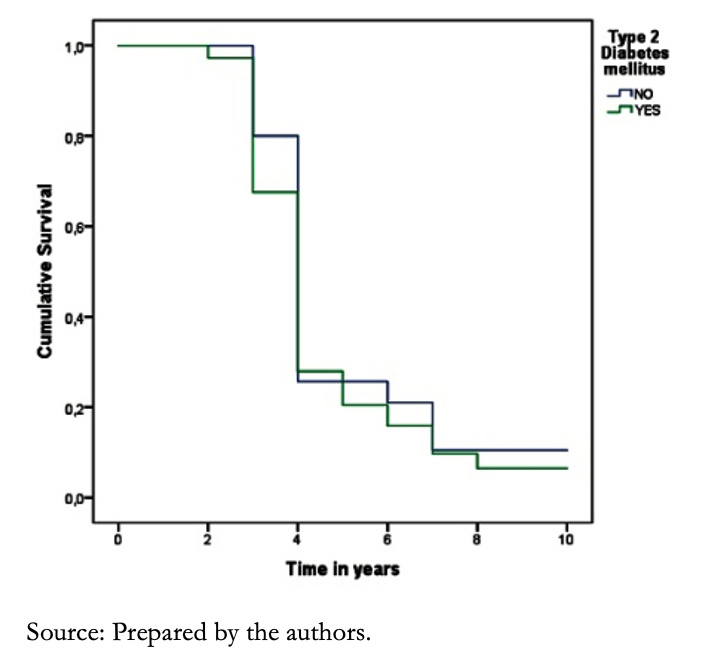 Figure 8. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figure 8. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus.

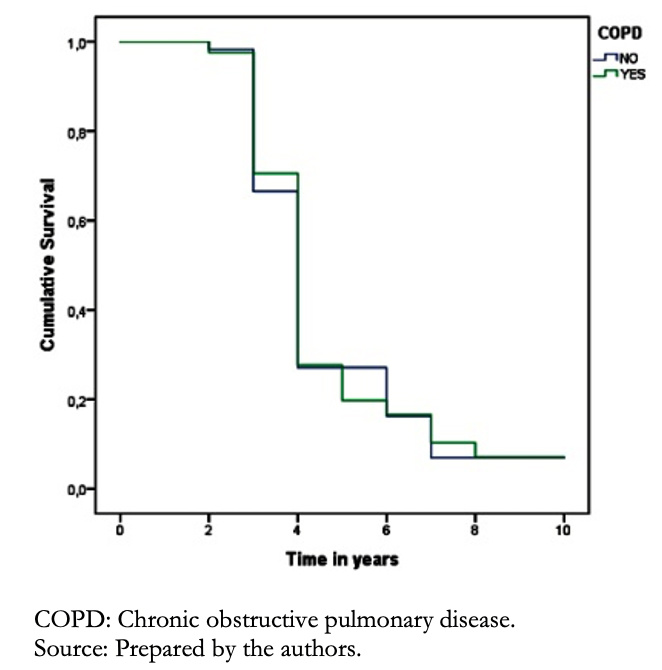 Figure 9. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Figure 9. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to the presence chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.

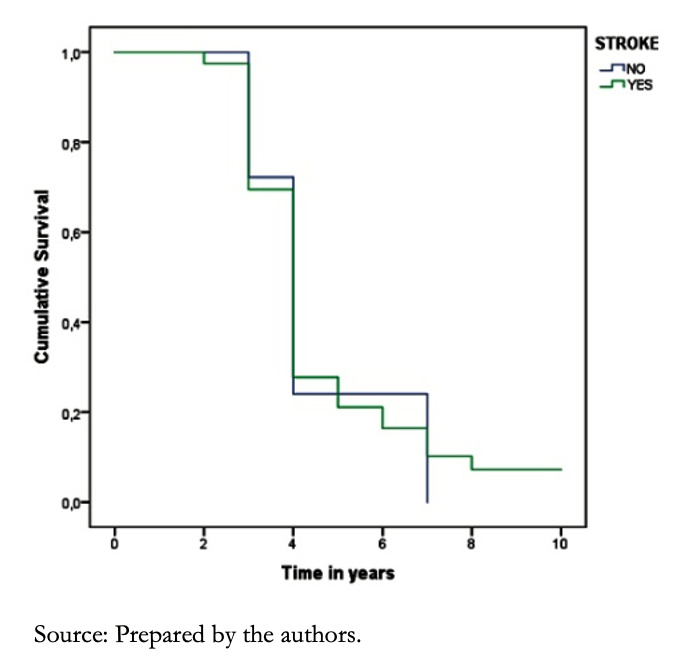 Figure 10. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to history of stroke.
