 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
INTRODUCCIÓN
Se postula que la acupuntura podría tener diversos beneficios para pacientes con enfermedad de Parkinson. No obstante, su real efectividad clínica aún es discutida.
MÉTODOS
Para responder esta pregunta utilizamos Epistemonikos, la mayor base de datos de revisiones sistemáticas en salud, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples fuentes de información, incluyendo MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, entre otras. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas, reanalizamos los datos de los estudios primarios, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos una tabla de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE.
RESULTADOS Y CONCLUSIONES
Identificamos nueve revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 53 estudios primarios, de los cuales 45 corresponden a ensayos aleatorizados. Concluimos que la acupuntura podría tener un efecto mínimo en mejorar los síntomas motores y la discapacidad en la enfermedad de Parkinson, pero la certeza de la evidencia es baja.
La enfermedad de Parkinson es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa crónica frecuente. El tratamiento de elección es la levodopa, pero a largo plazo su efectividad disminuye y pueden aparecer efectos adversos como deterioro de fin de dosis y discinesias. En este contexto, muchos pacientes buscan terapias complementarias, entre ellas la acupuntura, la cual se cree ejercería efectos sistémicos por medio de su acción local. De esta forma lograría una mejoría sobre los síntomas motores del Parkinson y el grado de discapacidad. No obstante, aún no está claro cuál es su real efecto clínico en esta enfermedad.
Para responder esta pregunta utilizamos Epistemonikos, la mayor base de datos de revisiones sistemáticas en salud, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples fuentes de información, incluyendo MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, entre otras. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas y reanalizamos los datos de los estudios primarios. Con esta información, generamos un resumen estructurado denominado FRISBEE (Friendly Summaries of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), siguiendo un formato preestablecido, que incluye mensajes clave, un resumen del conjunto de evidencia (presentado como matriz de evidencia en Epistemonikos), metanálisis del total de los estudios cuando sea posible, una tabla de resumen de resultados con el método GRADE y una sección de otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión.
|
Mensajes clave
|
|
Cuál es la evidencia |
Encontramos nueve revisiones sistemáticas [1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9], que incluyen 53 estudios primarios [10],[11],[12],[13],[14], |
|
Qué tipo de pacientes incluyeron los estudios* |
Se incluyeron pacientes con enfermedad de Parkinson con o sin complicaciones motoras. No obstante, no se detalla el grado de progresión de la enfermedad, ni la proporción de pacientes con compromiso cognitivo y otras manifestaciones no motoras. |
|
Qué tipo de intervenciones incluyeron los estudios* |
En 16 ensayos se utilizó acupuntura tradicional [18],[19],[21],[23], En 33 ensayos se comparó contra no uso de acupuntura [19],[20], |
|
Qué tipo de desenlaces midieron |
De los múltiples desenlaces medidos por los ensayos, las revisiones sistemáticas presentaron de manera agrupada los siguientes:
El seguimiento fluctuó entre 4 semanas y 3 meses. |
* La información sobre los estudios primarios es extraída desde las revisiones sistemáticas identificadas, no directamente desde los estudios, a menos que se especifique lo contrario.
Cuál es la evidencia
La información sobre los efectos de la acupuntura sobre los síntomas motores está basada en seis ensayos aleatorizados [21],[29],[31],[34],[41],[59] que incluyen 396 pacientes. El resto de los ensayos no reportaron los desenlaces de interés o lo hicieron de una forma que no permitió su incorporación en el metanálisis.
Todos los ensayos reportaron síntomas motores medidos en escala UPDRS III (396 pacientes). Cuatro ensayos [28],[34],[61],[62] reportaron grado de discapacidad medido en Webster (208 pacientes) y cuatro ensayos [23],[24],[44],[55] reportaron el desenlace efectos adversos (150 pacientes).
