 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Palabras clave: Ménière, Gentamicin, Epistemonikos, GRADE.
INTRODUCCION
La enfermedad de Ménière es una anomalía del oído interno de etiología multifactorial, caracterizada por episodios de vértigo espontáneo y recurrente, hipoacusia fluctuante y tinnitus. La terapia con gentamicina intratimpánica para la enfermedad de Ménière ha sido utilizada buscando reducir la intensidad y frecuencia de las crisis, pero se ha asociado a pérdida auditiva, por lo que existe controversia respecto a su eficacia y seguridad.
MÉTODOS
Realizamos una búsqueda en Epistemonikos, la mayor base de datos de revisiones sistemáticas en salud, la cual es mantenida mediante el cribado de múltiples fuentes de información, incluyendo MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, entre otras. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas, analizamos los datos de los estudios primarios, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos una tabla de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE.
RESULTADOS Y CONCLUSIONES
Identificamos 13 revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyeron 80 estudios primarios, de los cuales tres corresponden a ensayos aleatorizados. Concluimos que la gentamicina intratimpánica podría reducir el control del vértigo y resultar en poca o nula diferencia sobre el tinnitus, pero la certeza de evidencia es baja. Además, no es posible establecer con claridad si el uso de gentamicina intratimpánica disminuye la audición o la frecuencia de los ataques de vértigo porque la certeza de la evidencia existente ha sido evaluada como muy baja.
La enfermedad de Ménière en una enfermedad crónica, incapacitante y progresiva, caracterizada por vértigo espontáneo episódico recurrente, pérdida de la audición, plenitud aural y tinnitus. El tratamiento inicial consiste en hacer modificaciones al estilo de vida, incluyendo dieta hiposódica y medicamentos diuréticos y betahistina. No obstante, se estima que el 10% [1] de los pacientes es refractario al manejo inicial, es decir, siguen presentando al menos un ataque por mes junto con pérdida auditiva sensorial durante seis meses o más [2], por lo que se plantean otras alternativas de tratamiento, incluyendo intervenciones quirúrgicas de mayor costo y con mayores complicaciones asociadas.
Debido a que no existe un manejo estándar para la enfermedad de Ménière refractaria, múltiples alternativas han sido propuestas, entre ellas, el uso de aminoglucósidos intratimpánicos, específicamente gentamicina, considerada una terapia mínimamente invasiva. La gentamicina actúa a nivel del oído interno, produciendo la ablación parcial o total del órgano vestibular, principalmente en las células ciliadas vestibulares, resultando en control del vértigo con menor daño sobre la función coclear [1]. Sin embargo, no existe un consenso sobre el protocolo para la administración intratimpánica de gentamicina, ni claridad en torno a su efectividad y seguridad.
Realizamos una búsqueda en Epistemonikos, la mayor base de datos de revisiones sistemáticas en salud, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples fuentes de información, incluyendo MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, entre otras. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas y analizamos los datos de los estudios primarios. Con esta información, generamos un resumen estructurado denominado FRISBEE (Friendly Summaries of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), siguiendo un formato preestablecido, que incluye mensajes clave, un resumen del conjunto de evidencia (presentado como matriz de evidencia en Epistemonikos), metanálisis del total de los estudios cuando sea posible, una tabla de resumen de resultados con el método GRADE y una sección de otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión.
|
Mensajes clave
|
|
Cuál es la evidencia |
Encontramos 13 revisiones sistemáticas [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10],[11], [12], [13], [14], [15], que incluyeron 80 estudios primarios [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24], [25], [26], [27], [28], [29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [34], [35], [36], [37], [38], [39], [40], [41], [42], [43], [44], [45], [46], [47], [48], [49], [50], [51], [52], [53], [54], [55], [56], [57], [58], [59], [60], [61], [62], [63], [64], [65], [66], [67], [68], [69], [70], [71], [72], [73], [74], [75], [76], [77], [78], [79], [80], [81], [82], [83], [84], [85], [86], [87], [88], [89], [90], [91], [92], [93], [94], [95], de los cuales tres corresponden a ensayos aleatorizados [23], [73], [87]. Esta tabla y el resumen en general se basan en estos últimos, dado que los estudios observacionales no aumentaban la certeza de la evidencia existente, ni entregaban información adicional relevante. |
|
Qué tipo de pacientes incluyeron los estudios* |
Todos los ensayos [23], [73], [87] incluyeron pacientes con enfermedad de Ménière, utilizando los criterios de la guía clínica de 1995 de la American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) para diagnóstico de enfermedad de Ménière unilateral. Dos de los ensayos seleccionaron pacientes sin previa intervención quirúrgica [73], [87] y todos incluyeron pacientes refractarios al manejo conservador, definido como falla luego de seis meses [23], [87] o falla luego de tratamiento con betahistina [73]. En uno de los ensayos [73] se incluyeron pacientes que presentaron respuesta calórica positiva medido por electronistagmografía. |
|
Qué tipo de intervenciones incluyeron los estudios* |
Dos ensayos utilizaron gentamicina intratimpánica a 30 mg/ml con un protocolo de titulación semanal [73], [87]. Un ensayo utilizó una dosis de 0,4 ml [73] y el otro de cuatro ml [87]. Uno de ellos instaló un tubo de ventilación en la membrana timpánica cuatro semanas previo al inicio del tratamiento por donde se inyectaba la gentamicina [73], a diferencia del segundo ensayo que usó punción timpánica [87]. El ensayo restante [23], utilizó gentamicina a 40 mg/ml semanal sin definir el volumen. El número de inyecciones difirió entre uno [87] a cuatro [23], [73]. Todos los ensayos compararon contra placebo. Uno de los ensayos inyectó cuatro ml de una solución amortiguadora [87], otro ensayo utilizó 0,4 ml semanal por cuatro semanas [73]. El ensayo restante utilizó NaCl al 0,9% sin especificar dosis [23]. |
|
Qué tipo de desenlaces midieron |
Los ensayos reportaron múltiples desenlaces, los cuales fueron agrupados por las revisiones sistemáticas de la siguiente manera: Control del vértigo: se midió según el número de ataques por año y mediante la intensidad del vértigo.
El seguimiento promedio de los ensayos fue de 17,7 meses con un rango entre seis y 28 meses [23], [73], [87]. |
*La información sobre los estudios primarios es extraída desde las revisiones sistemáticas identificadas, no directamente desde los estudios, a menos que se especifique lo contrario.
