 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Palabras clave: Silver diamine fluoride, Dental atraumatic restorative treatment, Caries arrest, primary teeth, Epistemonikos, GRADE.
INTRODUCTION
Cavitated carious lesions in primary and mixed dentition require prompt treatment to control caries progression. Silver diamine fluoride has emerged as an alternative to the atraumatic restorative technique due to its easy application. However, there is still uncertainty regarding its effectiveness and safety.
METHODS
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a metanalysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified ten systematic reviews, including two studies overall, which are randomized trials. We concluded that silver diamine fluoride compared to the atraumatic restorative technique may increase the arrest of caries in primary and mixed first phase dentition, however, the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as low. On the other hand, treatment with silver diamine fluoride compared to the atraumatic restorative technique (ART) probably increases the risk of adverse events.
The worldwide prevalence of caries in children under 5 and 6 years old varies between 49% and 64.4% according to data from the World Health Organization [1]. Dental caries affects general health, having a negative impact on growth, quality of life and cognitive development, besides oral health [2].To treat cavitated carious lesions, the atraumatic restorative technique (ART), is not always feasible to perform due to its complexity, material resources required, and behavior management of the pediatric patient. Silver diamine fluoride has emerged as an alternative to atraumatic restorative technique since it inhibits cariogenic biofilm formation and generates a highly remineralized dentin surface, rich in calcium and phosphate ions [3], [4]. Among the silver diamine fluoride benefits, its non-invasive features characterized by a simple application technique stands out, therefore, it appears to be a promising treatment for young children, patients with bad behavior or special needs. However, there is still uncertainty regarding its effectiveness and safety.
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We identified ten systematic reviews [2], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13] including two studies overall [14], [15] , of which both were randomized trials. The table and summary in general are based on the latter. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
Both trials included children (3 to 6 years) with primary and mixed first phase dentition, with cavitated caries lesions without pulp injury [14], [15]. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
All trials evaluated the use of silver diamine fluoride compared to atraumatic restorative technique (ART). One trial [14] evaluated 38% silver diamine fluoride in two different application schemes: in one group was applied every six months, and in the second group every 12 months. The second trial [15], administered 30% silver diamine fluoride as a single dose. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The trials evaluated multiple outcomes, which were grouped by the systematic reviews as follows:
|
* Information about primary studies is not extracted directly from primary studies but from identified systematic reviews, unless otherwise stated.
The information on the effects of silver diamine fluoride compared to the atraumatic restorative technique (ART) is based on two randomized clinical trials [14], [15]. One of them [14] included two groups that received silver diamine fluoride in different application doses, so they were considered separately. Both trials measured the arrest of caries lesions [14], [15] (303 patients, 953 teeth). No review allowed the extraction of data from adverse events for silver diamine fluoride or atraumatic restorative technique, so the information on this outcome is presented as a narrative synthesis. No systematic review measured pain or patient and parent acceptance and perception outcomes.