El resumen de los resultados es el siguiente:
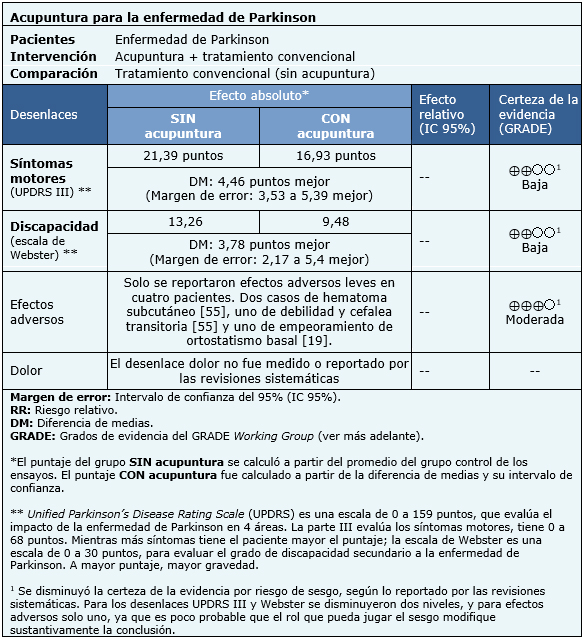
|
A quién se aplica y a quién no se aplica esta evidencia |
|
| Sobre los desenlaces incluidos en este resumen |
|
| Balance riesgo/beneficio y certeza de la evidencia |
|
| Consideraciones de recursos |
|
| Qué piensan los pacientes y sus tratantes |
|
| Diferencias entre este resumen y otras fuentes |
|
| ¿Puede que cambie esta información en el futuro? |
|
Mediante métodos automatizados y colaborativos recopilamos toda la evidencia relevante para la pregunta de interés y la presentamos en una matriz de evidencia.
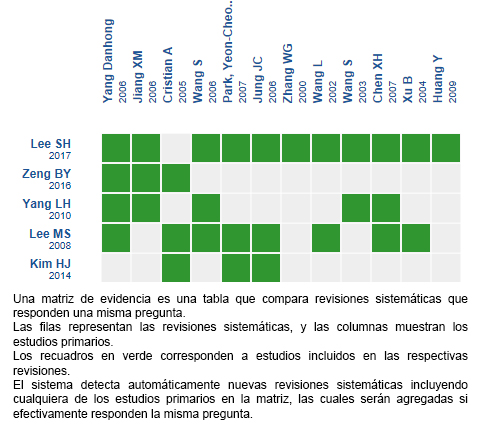
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva: Acupuntura para la enfermedad de Parkinson
Si con posterioridad a la publicación de este resumen se publican nuevas revisiones sistemáticas sobre este tema, en la parte superior de la matriz se mostrará un aviso de “nueva evidencia”. Si bien el proyecto contempla la actualización periódica de estos resúmenes, los usuarios están invitados a comentar en la página web de Medwave o contactar a los autores mediante correo electrónico si creen que hay evidencia que motive una actualización más precoz.
Luego de crear una cuenta en Epistemonikos, al guardar las matrices recibirá notificaciones automáticas cada vez que exista nueva evidencia que potencialmente responda a esta pregunta.
Este artículo es parte del proyecto síntesis de evidencia de Epistemonikos. Se elabora con una metodología preestablecida, siguiendo rigurosos estándares metodológicos y proceso de revisión por pares interno. Cada uno de estos artículos corresponde a un resumen, denominado FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), cuyo principal objetivo es sintetizar el conjunto de evidencia de una pregunta específica, en un formato amigable a los profesionales clínicos. Sus principales recursos se basan en la matriz de evidencia de Epistemonikos y análisis de resultados usando metodología GRADE. Mayores detalles de los métodos para elaborar este FRISBEE están descritos aquí (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
La Fundación Epistemonikos es una organización que busca acercar la información a quienes toman decisiones en salud, mediante el uso de tecnologías. Su principal desarrollo es la base de datos Epistemonikos (www.epistemonikos.org).
Declaración de conflictos de intereses
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses con la materia de este artículo.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

INTRODUCTION
It has been proposed that acupuncture has several benefits for patients with Parkinson’s disease. However, its real clinical effect is still under discussion.
METHODS
To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified nine systematic reviews including 53 studies overall, of which 45 were randomized trials. We concluded acupuncture might have a small effect in improving motor symptoms and disability in Parkinson’s disease, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
 Autores:
José Otayza[1,2], Carlos Juri[2,3]
Autores:
José Otayza[1,2], Carlos Juri[2,3]

Citación: Otayza J, Juri C. Is acupuncture an alternative for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease?. Medwave 2018 May-Jun;18(3):e7197 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2018.03.7197
Fecha de envío: 12/12/2017
Fecha de aceptación: 28/12/2017
Fecha de publicación: 3/5/2018
Origen: Este artículo es producto del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project de la Fundación Epistemonikos, en colaboración con Medwave para su publicación.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares sin ciego por parte del equipo metodológico del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project.