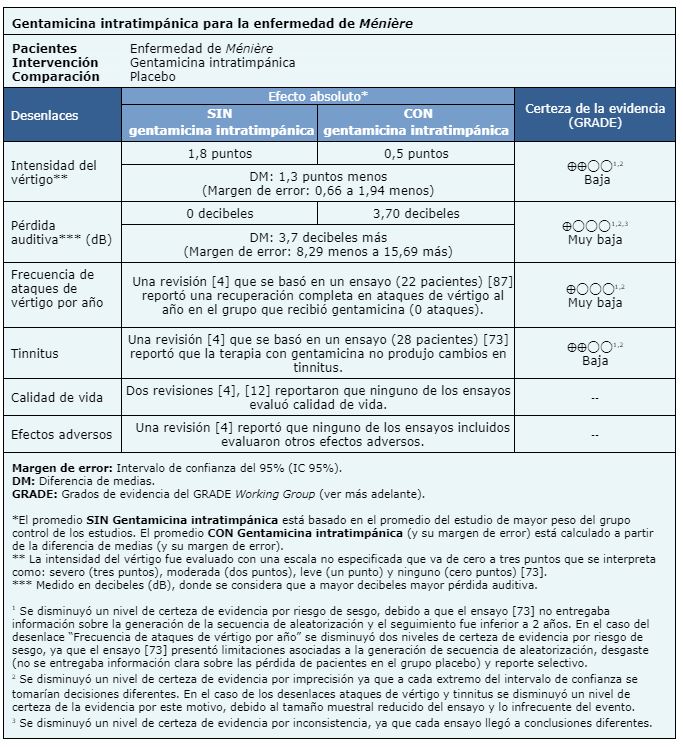
La información sobre los efectos de la gentamicina intratimpánica sobre la enfermedad de Ménière refractaria está basada en tres ensayos aleatorizados que incluyeron 60 pacientes [23], [73], [87].
Un ensayo midió la reducción de la intensidad del vértigo (28 pacientes) [73] y tres ensayos reportaron pérdida de la audición (60 pacientes) [24], [73], [87]. Ninguna revisión permitió la extracción de datos de la frecuencia de los ataques de vértigo por año y del tinnitus de manera que pudieran ser incorporados a un metanálisis, por lo tanto la información de dicho desenlace se presenta como síntesis narrativa. Ninguno de los ensayos reportó la calidad de vida y efectos adversos.
El resumen de los resultados es el siguiente:
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva de esta tabla (Interactive Summary of Findings - iSoF)

| A quién se aplica y a quién no se aplica esta evidencia |
|
| Sobre los desenlaces incluidos en este resumen |
|
| Balance daño/beneficio y certeza de la evidencia |
|
| Consideraciones de recursos |
|
| Qué piensan los pacientes y sus tratantes |
|
| Diferencias entre este resumen y otras fuentes |
|
| ¿Puede que cambie esta información en el futuro? |
|
Recopilamos toda la evidencia relevante para la pregunta de interés y la presentamos en una matriz de evidencia mediante métodos automatizados y colaborativos.
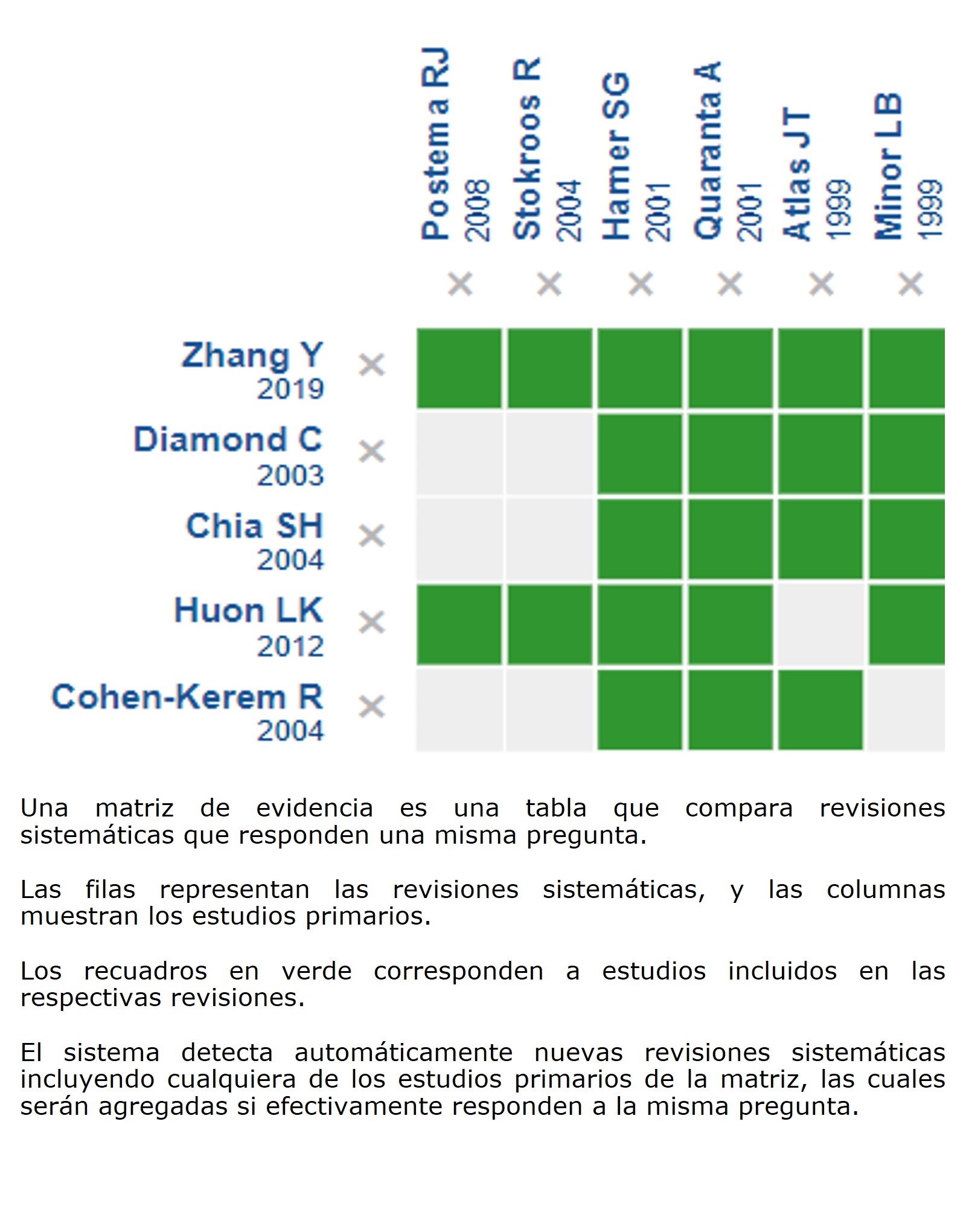
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva: Gentamicina intratimpánica comparado con placebo o no tratamiento para enfermedad de Meniere
Notas
Si con posterioridad a la publicación de este resumen se publican nuevas revisiones sistemáticas sobre este tema, en la parte superior de la matriz se mostrará un aviso de “nueva evidencia”. Si bien el proyecto contempla la actualización periódica de estos resúmenes, los usuarios están invitados a comentar en la página web de Medwave o contactar a los autores mediante correo electrónico si creen que hay evidencia que motive una actualización más precoz.
Luego de crear una cuenta en Epistemonikos, al guardar las matrices recibirá notificaciones automáticas cada vez que exista nueva evidencia que potencialmente responda a esta pregunta.