Figure 10. Survival curves of patients with heart failure according to history of stroke.

Introduction
In western countries, it is estimated that one to two people per 100 adults have heart failure. In Latin America, and particularly in Ecuador, few studies have assessed survival in this disease. For this reason, this study aimed to determine survival and prognostic factors based on clinical and socio-demographic characteristics.
Methods
We did a single-center study of survival analysis in 228 patients with heart failure between 2015 and 2019. Survival analysis was done by the actuarial method and a multivariate Cox regression analysis.
Results
Overall survival at the first year was 86% and at five years was 46%. Heart failure etiology (hazard ratio, 1.162: 95% confidence interval, 1.001 to 1.349; P = 0.049), ethnicity (1.415; 10.1 to 199; P = 0.043), age (1.035; 1.011 to 1.06; P = 0.04) and altered values of basal creatinine (1.21; 1.002 to 1.461; P = 0.048) were associated with worse prognosis.
Conclusions
Global survival time was similar to other international studies. Etiology, ethnicity, creatinine values, and age were factors associated with a worse vital prognosis.
 Autores:
Alvaro Francisco Gudiño-Gomezjurado[1], René Buitrón-Andrade[2]
Autores:
Alvaro Francisco Gudiño-Gomezjurado[1], René Buitrón-Andrade[2]

Citación: Gudiño-Gomezjurado AF, Buitrón-Andrade R. Survival analysis of patients with heart failure in the Ecuadorian Andean population. Medwave 2021;21(07):e8440 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2021.07.8440
Fecha de envío: 22/1/2021
Fecha de aceptación: 5/7/2021
Fecha de publicación: 16/8/2021
Origen: No solicitado.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares externa, por tres árbitros a doble ciego.

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Taylor CJ, Ryan R, Nichols L, Gale N, Hobbs FR, Marshall T. Survival following a diagnosis of heart failure in primary care. Fam Pract. 2017 Apr 1;34(2):161-168. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Taylor CJ, Ryan R, Nichols L, Gale N, Hobbs FR, Marshall T. Survival following a diagnosis of heart failure in primary care. Fam Pract. 2017 Apr 1;34(2):161-168. | CrossRef | PubMed | Crespo-Leiro MG, Anker SD, Maggioni AP, Coats AJ, Filippatos G, Ruschitzka F, et al. European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Long-Term Registry (ESC-HF-LT): 1-year follow-up outcomes and differences across regions. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016 Jun;18(6):613-25. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Crespo-Leiro MG, Anker SD, Maggioni AP, Coats AJ, Filippatos G, Ruschitzka F, et al. European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Long-Term Registry (ESC-HF-LT): 1-year follow-up outcomes and differences across regions. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016 Jun;18(6):613-25. | CrossRef | PubMed | Bocchi EA, Arias A, Verdejo H, Diez M, Gómez E, Castro P; Interamerican Society of Cardiology. The reality of heart failure in Latin America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Sep 10;62(11):949-58. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bocchi EA, Arias A, Verdejo H, Diez M, Gómez E, Castro P; Interamerican Society of Cardiology. The reality of heart failure in Latin America. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Sep 10;62(11):949-58. | CrossRef | PubMed | Dokainish H, Teo K, Zhu J, Roy A, AlHabib KF, ElSayed A, et al. Global mortality variations in patients with heart failure: results from the International Congestive Heart Failure (INTER-CHF) prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Jul;5(7):e665-e672. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dokainish H, Teo K, Zhu J, Roy A, AlHabib KF, ElSayed A, et al. Global mortality variations in patients with heart failure: results from the International Congestive Heart Failure (INTER-CHF) prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Jul;5(7):e665-e672. | CrossRef | PubMed | Villacís B, Carrillo D. Estadística Demográfica en el Ecuador: Diagnóstico y Propuestas. Inec; 2011;86. [Internet] | Link |