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Kim HJ, Jeon BS. Is acupuncture efficacious therapy in Parkinson's disease? J Neurol Sci. 2014 Jun 15;341(1-2):1-7. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kim HJ, Jeon BS. Is acupuncture efficacious therapy in Parkinson's disease? J Neurol Sci. 2014 Jun 15;341(1-2):1-7. | CrossRef | PubMed | Lam YC, Kum WF, Durairajan SS, Lu JH, Man SC, Xu M, Zhang XF, Huang XZ, Li M. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. J Altern Complement Med. 2008 Jul;14(6):663-71. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lam YC, Kum WF, Durairajan SS, Lu JH, Man SC, Xu M, Zhang XF, Huang XZ, Li M. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. J Altern Complement Med. 2008 Jul;14(6):663-71. | CrossRef | PubMed | Lee HS, Park HL, Lee SJ, Shin BC, Choi JY, Lee MS. Scalp acupuncture for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):297-306. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lee HS, Park HL, Lee SJ, Shin BC, Choi JY, Lee MS. Scalp acupuncture for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):297-306. | CrossRef | PubMed | Lee MS, Shin BC, Choi SM, Kim JY. Randomized clinical trials of constitutional acupuncture: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2009 Sep;6 Suppl 1:59-64. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Lee MS, Shin BC, Choi SM, Kim JY. Randomized clinical trials of constitutional acupuncture: a systematic review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2009 Sep;6 Suppl 1:59-64. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Lee MS, Shin BC, Kong JC, Ernst E. Effectiveness of acupuncture for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Mov Disord. 2008 Aug 15;23(11):1505-15. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lee MS, Shin BC, Kong JC, Ernst E. Effectiveness of acupuncture for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Mov Disord. 2008 Aug 15;23(11):1505-15. | CrossRef | PubMed | Lee SH, Lim S. Clinical effectiveness of acupuncture on Parkinson disease: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jan;96(3):e5836. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Lee SH, Lim S. Clinical effectiveness of acupuncture on Parkinson disease: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jan;96(3):e5836. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Yang Lihong, Du Yuan Hao Xiong Jun, Liu Jialin, Wang Yunna, Li Ying, Li & Lina. (2010). Systematic review of the efficacy of acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease. Chinese Journal of Evidence, 10 (6), 711-717.
Yang Lihong, Du Yuan Hao Xiong Jun, Liu Jialin, Wang Yunna, Li Ying, Li & Lina. (2010). Systematic review of the efficacy of acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease. Chinese Journal of Evidence, 10 (6), 711-717.  Zeng BY, Zhao K. Effect of Acupuncture on the Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease--A Review of Clinical Studies. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 May;22(5):333-41. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zeng BY, Zhao K. Effect of Acupuncture on the Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease--A Review of Clinical Studies. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 May;22(5):333-41. | CrossRef | PubMed | Zhang G, Xiong N, Zhang Z, Liu L, Huang J, Yang J, Wu J, Lin Z, Wang T. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunct therapy for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 10;10(3):e0118498. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC |
Zhang G, Xiong N, Zhang Z, Liu L, Huang J, Yang J, Wu J, Lin Z, Wang T. Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunct therapy for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 10;10(3):e0118498. | CrossRef | PubMed | PMC | Zou Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture treatment of Parkinson’s syndrome. J Acupunct Tuina Sci 2006. | Link |
Zou Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture treatment of Parkinson’s syndrome. J Acupunct Tuina Sci 2006. | Link | Yuan Y, Chen F, Yang JS. [Forty-nine cases of Parkinson's disease treated by acupuncture adjunctive therapy]. Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion 2014 01/28;34(1):53-54. | Link |
Yuan Y, Chen F, Yang JS. [Forty-nine cases of Parkinson's disease treated by acupuncture adjunctive therapy]. Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion 2014 01/28;34(1):53-54. | Link | Ren XM. Fifty cases of Parkinson’s disease treated by acupuncture combined with madopar. J Tradit Chin Med 2008. | Link |