Este artículo es parte del proyecto síntesis de evidencia de Epistemonikos. Se elabora con una metodología preestablecida, siguiendo rigurosos estándares metodológicos y proceso de revisión por pares interno. Cada uno de estos artículos corresponde a un resumen, denominado FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), cuyo principal objetivo es sintetizar el conjunto de evidencia de una pregunta específica, en un formato amigable a los profesionales clínicos. Sus principales recursos se basan en la matriz de evidencia de Epistemonikos y análisis de resultados usando metodología GRADE. Mayores detalles de los métodos para elaborar este FRISBEE están descritos aquí.
La Fundación Epistemonikos es una organización que busca acercar la información a quienes toman decisiones en salud, mediante el uso de tecnologías. Su principal desarrollo es la base de datos Epistemonikos.
Declaración de conflictos de intereses
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses con la materia de este artículo.

INTRODUCTION
Ménière's disease is a multifactorial disorder affecting the inner ear, characterized by episodes of spontaneous and recurrent vertigo, fluctuating hearing loss and tinnitus. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy has been used to reduce the intensity and frequency of attacks in intractable Ménière's disease, but it is associated with hearing loss. There is controversy regarding its efficacy and safety.
METHODS
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified 13 systematic reviews that included 80 primary studies overall, of which three correspond to randomized trials. We concluded that intratympanic gentamicin may improve the control of vertigo, and result in little or no difference to tinnitus, but the certainty of the evidence is low. Furthermore, we are uncertain whether intratympanic gentamicin reduces hearing or the frequency of vertigo attacks as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
 Autores:
Fernanda de Amesti[1,2], Maria Jesus Santander [2,3], Matias Winter[2,3]
Autores:
Fernanda de Amesti[1,2], Maria Jesus Santander [2,3], Matias Winter[2,3]

Citación: de Amesti , Santander , Winter . Intratympanic gentamicin compared with placebo for Ménière's disease . Medwave 2022;22(02):e8695 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2022.02.8695
Fecha de publicación: 22/3/2022
Origen: Este artículo es producto del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project de la Fundación Epistemonikos, en colaboración con Medwave para su publicación.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares sin ciego por parte del equipo metodológico del Centro Evidencia UC Synthesis Project

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Ren H, Yin T, Lu Y, Kong W, Ren J. Intratympanic dexamethasone injections for
refractory Meniere' s disease. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):6016-23
| PubMed | PMC |
Ren H, Yin T, Lu Y, Kong W, Ren J. Intratympanic dexamethasone injections for
refractory Meniere' s disease. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):6016-23
| PubMed | PMC | Ballard DP, Sukato DC, Timashpolsky A, Babu SC, Rosenfeld RM, Hanson M. Quality-of-Life Outcomes following Surgical Treatment of Ménière's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Feb;160(2):232-238 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ballard DP, Sukato DC, Timashpolsky A, Babu SC, Rosenfeld RM, Hanson M. Quality-of-Life Outcomes following Surgical Treatment of Ménière's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Feb;160(2):232-238 | CrossRef | PubMed | Pullens B, van Benthem PP. Intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease or syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD008234 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Pullens B, van Benthem PP. Intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease or syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD008234 | CrossRef | PubMed | Cao Z, Yue F, Huang W, Rajenderkumar D, Zhao F. Different medications for the treatment of Ménière's disease by intratympanic injection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2019 Apr 26 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Cao Z, Yue F, Huang W, Rajenderkumar D, Zhao F. Different medications for the treatment of Ménière's disease by intratympanic injection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Otolaryngol. 2019 Apr 26 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chia SH, Gamst AC, Anderson JP, Harris JP. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Ménière's disease: a meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2004 Jul;25(4):544-52 | PubMed |
Chia SH, Gamst AC, Anderson JP, Harris JP. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Ménière's disease: a meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2004 Jul;25(4):544-52 | PubMed | Cohen-Kerem R, Kisilevsky V, Einarson TR, Kozer E, Koren G, Rutka JA. Intratympanic gentamicin for Menière's disease: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2004 Dec;114(12):2085-91 | PubMed |
Cohen-Kerem R, Kisilevsky V, Einarson TR, Kozer E, Koren G, Rutka JA. Intratympanic gentamicin for Menière's disease: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2004 Dec;114(12):2085-91 | PubMed | Diamond C, O'Connell DA, Hornig JD, Liu R. Systematic review of intratympanic gentamicin in Meniere's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2003 Dec;32(6):351-61 | PubMed |
Diamond C, O'Connell DA, Hornig JD, Liu R. Systematic review of intratympanic gentamicin in Meniere's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2003 Dec;32(6):351-61 | PubMed | Hao, Weiming and Yu, Huiqian and Li, Huawei, Effects of Intratympanic Gentamicin and Intratympanic Glucocorticoids in Ménière’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials (April 12, 2019) | Link |
Hao, Weiming and Yu, Huiqian and Li, Huawei, Effects of Intratympanic Gentamicin and Intratympanic Glucocorticoids in Ménière’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials (April 12, 2019) | Link | Huon LK, Fang TY, Wang PC. Outcomes of intratympanic gentamicin injection to treat Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2012 Jul;33(5):706-14 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Huon LK, Fang TY, Wang PC. Outcomes of intratympanic gentamicin injection to treat Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2012 Jul;33(5):706-14 | CrossRef | PubMed | Marques PS, Dias CC, Perez-Fernandez N, Spratley J. Instrumental head impulse test changes after intratympanic gentamicin for unilateral definite Ménière's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Oct;45(5):943-951 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Marques PS, Dias CC, Perez-Fernandez N, Spratley J. Instrumental head impulse test changes after intratympanic gentamicin for unilateral definite Ménière's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Oct;45(5):943-951 | CrossRef | PubMed | Syed MI, Ilan O, Nassar J, Rutka JA. Intratympanic therapy in Meniere's syndrome or disease: up to date evidence for clinical practice. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015 Dec;40(6):682-90 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Syed MI, Ilan O, Nassar J, Rutka JA. Intratympanic therapy in Meniere's syndrome or disease: up to date evidence for clinical practice. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015 Dec;40(6):682-90 | CrossRef | PubMed | Tuvang, E. (2016). Syed, M., Ilan, O., Nassar, J. and Rutka, J. (2015). Intratympanic therapy in Meniere's syndrome or disease: up to date evidence for clinical practice. Clinical Otolaryngology, 40(6), pp.682-690. Umeå University, Sweden | Link |