Villacís B, Carrillo D. Estadística Demográfica en el Ecuador: Diagnóstico y Propuestas. Inec; 2011;86. [Internet] | Link | Maggioni AP. Epidemiology of Heart Failure in Europe. Heart Fail Clin. 2015 Oct;11(4):625-35. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Maggioni AP. Epidemiology of Heart Failure in Europe. Heart Fail Clin. 2015 Oct;11(4):625-35. | CrossRef | PubMed | Cowie MR, Wood DA, Coats AJ, Thompson SG, Suresh V, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. Survival of patients with a new diagnosis of heart failure: a population based study. Heart. 2000 May;83(5):505-10. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Cowie MR, Wood DA, Coats AJ, Thompson SG, Suresh V, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. Survival of patients with a new diagnosis of heart failure: a population based study. Heart. 2000 May;83(5):505-10. | CrossRef | PubMed | Taylor CJ, Ordóñez-Mena JM, Roalfe AK, Lay-Flurrie S, Jones NR, Marshall T, et al. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000-2017: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2019 Feb 13;364:l223. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Taylor CJ, Ordóñez-Mena JM, Roalfe AK, Lay-Flurrie S, Jones NR, Marshall T, et al. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000-2017: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2019 Feb 13;364:l223. | CrossRef | PubMed | Ciapponi A, Alcaraz A, Calderón M, Matta MG, Chaparro M, Soto N, et al. Burden of Heart Failure in Latin America: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2016 Nov;69(11):1051-1060. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ciapponi A, Alcaraz A, Calderón M, Matta MG, Chaparro M, Soto N, et al. Burden of Heart Failure in Latin America: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2016 Nov;69(11):1051-1060. | CrossRef | PubMed | Sarría-Santamera A, Prado-Galbarro FJ, Martín-Martínez MA, Carmona R, Gamiño Arroyo AE, Sánchez-Piedra C, et al. Supervivencia de pacientes con insuficiencia cardiaca en atención primaria [Survival of patients with heart failure in primary care]. Aten Primaria. 2015 Aug-Sep;47(7):438-45. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sarría-Santamera A, Prado-Galbarro FJ, Martín-Martínez MA, Carmona R, Gamiño Arroyo AE, Sánchez-Piedra C, et al. Supervivencia de pacientes con insuficiencia cardiaca en atención primaria [Survival of patients with heart failure in primary care]. Aten Primaria. 2015 Aug-Sep;47(7):438-45. | CrossRef | PubMed | Frigola-Capell E, Comin-Colet J, Davins-Miralles J, Gich-Saladich IJ, Wensing M, Verdú-Rotellar JM. Supervivencia de pacientes ambulatorios con insuficiencia cardiaca crónica del área mediterránea. Un estudio de base poblacional. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2013;66:539–44. | CrossRef |
Frigola-Capell E, Comin-Colet J, Davins-Miralles J, Gich-Saladich IJ, Wensing M, Verdú-Rotellar JM. Supervivencia de pacientes ambulatorios con insuficiencia cardiaca crónica del área mediterránea. Un estudio de base poblacional. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2013;66:539–44. | CrossRef | Koudstaal S, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Denaxas S, Gho JMIH, Shah AD, Yu N, et al. Prognostic burden of heart failure recorded in primary care, acute hospital admissions, or both: a population-based linked electronic health record cohort study in 2.1 million people. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017 Sep;19(9):1119-1127. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Koudstaal S, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Denaxas S, Gho JMIH, Shah AD, Yu N, et al. Prognostic burden of heart failure recorded in primary care, acute hospital admissions, or both: a population-based linked electronic health record cohort study in 2.1 million people. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017 Sep;19(9):1119-1127. | CrossRef | PubMed | Bocchi EA. Heart failure in South America. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2013 May;9(2):147-56. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bocchi EA. Heart failure in South America. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2013 May;9(2):147-56. | CrossRef | PubMed | Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Kupka MJ, Ho KK, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002 Oct 31;347(18):1397-402. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Kupka MJ, Ho KK, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002 Oct 31;347(18):1397-402. | CrossRef | PubMed | Gomez-Soto FM, Andrey JL, Garcia-Egido AA, Escobar MA, Romero SP, Garcia- Arjona R, et al. Incidence and mortality of heart failure: a community-based study. Int J Cardiol. 2011 Aug 18;151(1):40-5. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gomez-Soto FM, Andrey JL, Garcia-Egido AA, Escobar MA, Romero SP, Garcia- Arjona R, et al. Incidence and mortality of heart failure: a community-based study. Int J Cardiol. 2011 Aug 18;151(1):40-5. | CrossRef | PubMed | Gerber Y, Weston SA, Redfield MM, Chamberlain AM, Manemann SM, Jiang R, et al. A contemporary appraisal of the heart failure epidemic in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 2000 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Jun;175(6):996-1004. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gerber Y, Weston SA, Redfield MM, Chamberlain AM, Manemann SM, Jiang R, et al. A contemporary appraisal of the heart failure epidemic in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 2000 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2015 Jun;175(6):996-1004. | CrossRef | PubMed | Taylor CJ, Ordóñez-Mena JM, Roalfe AK, Lay-Flurrie S, Jones NR, Marshall T, et al. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000-2017: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2019;364:1–10. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Taylor CJ, Ordóñez-Mena JM, Roalfe AK, Lay-Flurrie S, Jones NR, Marshall T, et al. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000-2017: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2019;364:1–10. | CrossRef | PubMed | Loehr LR, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Folsom AR, Chambless LE. Heart failure incidence and survival (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study). Am J Cardiol. 2008 Apr 1;101(7):1016-22. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Loehr LR, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Folsom AR, Chambless LE. Heart failure incidence and survival (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study). Am J Cardiol. 2008 Apr 1;101(7):1016-22. | CrossRef | PubMed | Woods JA, Katzenellenbogen JM, Davidson PM, Thompson SC. Heart failure among Indigenous Australians: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2012 Nov 1;12:99. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Woods JA, Katzenellenbogen JM, Davidson PM, Thompson SC. Heart failure among Indigenous Australians: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2012 Nov 1;12:99. | CrossRef | PubMed | Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Alcohol consumption and risk of heart failure: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015 Apr;17(4):367-73. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Alcohol consumption and risk of heart failure: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015 Apr;17(4):367-73. | CrossRef | PubMed | Suskin N, Sheth T, Negassa A, Yusuf S. Relationship of current and past smoking to mortality and morbidity in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001 May;37(6):1677-82. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Suskin N, Sheth T, Negassa A, Yusuf S. Relationship of current and past smoking to mortality and morbidity in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001 May;37(6):1677-82. | CrossRef | PubMed | Saltzman HE. Arrhythmias and heart failure. Cardiol Clin. 2014 Feb;32(1):125-33, ix. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Saltzman HE. Arrhythmias and heart failure. Cardiol Clin. 2014 Feb;32(1):125-33, ix. | CrossRef | PubMed | Witt BJ, Brown RD Jr, Jacobsen SJ, Weston SA, Ballman KV, Meverden RA, et al. Ischemic stroke after heart failure: a community-based study. Am Heart J. 2006 Jul;152(1):102-9. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Witt BJ, Brown RD Jr, Jacobsen SJ, Weston SA, Ballman KV, Meverden RA, et al. Ischemic stroke after heart failure: a community-based study. Am Heart J. 2006 Jul;152(1):102-9. | CrossRef | PubMed | Park CS, Park JJ, Oh IY, Yoon CH, Choi DJ, Park HA, et al. Relation of Renal Function with Left Ventricular Systolic Function and NT-proBNP Level and Its Prognostic Implication in Heart Failure with Preserved versus Reduced Ejection Fraction: an analysis from the Korean Heart Failure (KorHF) Registry. Korean Circ J. 2017 Sep;47(5):727-741. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Park CS, Park JJ, Oh IY, Yoon CH, Choi DJ, Park HA, et al. Relation of Renal Function with Left Ventricular Systolic Function and NT-proBNP Level and Its Prognostic Implication in Heart Failure with Preserved versus Reduced Ejection Fraction: an analysis from the Korean Heart Failure (KorHF) Registry. Korean Circ J. 2017 Sep;47(5):727-741. | CrossRef | PubMed |