The summary of findings is as follows:
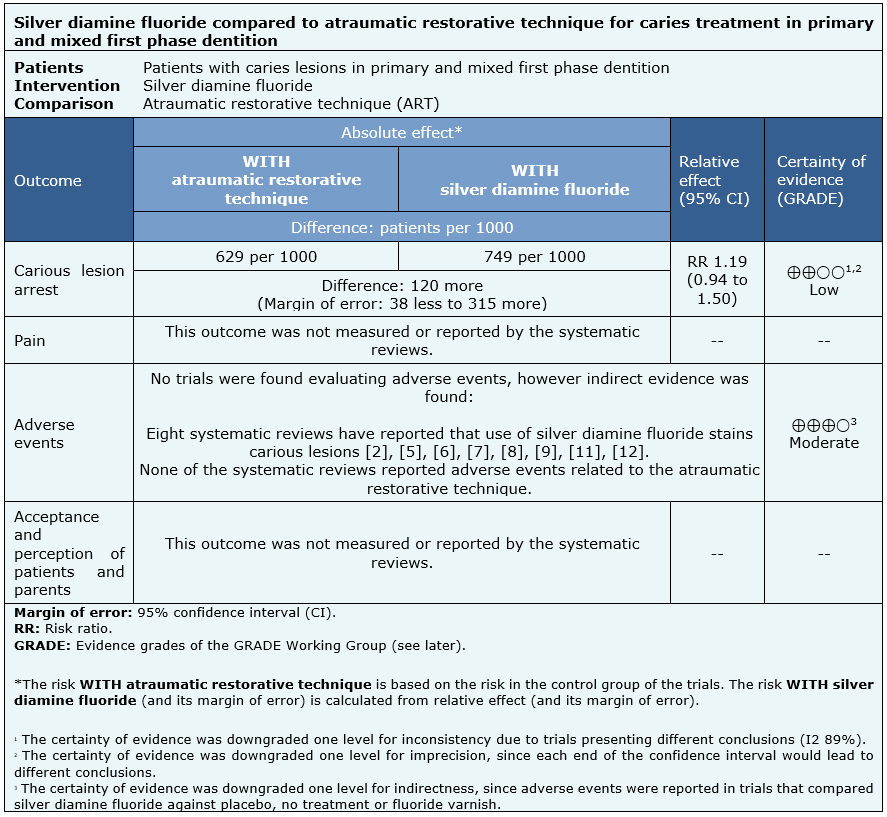
| Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF) |
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
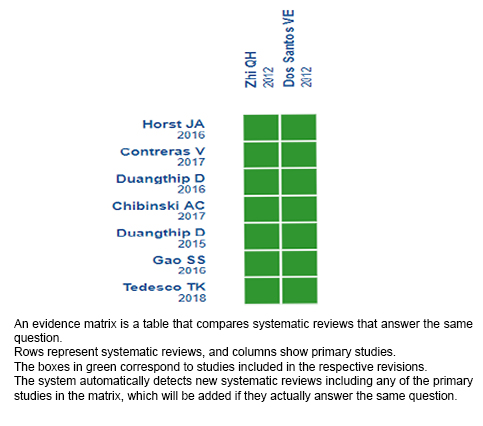
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Silver diamine fluoride compared to atraumatic restorative technique for the treatment of caries in primary and mixed first phase dentition.
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

INTRODUCTION
Cavitated carious lesions in primary and mixed dentition require prompt treatment to control caries progression. Silver diamine fluoride has emerged as an alternative to the atraumatic restorative technique due to its easy application. However, there is still uncertainty regarding its effectiveness and safety.
METHODS
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a metanalysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified ten systematic reviews, including two studies overall, which are randomized trials. We concluded that silver diamine fluoride compared to the atraumatic restorative technique may increase the arrest of caries in primary and mixed first phase dentition, however, the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as low. On the other hand, treatment with silver diamine fluoride compared to the atraumatic restorative technique (ART) probably increases the risk of adverse events.
 Autores:
Juan Pablo Vargas[1,2], Macarena Uribe[1,2], Duniel Ortuño[1,2], Francisca Verdugo-Paiva[2,3]
Autores:
Juan Pablo Vargas[1,2], Macarena Uribe[1,2], Duniel Ortuño[1,2], Francisca Verdugo-Paiva[2,3]

Citación: Vargas JP, Uribe M, Ortuño D, Verdugo-Paiva F. Silver diamine fluoride compared to atraumatic restorative technique for the treatment of caries in primary and mixed first phase dentition. Medwave 2020;20(07):e8002 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2020.07.8002
Fecha de envío: 26/12/2019
Fecha de aceptación: 2/6/2020
Fecha de publicación: 25/8/2020
Origen: Este artículo es producto del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project de la Fundación Epistemonikos, en colaboración con Medwave para su publicación.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares sin ciego por parte del equipo metodológico del Centro Evidencia UC en colaboración con Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project.

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Frencken JE, Sharma P, Stenhouse L, Green D, Laverty D, Dietrich T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis - a comprehensive review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology [Internet]. 2017 Mar 2 [cited 2019 Jun 11];44:S94–105.
Frencken JE, Sharma P, Stenhouse L, Green D, Laverty D, Dietrich T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis - a comprehensive review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology [Internet]. 2017 Mar 2 [cited 2019 Jun 11];44:S94–105.  Gao SS, Zhao IS, Hiraishi N, Duangthip D, Mei ML, Lo ECM, Chu CH. Clinical Trials of Silver Diamine Fluoride in Arresting Caries among Children: A Systematic Review. JDR clinical and translational research. 2016;1(3):201-210.
Gao SS, Zhao IS, Hiraishi N, Duangthip D, Mei ML, Lo ECM, Chu CH. Clinical Trials of Silver Diamine Fluoride in Arresting Caries among Children: A Systematic Review. JDR clinical and translational research. 2016;1(3):201-210.  Rosenblatt A, Stamford T, Niederman R: Silver diamine fluoride: a caries “silver-fluoride bullet”. J Dent Res 2009;88:116–125.