Tuvang, E. (2016). Syed, M., Ilan, O., Nassar, J. and Rutka, J. (2015). Intratympanic therapy in Meniere's syndrome or disease: up to date evidence for clinical practice. Clinical Otolaryngology, 40(6), pp.682-690. Umeå University, Sweden | Link | Vlastarakos PV, Iacovou E, Nikolopoulos TP. Is gentamycin delivery via sustained-release vehicles a safe and effective treatment for refractory Meniere's disease? A critical analysis of published interventional studies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1309-1315 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Vlastarakos PV, Iacovou E, Nikolopoulos TP. Is gentamycin delivery via sustained-release vehicles a safe and effective treatment for refractory Meniere's disease? A critical analysis of published interventional studies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1309-1315 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zhang Y, Fu J, Lin H, Shen C, Wang X, Wu J. The Clinical Outcomes After Intratympanic Gentamicin Injection to Treat Menière's Disease: A Meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2019 Apr;40(4):419-429 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zhang Y, Fu J, Lin H, Shen C, Wang X, Wu J. The Clinical Outcomes After Intratympanic Gentamicin Injection to Treat Menière's Disease: A Meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol. 2019 Apr;40(4):419-429 | CrossRef | PubMed | Atlas JT, Parnes LS. Intratympanic gentamicin titration therapy for intractable Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1999 May;20(3):357-63 | PubMed |
Atlas JT, Parnes LS. Intratympanic gentamicin titration therapy for intractable Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1999 May;20(3):357-63 | PubMed | Beck C. Intratympanic application of gentamicin for treatment of Menière's disease. Keio J Med. 1986 Mar;35(1):36-41 | PubMed |
Beck C. Intratympanic application of gentamicin for treatment of Menière's disease. Keio J Med. 1986 Mar;35(1):36-41 | PubMed | Beck C, Schmidt CL. 10 years of experience with intratympanally applied streptomycin (gentamycin) in the therapy of Morbus Menière. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1978 Sep 28;221(2):149-52 | PubMed |
Beck C, Schmidt CL. 10 years of experience with intratympanally applied streptomycin (gentamycin) in the therapy of Morbus Menière. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1978 Sep 28;221(2):149-52 | PubMed | Bertino G, Durso D, Manfrin M, Casati L, Mira E. Intratympanic gentamicin in monolateral Meniere's disease: our experience. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006 Mar;263(3):271-5 | PubMed |
Bertino G, Durso D, Manfrin M, Casati L, Mira E. Intratympanic gentamicin in monolateral Meniere's disease: our experience. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006 Mar;263(3):271-5 | PubMed | Bodmer D, Morong S, Stewart C, Alexander A, Chen JM, Nedzelski JM. Long-term vertigo control in patients after intratympanic gentamicin instillation for Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2007 Dec;28(8):1140-4 | PubMed |
Bodmer D, Morong S, Stewart C, Alexander A, Chen JM, Nedzelski JM. Long-term vertigo control in patients after intratympanic gentamicin instillation for Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2007 Dec;28(8):1140-4 | PubMed | Boleas-Aguirre MS, Sánchez-Ferrandiz N, Guillén-Grima F, Perez N. Long-term disability of class A patients with Ménière's disease after treatment with intratympanic gentamicin. Laryngoscope. 2007 Aug;117(8):1474-81 | PubMed |
Boleas-Aguirre MS, Sánchez-Ferrandiz N, Guillén-Grima F, Perez N. Long-term disability of class A patients with Ménière's disease after treatment with intratympanic gentamicin. Laryngoscope. 2007 Aug;117(8):1474-81 | PubMed | Bottrill I, Wills AD, Mitchell AL. Intratympanic gentamicin for unilateral Meniere's disease: results of therapy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2003 Apr;28(2):133-41 | PubMed |
Bottrill I, Wills AD, Mitchell AL. Intratympanic gentamicin for unilateral Meniere's disease: results of therapy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2003 Apr;28(2):133-41 | PubMed | Bremer HG, van Rooy I, Pullens B, Colijn C, Stegeman I, van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, van Benthem PP, Klis SF, Grolman W, Bruintjes TD. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Ménière's disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on dose efficacy - results of a prematurely ended study. Trials. 2014 Aug 18;15:328 | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Bremer HG, van Rooy I, Pullens B, Colijn C, Stegeman I, van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, van Benthem PP, Klis SF, Grolman W, Bruintjes TD. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Ménière's disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on dose efficacy - results of a prematurely ended study. Trials. 2014 Aug 18;15:328 | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Carey JP, Minor LB, Peng GC, Della Santina CC, Cremer PD, Haslwanter T. Changes in the three-dimensional angular vestibulo-ocular reflex following intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2002 Dec;3(4):430-43 | PubMed | PMC |
Carey JP, Minor LB, Peng GC, Della Santina CC, Cremer PD, Haslwanter T. Changes in the three-dimensional angular vestibulo-ocular reflex following intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2002 Dec;3(4):430-43 | PubMed | PMC | Casani A, Nuti D, Franceschini SS, Gaudini E, Dallan I. Transtympanic gentamicin and fibrin tissue adhesive for treatment of unilateral Menière's disease: effects on vestibular function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005 Dec;133(6):929-35 | PubMed |
Casani A, Nuti D, Franceschini SS, Gaudini E, Dallan I. Transtympanic gentamicin and fibrin tissue adhesive for treatment of unilateral Menière's disease: effects on vestibular function. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005 Dec;133(6):929-35 | PubMed | Corsten, M., Marsan, J., Schramm, D. and Robichaud, J. (1997). Treatment of intractable Menière's disease with intratympanic gentamicin: review of the University of Ottawa experience. J Otolaryngol., [online] 26(6), pp.361-4 | Link |
Corsten, M., Marsan, J., Schramm, D. and Robichaud, J. (1997). Treatment of intractable Menière's disease with intratympanic gentamicin: review of the University of Ottawa experience. J Otolaryngol., [online] 26(6), pp.361-4 | Link | Crane BT, Minor LB, Della Santina CC, Carey JP. Middle ear exploration in patients with Ménière's disease who have failed outpatient intratympanic gentamicin therapy. Otol Neurotol. 2009 Aug;30(5):619-24 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Crane BT, Minor LB, Della Santina CC, Carey JP. Middle ear exploration in patients with Ménière's disease who have failed outpatient intratympanic gentamicin therapy. Otol Neurotol. 2009 Aug;30(5):619-24 | CrossRef | PubMed | Daneshi A, Jahandideh H, Pousti SB, Mohammadi S. One-shot, low-dosage intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease: Clinical, posturographic and vestibular test findings. Iran J Neurol. 2014;13(1):33-9 | PubMed | PMC |
Daneshi A, Jahandideh H, Pousti SB, Mohammadi S. One-shot, low-dosage intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease: Clinical, posturographic and vestibular test findings. Iran J Neurol. 2014;13(1):33-9 | PubMed | PMC | De Beer L, Stokroos R, Kingma H. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for intractable Ménière's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007 Jun;127(6):605-12. PubMed PMID: 17503229.
De Valck CF, Van Rompaey V, Wuyts EL, Van de Heyning PH. Tenotomy of the tensor tympani and stapedius tendons in Ménière's disease. B-ENT. 2009;5(1):1-6
| PubMed |
De Beer L, Stokroos R, Kingma H. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for intractable Ménière's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007 Jun;127(6):605-12. PubMed PMID: 17503229.
De Valck CF, Van Rompaey V, Wuyts EL, Van de Heyning PH. Tenotomy of the tensor tympani and stapedius tendons in Ménière's disease. B-ENT. 2009;5(1):1-6
| PubMed | DeCicco, M., Hoffer, M. and RD, K. (1998). Round-window microcatheter administered microdose gentamicin: results from treatment of tinnitus associated with Ménière’s disease. Int Tin- nitus J. | Link |
DeCicco, M., Hoffer, M. and RD, K. (1998). Round-window microcatheter administered microdose gentamicin: results from treatment of tinnitus associated with Ménière’s disease. Int Tin- nitus J. | Link | Delgado LP, Rodrigo JF, Peña PA. Intratympanic gentamicin in Ménière's disease: our experience. J Laryngol Otol. 2011 Apr;125(4):363-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Delgado LP, Rodrigo JF, Peña PA. Intratympanic gentamicin in Ménière's disease: our experience. J Laryngol Otol. 2011 Apr;125(4):363-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | De Valck CF, Van Rompaey V, Wuyts EL, Van de Heyning PH. Tenotomy of the tensor tympani and stapedius tendons in Ménière's disease. B-ENT. 2009;5(1):1-6 | PubMed |
De Valck CF, Van Rompaey V, Wuyts EL, Van de Heyning PH. Tenotomy of the tensor tympani and stapedius tendons in Ménière's disease. B-ENT. 2009;5(1):1-6 | PubMed | Driscoll CL, Kasperbauer JL, Facer GW, Harner SG, Beatty CW. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin and the treatment of Meniere's disease: preliminary results. Laryngoscope. 1997 Jan;107(1):83-9 | PubMed |
Driscoll CL, Kasperbauer JL, Facer GW, Harner SG, Beatty CW. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin and the treatment of Meniere's disease: preliminary results. Laryngoscope. 1997 Jan;107(1):83-9 | PubMed | Eklund S, Pyykkö I, Aalto H, Ishizaki H, Vasama JP. Effect of intratympanic gentamicin on hearing and tinnitus in Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1999 May;20(3):350-6 | PubMed |
Eklund S, Pyykkö I, Aalto H, Ishizaki H, Vasama JP. Effect of intratympanic gentamicin on hearing and tinnitus in Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1999 May;20(3):350-6 | PubMed | Gabra N, Saliba I. The effect of intratympanic methylprednisolone and gentamicin injection on Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Apr;148(4):642-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gabra N, Saliba I. The effect of intratympanic methylprednisolone and gentamicin injection on Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Apr;148(4):642-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gayathri, H. and Rao, S. (2010). Low dose intratympanic gentamicin for controlof intractable vertigo. Indian J Otol. | Link |
Gayathri, H. and Rao, S. (2010). Low dose intratympanic gentamicin for controlof intractable vertigo. Indian J Otol. | Link | Harner SG, Driscoll CL, Facer GW, Beatty CW, McDonald TJ. Long-term follow-up of transtympanic gentamicin for Ménière's syndrome. Otol Neurotol. 2001 Mar;22(2):210-4 | PubMed |
Harner SG, Driscoll CL, Facer GW, Beatty CW, McDonald TJ. Long-term follow-up of transtympanic gentamicin for Ménière's syndrome. Otol Neurotol. 2001 Mar;22(2):210-4 | PubMed | Helling K, Schönfeld U, Clarke AH. Treatment of Ménière's disease by low-dosage intratympanic gentamicin application: effect on otolith function. Laryngoscope. 2007 Dec;117(12):2244-50 | PubMed |
Helling K, Schönfeld U, Clarke AH. Treatment of Ménière's disease by low-dosage intratympanic gentamicin application: effect on otolith function. Laryngoscope. 2007 Dec;117(12):2244-50 | PubMed | Hill SL 3rd, Digges EN, Silverstein H. Long-term follow-up after gentamicin application via the Silverstein MicroWick in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006 Aug;85(8):494, 496, 498 | PubMed |
Hill SL 3rd, Digges EN, Silverstein H. Long-term follow-up after gentamicin application via the Silverstein MicroWick in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006 Aug;85(8):494, 496, 498 | PubMed | Hirsch BE, Kamerer DB. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Ménière's disease. Am J Otol. 1997 Jan;18(1):44-51 | PubMed |
Hirsch BE, Kamerer DB. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Ménière's disease. Am J Otol. 1997 Jan;18(1):44-51 | PubMed | Hoffer ME, Kopke RD, Weisskopf P, Gottshall K, Allen K, Wester D. Microdose gentamicin administration via the round window microcatheter: results in patients with Meniere's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Oct;942:46-51 | PubMed |
Hoffer ME, Kopke RD, Weisskopf P, Gottshall K, Allen K, Wester D. Microdose gentamicin administration via the round window microcatheter: results in patients with Meniere's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Oct;942:46-51 | PubMed | Horii A, Saika T, Uno A, Nishiike S, Mitani K, Nishimura M, Kitahara T, Fukushima M, Nakagawa A, Masumura C, Sasaki T, Kizawa K, Kubo T. Factors relating to the vertigo control and hearing changes following intratympanic gentamicin for intractable Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2006 Sep;27(6):896-900 | PubMed |
Horii A, Saika T, Uno A, Nishiike S, Mitani K, Nishimura M, Kitahara T, Fukushima M, Nakagawa A, Masumura C, Sasaki T, Kizawa K, Kubo T. Factors relating to the vertigo control and hearing changes following intratympanic gentamicin for intractable Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2006 Sep;27(6):896-900 | PubMed | Hsieh LC, Lin HC, Tsai HT, Ko YC, Shu MT, Lin LH. High-dose intratympanic gentamicin instillations for treatment of Meniere's disease: long-term results. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009 Dec;129(12):1420-4 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Hsieh LC, Lin HC, Tsai HT, Ko YC, Shu MT, Lin LH. High-dose intratympanic gentamicin instillations for treatment of Meniere's disease: long-term results. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009 Dec;129(12):1420-4 | CrossRef | PubMed | Inoue H, Uchi Y, Nogami K, Uemura T. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin treatment of Menière's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1994;251 Suppl 1:S12-4 | PubMed |
Inoue H, Uchi Y, Nogami K, Uemura T. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin treatment of Menière's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1994;251 Suppl 1:S12-4 | PubMed | Junet P, Karkas A, Dumas G, Quesada JL, Schmerber S. Vestibular results after intratympanic gentamicin therapy in disabling Menière's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Oct;273(10):3011-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Junet P, Karkas A, Dumas G, Quesada JL, Schmerber S. Vestibular results after intratympanic gentamicin therapy in disabling Menière's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Oct;273(10):3011-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Jung J, Chun J, Kim N, Kim Y, Lee WS. Evaluation of quality of life after intratympanic streptomycin injection in patients with Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2008 Sep;29(6):816-23 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Jung J, Chun J, Kim N, Kim Y, Lee WS. Evaluation of quality of life after intratympanic streptomycin injection in patients with Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2008 Sep;29(6):816-23 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kaasinen S, Pyykkö I, Ishizaki H, Aalto H. Intratympanic gentamicin in Meniere's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998 Jun;118(3):294-8 | PubMed |