Rosenblatt A, Stamford T, Niederman R: Silver diamine fluoride: a caries “silver-fluoride bullet”. J Dent Res 2009;88:116–125.  Mei ML, Ito L, Cao Y, Li Q, Lo EC, Chu C: Inhibitory effect of silver diamine fluoride on dentine demineralisation and collagen degradation. J Dent 2013;41:809–817.
Mei ML, Ito L, Cao Y, Li Q, Lo EC, Chu C: Inhibitory effect of silver diamine fluoride on dentine demineralisation and collagen degradation. J Dent 2013;41:809–817.  Oliveira BH, Rajendra A, Veitz-Keenan A, Niederman R. The Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride in Preventing Caries in the Primary Dentition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Caries research. 2019;53(1):24-32.
Oliveira BH, Rajendra A, Veitz-Keenan A, Niederman R. The Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride in Preventing Caries in the Primary Dentition: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Caries research. 2019;53(1):24-32.  Gao SS, Zhang S, Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu CH. Caries remineralisation and arresting effect in children by professionally applied fluoride treatment - a systematic review. BMC oral health. 2016;16:12.
Gao SS, Zhang S, Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu CH. Caries remineralisation and arresting effect in children by professionally applied fluoride treatment - a systematic review. BMC oral health. 2016;16:12.  Horst JA, Ellenikiotis H, Milgrom PL. UCSF Protocol for Caries Arrest Using Silver Diamine Fluoride: Rationale, Indications and Consent. Journal of the California Dental Association. 2016;44(1):16-28.
Horst JA, Ellenikiotis H, Milgrom PL. UCSF Protocol for Caries Arrest Using Silver Diamine Fluoride: Rationale, Indications and Consent. Journal of the California Dental Association. 2016;44(1):16-28.  Contreras V, Toro MJ, Elías-Boneta AR, Encarnación-Burgos A. Effectiveness of silver diamine fluoride in caries prevention and arrest: a systematic literature review. General dentistry. 2017;65(3):22-29.
Contreras V, Toro MJ, Elías-Boneta AR, Encarnación-Burgos A. Effectiveness of silver diamine fluoride in caries prevention and arrest: a systematic literature review. General dentistry. 2017;65(3):22-29.  Duangthip D, Jiang M, Chu CH, Lo EC. Restorative approaches to treat dentin caries in preschool children: systematic review. European journal of paediatric dentistry : official journal of European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry. 2016;17(2):113-121.
Duangthip D, Jiang M, Chu CH, Lo EC. Restorative approaches to treat dentin caries in preschool children: systematic review. European journal of paediatric dentistry : official journal of European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry. 2016;17(2):113-121.  Tedesco TK, Gimenez T, Floriano I, Montagner AF, Camargo LB, Calvo AFB, Morimoto S, Raggio DP. Scientific evidence for the management of dentin caries lesions in pediatric dentistry: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PloS one. 2018;13(11):e0206296.
Tedesco TK, Gimenez T, Floriano I, Montagner AF, Camargo LB, Calvo AFB, Morimoto S, Raggio DP. Scientific evidence for the management of dentin caries lesions in pediatric dentistry: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PloS one. 2018;13(11):e0206296.  Chibinski AC, Wambier LM, Feltrin J, Loguercio AD, Wambier DS, Reis A. Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Caries research. 2017;51(5):527-541.
Chibinski AC, Wambier LM, Feltrin J, Loguercio AD, Wambier DS, Reis A. Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Caries research. 2017;51(5):527-541.  Duangthip D, Jiang M, Chu CH, Lo EC. Non-surgical treatment of dentin caries in preschool children - systematic review. BMC oral health. 2015;15(1):44.
Duangthip D, Jiang M, Chu CH, Lo EC. Non-surgical treatment of dentin caries in preschool children - systematic review. BMC oral health. 2015;15(1):44.  Sharma G, Puranik MP, K R S. Approaches to Arresting Dental Caries: An Update. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research : JCDR. 2015;9(5):ZE08-11.
Sharma G, Puranik MP, K R S. Approaches to Arresting Dental Caries: An Update. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research : JCDR. 2015;9(5):ZE08-11.  Zhi QH, Lo EC, Lin HC. Randomized clinical trial on effectiveness of silver diamine fluoride and glass ionomer in arresting dentine caries in preschool children. Journal of dentistry. 2012;40(11):962-7.
Zhi QH, Lo EC, Lin HC. Randomized clinical trial on effectiveness of silver diamine fluoride and glass ionomer in arresting dentine caries in preschool children. Journal of dentistry. 2012;40(11):962-7.  Dos Santos VE, de Vasconcelos FM, Ribeiro AG, Rosenblatt A. Paradigm shift in the effective treatment of caries in schoolchildren at risk. International dental journal. 2012;62(1):47-51.