Kaasinen S, Pyykkö I, Ishizaki H, Aalto H. Intratympanic gentamicin in Meniere's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998 Jun;118(3):294-8 | PubMed | Kaplan DM, Nedzelski JM, Chen JM, Shipp DB. Intratympanic gentamicin for the treatment of unilateral Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2000 Aug;110(8):1298-305 | PubMed |
Kaplan DM, Nedzelski JM, Chen JM, Shipp DB. Intratympanic gentamicin for the treatment of unilateral Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2000 Aug;110(8):1298-305 | PubMed | Kaplan DM, Nedzelski JM, Al-Abidi A, Chen JM, Shipp DB. Hearing loss following intratympanic instillation of gentamicin for the treatment of unilateral Meniere's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2002 Apr;31(2):106-11 | PubMed |
Kaplan DM, Nedzelski JM, Al-Abidi A, Chen JM, Shipp DB. Hearing loss following intratympanic instillation of gentamicin for the treatment of unilateral Meniere's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2002 Apr;31(2):106-11 | PubMed | Katzenell U, Gordon M, Page M. Intratympanic gentamicin injections for the treatment of Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Nov;143(5 Suppl 3):S24-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Katzenell U, Gordon M, Page M. Intratympanic gentamicin injections for the treatment of Ménière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Nov;143(5 Suppl 3):S24-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kyrodimos E, Aidonis I, Sismanis A. Hearing results following intratympanic gentamicin perfusion for Ménière's disease. J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Apr;123(4):379-82 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kyrodimos E, Aidonis I, Sismanis A. Hearing results following intratympanic gentamicin perfusion for Ménière's disease. J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Apr;123(4):379-82 | CrossRef | PubMed | Laitakari K. Intratympanic gentamycin in severe Ménière's disease. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1990 Dec;15(6):545-8 | PubMed |
Laitakari K. Intratympanic gentamycin in severe Ménière's disease. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1990 Dec;15(6):545-8 | PubMed | Lange G, Maurer J, Mann W. Long-term results after interval therapy with intratympanic gentamicin for Menière's disease. Laryngoscope. 2004 Jan;114(1):102-5 | PubMed |
Lange G, Maurer J, Mann W. Long-term results after interval therapy with intratympanic gentamicin for Menière's disease. Laryngoscope. 2004 Jan;114(1):102-5 | PubMed | Lange G. Transtympanic gentamycin in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 1995;116(2):151-2 | PubMed |
Lange G. Transtympanic gentamycin in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 1995;116(2):151-2 | PubMed | Leone CA, Mosca F, Mincione A. [Ablation therapy with gentamycin in the treatment of Meniere's disease]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2000 Oct;20(5):322-9 | PubMed |
Leone CA, Mosca F, Mincione A. [Ablation therapy with gentamycin in the treatment of Meniere's disease]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2000 Oct;20(5):322-9 | PubMed | Lin FR, Migliaccio AA, Haslwanter T, Minor LB, Carey JP. Angular vestibulo-ocular reflex gains correlate with vertigo control after intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Meniere's disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005 Oct;114(10):777-85 | PubMed | PMC |
Lin FR, Migliaccio AA, Haslwanter T, Minor LB, Carey JP. Angular vestibulo-ocular reflex gains correlate with vertigo control after intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Meniere's disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005 Oct;114(10):777-85 | PubMed | PMC | Liu H, Zhang T, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Dai C. End-point indicators of low-dose intra-tympanic gentamicin in management of Ménière's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017 Feb;137(2):136-143 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Liu H, Zhang T, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Dai C. End-point indicators of low-dose intra-tympanic gentamicin in management of Ménière's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017 Feb;137(2):136-143 | CrossRef | PubMed | Longridge NS, Mallinson AI. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin treatment for dizziness in Ménière's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2000 Feb;29(1):35-9 | PubMed |
Longridge NS, Mallinson AI. Low-dose intratympanic gentamicin treatment for dizziness in Ménière's disease. J Otolaryngol. 2000 Feb;29(1):35-9 | PubMed | MacKeith SA, Whiteside OJ, Mawby T, Bottrill ID. Middle ear gentamicin-soaked pledgets in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2014 Feb;35(2):305-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
MacKeith SA, Whiteside OJ, Mawby T, Bottrill ID. Middle ear gentamicin-soaked pledgets in the treatment of Ménière's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2014 Feb;35(2):305-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Magnusson M, Padoan S. Delayed onset of ototoxic effects of gentamicin in treatment of Menière's disease. Rationale for extremely low dose therapy. Acta Otolaryngol. 1991;111(4):671-6 | PubMed |
Magnusson M, Padoan S. Delayed onset of ototoxic effects of gentamicin in treatment of Menière's disease. Rationale for extremely low dose therapy. Acta Otolaryngol. 1991;111(4):671-6 | PubMed | Marques P, Manrique-Huarte R, Perez-Fernandez N. Single intratympanic gentamicin injection in Ménière's disease: VOR change and prognostic usefulness. Laryngoscope. 2015 Aug;125(8):1915-20 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Marques P, Manrique-Huarte R, Perez-Fernandez N. Single intratympanic gentamicin injection in Ménière's disease: VOR change and prognostic usefulness. Laryngoscope. 2015 Aug;125(8):1915-20 | CrossRef | PubMed | Martin E, Perez N. Hearing loss after intratympanic gentamicin therapy for unilateral Ménière's Disease. Otol Neurotol. 2003 Sep;24(5):800-6 | PubMed |
Martin E, Perez N. Hearing loss after intratympanic gentamicin therapy for unilateral Ménière's Disease. Otol Neurotol. 2003 Sep;24(5):800-6 | PubMed | Marzo SJ, Leonetti JP. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for persistent vertigo after endolymphatic sac surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Jan;126(1):31-3 | PubMed |
Marzo SJ, Leonetti JP. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for persistent vertigo after endolymphatic sac surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Jan;126(1):31-3 | PubMed | McFeely WJ, Singleton GT, Rodriguez FJ, Antonelli PJ. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998 May;118(5):589-96 | PubMed |
McFeely WJ, Singleton GT, Rodriguez FJ, Antonelli PJ. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment for Meniere's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998 May;118(5):589-96 | PubMed | Minor LB. Intratympanic gentamicin for control of vertigo in Meniere's disease: vestibular signs that specify completion of therapy. Am J Otol. 1999 Mar;20(2):209-19 | PubMed |
Minor LB. Intratympanic gentamicin for control of vertigo in Meniere's disease: vestibular signs that specify completion of therapy. Am J Otol. 1999 Mar;20(2):209-19 | PubMed | Murofushi T, Halmagyi GM, Yavor RA. Intratympanic gentamicin in Ménière's disease: results of therapy. Am J Otol. 1997 Jan;18(1):52-7 | PubMed |
Murofushi T, Halmagyi GM, Yavor RA. Intratympanic gentamicin in Ménière's disease: results of therapy. Am J Otol. 1997 Jan;18(1):52-7 | PubMed | Nedzelski JM, Chiong CM, Fradet G, Schessel DA, Bryce GE, Pfleiderer AG. Intratympanic gentamicin instillation as treatment of unilateral Menière's disease: update of an ongoing study. Am J Otol. 1993 May;14(3):278-82 | PubMed |
Nedzelski JM, Chiong CM, Fradet G, Schessel DA, Bryce GE, Pfleiderer AG. Intratympanic gentamicin instillation as treatment of unilateral Menière's disease: update of an ongoing study. Am J Otol. 1993 May;14(3):278-82 | PubMed | Paradis J, Hu A, Parnes LS. Endolymphatic sac surgery versus intratympanic gentamicin for the treatment of intractable Ménière's disease: a retrospective review with survey. Otol Neurotol. 2013 Oct;34(8):1434-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Paradis J, Hu A, Parnes LS. Endolymphatic sac surgery versus intratympanic gentamicin for the treatment of intractable Ménière's disease: a retrospective review with survey. Otol Neurotol. 2013 Oct;34(8):1434-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Perez N, Martín E, García-Tapia R. Intratympanic gentamicin for intractable Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2003 Mar;113(3):456-64 | PubMed |
Perez N, Martín E, García-Tapia R. Intratympanic gentamicin for intractable Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2003 Mar;113(3):456-64 | PubMed | Perez N, Martin E, Zubieta JL, Romero MD, Garcia-Tapia R. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with Ménière's disease treated with intratympanic gentamycin. Laryngoscope. 2002 Jun;112(6):1104-9 | PubMed |
Perez N, Martin E, Zubieta JL, Romero MD, Garcia-Tapia R. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with Ménière's disease treated with intratympanic gentamycin. Laryngoscope. 2002 Jun;112(6):1104-9 | PubMed | Pfleiderer AG. The current role of local intratympanic gentamicin therapy in the management of unilateral Menière's disease. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1998 Feb;23(1):34-41 | PubMed |
Pfleiderer AG. The current role of local intratympanic gentamicin therapy in the management of unilateral Menière's disease. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1998 Feb;23(1):34-41 | PubMed | Postema RJ, Kingma CM, Wit HP, Albers FW, Van Der Laan BF. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for control of vertigo in unilateral Menire's disease: a prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008 Aug;128(8):876-80 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Postema RJ, Kingma CM, Wit HP, Albers FW, Van Der Laan BF. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for control of vertigo in unilateral Menire's disease: a prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008 Aug;128(8):876-80 | CrossRef | PubMed | Quaglieri S, Gatti O, Rebecchi E, Manfrin M, Tinelli C, Mira E, Benazzo M. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment 'as needed' for Meniere's disease. Long-term analysis using the Kaplan-Meier method. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Jun;271(6):1443-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Quaglieri S, Gatti O, Rebecchi E, Manfrin M, Tinelli C, Mira E, Benazzo M. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment 'as needed' for Meniere's disease. Long-term analysis using the Kaplan-Meier method. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Jun;271(6):1443-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Quaranta A, Aloisi A, De Benedittis G, Scaringi A. Intratympanic therapy for Ménière's disease. High-concentration gentamicin with round-window protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Nov 28;884:410-24 | PubMed |
Quaranta A, Aloisi A, De Benedittis G, Scaringi A. Intratympanic therapy for Ménière's disease. High-concentration gentamicin with round-window protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Nov 28;884:410-24 | PubMed | Quaranta A, Scaringi A, Aloidi A, Quaranta N, Salonna I. Intratympanic therapy for Ménière's disease: effect of administration of low concentration of gentamicin. Acta Otolaryngol. 2001 Apr;121(3):387-92 | PubMed |
Quaranta A, Scaringi A, Aloidi A, Quaranta N, Salonna I. Intratympanic therapy for Ménière's disease: effect of administration of low concentration of gentamicin. Acta Otolaryngol. 2001 Apr;121(3):387-92 | PubMed | Quaranta, A., Aloisi, A., De Benedittis, D. and Scaringi, A. (1999). Intratympanic therapy for Meniere’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. | Link |
Quaranta, A., Aloisi, A., De Benedittis, D. and Scaringi, A. (1999). Intratympanic therapy for Meniere’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. | Link | Rah YC, Han JJ, Park J, Choi BY, Koo JW. Management of intractable Ménière's disease after intratympanic injection of gentamicin. Laryngoscope. 2015 Apr;125(4):972-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Rah YC, Han JJ, Park J, Choi BY, Koo JW. Management of intractable Ménière's disease after intratympanic injection of gentamicin. Laryngoscope. 2015 Apr;125(4):972-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Rauch SD, Oas JG. Intratympanic gentamicin for treatment of intractable Meniere's disease: a preliminary report. Laryngoscope. 1997 Jan;107(1):49-55 | PubMed |
Rauch SD, Oas JG. Intratympanic gentamicin for treatment of intractable Meniere's disease: a preliminary report. Laryngoscope. 1997 Jan;107(1):49-55 | PubMed | Sala T. Transtympanic administration of aminoglycosides in patients with Menière's disease. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1988;245(5):293-6 | PubMed |
Sala T. Transtympanic administration of aminoglycosides in patients with Menière's disease. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1988;245(5):293-6 | PubMed | Sala T. Transtympanic gentamicin in the treatment of Meniére's disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1997 Jul;24(3):239-46 | PubMed |
Sala T. Transtympanic gentamicin in the treatment of Meniére's disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1997 Jul;24(3):239-46 | PubMed | Schoendorf J, Neugebauer P, Michel O. Continuous intratympanic infusion of gentamicin via a microcatheter in Menière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001 Feb;124(2):203-7 | PubMed |
Schoendorf J, Neugebauer P, Michel O. Continuous intratympanic infusion of gentamicin via a microcatheter in Menière's disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001 Feb;124(2):203-7 | PubMed | Seidman M. Continuous gentamicin therapy using an IntraEAR microcatheter for Meniere's disease: a retrospective study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Mar;126(3):244-56 | PubMed |
Seidman M. Continuous gentamicin therapy using an IntraEAR microcatheter for Meniere's disease: a retrospective study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Mar;126(3):244-56 | PubMed | Shamas IU. Short Term Results of Intra Tympanic Gentamicin and Dexamethasone on Hearing and Tinnitus in Meniere's disease: A Case Control Study. Int Tinnitus J. 2017 Jun 1;21(1):21-23 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Shamas IU. Short Term Results of Intra Tympanic Gentamicin and Dexamethasone on Hearing and Tinnitus in Meniere's disease: A Case Control Study. Int Tinnitus J. 2017 Jun 1;21(1):21-23 | CrossRef | PubMed | Shea PF, Richey PA, Wan JY, Stevens SR. Hearing results and quality of life after streptomycin/dexamethasone perfusion for Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2012 Jan;122(1):204-11 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Shea PF, Richey PA, Wan JY, Stevens SR. Hearing results and quality of life after streptomycin/dexamethasone perfusion for Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope. 2012 Jan;122(1):204-11 | CrossRef | PubMed | Silverstein H, Wazen J, Van Ess MJ, Daugherty J, Alameda YA. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment of patients with Ménière's disease with normal hearing. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Apr;142(4):570-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Silverstein H, Wazen J, Van Ess MJ, Daugherty J, Alameda YA. Intratympanic gentamicin treatment of patients with Ménière's disease with normal hearing. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 Apr;142(4):570-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Stokroos R, Kingma H. Selective vestibular ablation by intratympanic gentamicin in patients with unilateral active Ménière's disease: a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004 Mar;124(2):172-5 | PubMed |