Dos Santos VE, de Vasconcelos FM, Ribeiro AG, Rosenblatt A. Paradigm shift in the effective treatment of caries in schoolchildren at risk. International dental journal. 2012;62(1):47-51.  Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu CH. Clinical use of silver diamine fluoride in dental treatment. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2016;37(2):93-98.
Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu CH. Clinical use of silver diamine fluoride in dental treatment. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2016;37(2):93-98.  Wambier DS, Bosco VL. Use of cariostatic in pediatric dentistry: silver diamine fluoride. Rev Odontopediatr 1995 4: 35–41.
Wambier DS, Bosco VL. Use of cariostatic in pediatric dentistry: silver diamine fluoride. Rev Odontopediatr 1995 4: 35–41.  Crystal YO, Janal MN, Hamilton DS, Niederman R. Parental perceptions and acceptance of silver diamine fluoride staining. J Am Dent Assoc. 2017 Jul;148(7):510-518.e4.
Crystal YO, Janal MN, Hamilton DS, Niederman R. Parental perceptions and acceptance of silver diamine fluoride staining. J Am Dent Assoc. 2017 Jul;148(7):510-518.e4.  Crystal YO, Marghalani AA, Ureles SD, et al. Use of silver diamine fluoride for dental caries management in children and adolescents, including those with special health care needs. Pediatr Dent. 2017;39(5):135–145.
Crystal YO, Marghalani AA, Ureles SD, et al. Use of silver diamine fluoride for dental caries management in children and adolescents, including those with special health care needs. Pediatr Dent. 2017;39(5):135–145.  Slayton, Rebecca L. et al.Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on nonrestorative treatments for carious lesions.The Journal of the American Dental Association, Volume 149, Issue 10, 837 - 849.e19.
Slayton, Rebecca L. et al.Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on nonrestorative treatments for carious lesions.The Journal of the American Dental Association, Volume 149, Issue 10, 837 - 849.e19.  NCT03563534. Post-operative Pain After Silver Diamine Fluoride Application in Primary Molars With Deep Caries Versus Interim Restorative Therapy.
NCT03563534. Post-operative Pain After Silver Diamine Fluoride Application in Primary Molars With Deep Caries Versus Interim Restorative Therapy.  NCT03448107. Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments to Prevent Dental Caries Given to Rural Children in School-based Settings: Protocol for a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial.
NCT03448107. Comparative Effectiveness of Treatments to Prevent Dental Caries Given to Rural Children in School-based Settings: Protocol for a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial.  NCT03881020. Comparison of Silver Modified and Conventional Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Modalities in Primary Molars in a Group of Egyptian School Children. A Randomized Controlled Trial.
NCT03881020. Comparison of Silver Modified and Conventional Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Modalities in Primary Molars in a Group of Egyptian School Children. A Randomized Controlled Trial.  NCT03442309. Silver Diamine Fluoride Versus Therapeutic Sealants for the Arrest and Prevention of Dental Caries in Low-income Minority Children.
NCT03442309. Silver Diamine Fluoride Versus Therapeutic Sealants for the Arrest and Prevention of Dental Caries in Low-income Minority Children.  NCT03855527. Effectiveness of Silver Diamine Fluoride as Cavity Disinfectant After Atraumatic Restorative Treatment in Primary Teeth: A Randomized Clinical Trial.
NCT03855527. Effectiveness of Silver Diamine Fluoride as Cavity Disinfectant After Atraumatic Restorative Treatment in Primary Teeth: A Randomized Clinical Trial.  NCT03568474. Postoperative Pain After Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Glass Ionomer Versus Glass Ionomer Alone Following Minimal Caries Removal Technique in Asymptomatic Young Permanent Teeth With Deep Caries. A Randomized Pilot Study.
NCT03568474. Postoperative Pain After Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Glass Ionomer Versus Glass Ionomer Alone Following Minimal Caries Removal Technique in Asymptomatic Young Permanent Teeth With Deep Caries. A Randomized Pilot Study.  NCT03872986. Clinical Evaluation of Caries Sealing Technique on Primary Teeth Using Giomer and Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) With or Without Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF).
NCT03872986. Clinical Evaluation of Caries Sealing Technique on Primary Teeth Using Giomer and Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) With or Without Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF).  Oliveira BH, Niederman R, Rajendra A, Ruff R, et al. Does topical silver diamine fluoride control dental caries?. PROSPERO 2016 CRD42016036963.
Oliveira BH, Niederman R, Rajendra A, Ruff R, et al. Does topical silver diamine fluoride control dental caries?. PROSPERO 2016 CRD42016036963.