Stokroos R, Kingma H. Selective vestibular ablation by intratympanic gentamicin in patients with unilateral active Ménière's disease: a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004 Mar;124(2):172-5 | PubMed | Suryanarayanan R, Cook JA. Long-term results of gentamicin inner ear perfusion in Ménière's disease. J Laryngol Otol. 2004 Jul;118(7):489-95 | PubMed |
Suryanarayanan R, Cook JA. Long-term results of gentamicin inner ear perfusion in Ménière's disease. J Laryngol Otol. 2004 Jul;118(7):489-95 | PubMed | Suryanarayanan R, Srinivasan VR, O'Sullivan G. Transtympanic gentamicin treatment using Silverstein MicroWick in Ménière's disease patients: long term outcome. J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Jan;123(1):45-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Suryanarayanan R, Srinivasan VR, O'Sullivan G. Transtympanic gentamicin treatment using Silverstein MicroWick in Ménière's disease patients: long term outcome. J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Jan;123(1):45-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Thomsen J, Charabi S, Tos M. Preliminary results of a new delivery system for gentamicin to the inner ear in patients with Meniere's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000;257(7):362-5 | PubMed |
Thomsen J, Charabi S, Tos M. Preliminary results of a new delivery system for gentamicin to the inner ear in patients with Meniere's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000;257(7):362-5 | PubMed | Watanabe S, Kato I, Takahashi K, Yoshino K, Takeyama I. Indications and results of gentamycin injection into the middle ear of patients with meniére's disease. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1995;519:282-5 | PubMed |
Watanabe S, Kato I, Takahashi K, Yoshino K, Takeyama I. Indications and results of gentamycin injection into the middle ear of patients with meniére's disease. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1995;519:282-5 | PubMed | Wu IC, Minor LB. Long-term hearing outcome in patients receiving intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease. Laryngoscope. 2003 May;113(5):815-20 | PubMed |
Wu IC, Minor LB. Long-term hearing outcome in patients receiving intratympanic gentamicin for Ménière's disease. Laryngoscope. 2003 May;113(5):815-20 | PubMed | Yamazaki T, Hayashi M, Komatsuzaki A. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Menière's disease placed by a tubal catheter with systematic isosorbide. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1991;481:613-6 | PubMed |
Yamazaki T, Hayashi M, Komatsuzaki A. Intratympanic gentamicin therapy for Menière's disease placed by a tubal catheter with systematic isosorbide. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1991;481:613-6 | PubMed | Yetiser S, Kertmen M. Intratympanic gentamicin in Menière's disease: the impact on tinnitus. Int J Audiol. 2002 Sep;41(6):363-70 | PubMed |
Yetiser S, Kertmen M. Intratympanic gentamicin in Menière's disease: the impact on tinnitus. Int J Audiol. 2002 Sep;41(6):363-70 | PubMed | Youssef TF, Poe DS. Intratympanic gentamicin injection for the treatment of Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1998 Jul;19(4):435-42 | PubMed |
Youssef TF, Poe DS. Intratympanic gentamicin injection for the treatment of Meniere's disease. Am J Otol. 1998 Jul;19(4):435-42 | PubMed | Marín Garrido C, Fraile Rodrigo J, Naya Gálvez MJ, Samperiz LC, Hernández Montero E, Ortiz García A. [Intra-tympanic gentamicin in the treatment of Ménière's disease: preliminary results]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2002 May;53(5):326-32 | PubMed |
Marín Garrido C, Fraile Rodrigo J, Naya Gálvez MJ, Samperiz LC, Hernández Montero E, Ortiz García A. [Intra-tympanic gentamicin in the treatment of Ménière's disease: preliminary results]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2002 May;53(5):326-32 | PubMed | Nevoux J, Franco-Vidal V, Bouccara D, Parietti-Winkler C, Uziel A, Chays A, Dubernard X, Couloigner V, Darrouzet V, Mom T; Groupe de Travail de la SFORL. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategy in Menière's disease. Guidelines of the French Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Society (SFORL). Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Jan 3. pii: S1879-7296(16)30222-8
Nevoux J, Franco-Vidal V, Bouccara D, Parietti-Winkler C, Uziel A, Chays A, Dubernard X, Couloigner V, Darrouzet V, Mom T; Groupe de Travail de la SFORL. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategy in Menière's disease. Guidelines of the French Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Society (SFORL). Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2017 Jan 3. pii: S1879-7296(16)30222-8  Magnan, J., Özgirgin, O., Trabalzini, F., Lacour, M., Lopez, A., Magnusson, M., Alpin, E., Philippe, J., Nuti, D. and Mandala, M. (2018). European Position Statement on Diagnosis, and Treatment of Meniere’s Disease*. J Int Adv Otol, [online] 14(2), pp.317-321 | Link |
Magnan, J., Özgirgin, O., Trabalzini, F., Lacour, M., Lopez, A., Magnusson, M., Alpin, E., Philippe, J., Nuti, D. and Mandala, M. (2018). European Position Statement on Diagnosis, and Treatment of Meniere’s Disease*. J Int Adv Otol, [online] 14(2), pp.317-321 | Link | Weiming Hao, Huiqian Yu, Huawei Li. The effects of intratympanic therapy of Ménière’s disease: a network meta-analysis. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018114389 | Link |
Weiming Hao, Huiqian Yu, Huawei Li. The effects of intratympanic therapy of Ménière’s disease: a network meta-analysis. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018114389 | Link | Louise Devantier, Jesper Hvass Schmidt, Frank Liviu-Adelin Guldfred, Dan Dupont Hougaard, Bjarki Djurhuus, Mina Nicole Händel, Henriette Callesen. A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment of patients with Menieres disease with gentamicin. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018110119 | Link |
Louise Devantier, Jesper Hvass Schmidt, Frank Liviu-Adelin Guldfred, Dan Dupont Hougaard, Bjarki Djurhuus, Mina Nicole Händel, Henriette Callesen. A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment of patients with Menieres disease with gentamicin. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018110119 | Link | Kinga Harmat, Adrienne Németh. Efficacy and safety of intratympanic steroid and gentamicin treatment of Ménière’s disease: a meta-analysis. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018095413 | Link |
Kinga Harmat, Adrienne Németh. Efficacy and safety of intratympanic steroid and gentamicin treatment of Ménière’s disease: a meta-analysis. PROSPERO 2018 CRD42018095413 | Link |