Ren XM. Fifty cases of Parkinson’s disease treated by acupuncture combined with madopar. J Tradit Chin Med 2008. | Link | Shulman LM, Wen X, Weiner WJ, Bateman D, Minagar A, Duncan R, Konefal J. Acupuncture therapy for the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2002 Jul;17(4):799-802. | PubMed |
Shulman LM, Wen X, Weiner WJ, Bateman D, Minagar A, Duncan R, Konefal J. Acupuncture therapy for the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2002 Jul;17(4):799-802. | PubMed | Liang X, Chen F. The effects of the Seven Acupoints of the Cranial Base on health related quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Trad Chin Med 2014. | Link |
Liang X, Chen F. The effects of the Seven Acupoints of the Cranial Base on health related quality of life for patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Trad Chin Med 2014. | Link | Kang MK, Lee SH, Hong JM, Park SM, Kang JW, Park HJ. Effect of electroacupuncture on patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Korean Acupunct Moxibust Soc 2004. | Link |
Kang MK, Lee SH, Hong JM, Park SM, Kang JW, Park HJ. Effect of electroacupuncture on patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Korean Acupunct Moxibust Soc 2004. | Link | Ha JY, Lee SH, Yin CS, Park SM, Kang JW, Chang DI. The effect of manual acupuncture therapy on symptoms of the patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Korean Orient Med 2003. | Link |
Ha JY, Lee SH, Yin CS, Park SM, Kang JW, Chang DI. The effect of manual acupuncture therapy on symptoms of the patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J Korean Orient Med 2003. | Link | Eng ML, Lyons KE, Greene MS, Pahwa R. Open-label trial regarding the use of acupuncture and yin tui na in Parkinson's disease outpatients: a pilot study on efficacy, tolerability, and quality of life. J Altern Complement Med. 2006 May;12(4):395-9. | PubMed |
Eng ML, Lyons KE, Greene MS, Pahwa R. Open-label trial regarding the use of acupuncture and yin tui na in Parkinson's disease outpatients: a pilot study on efficacy, tolerability, and quality of life. J Altern Complement Med. 2006 May;12(4):395-9. | PubMed | Chae Y, Lee H, Kim H, Kim CH, Chang DI, Kim KM, Park HJ. Parsing brain activity associated with acupuncture treatment in Parkinson's diseases. Mov Disord. 2009 Sep 15;24(12):1794-802. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Chae Y, Lee H, Kim H, Kim CH, Chang DI, Kim KM, Park HJ. Parsing brain activity associated with acupuncture treatment in Parkinson's diseases. Mov Disord. 2009 Sep 15;24(12):1794-802. | CrossRef | PubMed | Chang XH, Zhang LZ, Li YJ. [Observation on therapeutic effect of acupuncture combined with medicine on Parkinson disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2008 Sep;28(9):645-7. Chinese. | PubMed |
Chang XH, Zhang LZ, Li YJ. [Observation on therapeutic effect of acupuncture combined with medicine on Parkinson disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2008 Sep;28(9):645-7. Chinese. | PubMed | Chen XH, Li Y, Kui Y. [Clinical observation on abdominal acupuncture plus Madopa for treatment of Parkinson's disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007 Aug;27(8):562-4. Chinese. | PubMed |
Chen XH, Li Y, Kui Y. [Clinical observation on abdominal acupuncture plus Madopa for treatment of Parkinson's disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007 Aug;27(8):562-4. Chinese. | PubMed | Chen YH, Yang FX, Zhang DY. Clinical research of electro-acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for Parkinson's disease. Chin J Rehabil 2012. | Link |
Chen YH, Yang FX, Zhang DY. Clinical research of electro-acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for Parkinson's disease. Chin J Rehabil 2012. | Link | Chen YL, Feng WJ, Zhang XL. [Parkinson's disease combined with overactive bladder syndrome treated with acupuncture and medication]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012 Mar;32(3):215-8. Chinese. | PubMed |
Chen YL, Feng WJ, Zhang XL. [Parkinson's disease combined with overactive bladder syndrome treated with acupuncture and medication]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012 Mar;32(3):215-8. Chinese. | PubMed | Cho SY, Shim SR, Rhee HY, Park HJ, Jung WS, Moon SK, Park JM, Ko CN, Cho KH, Park SU. Effectiveness of acupuncture and bee venom acupuncture in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012 Sep;18(8):948-52. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Cho SY, Shim SR, Rhee HY, Park HJ, Jung WS, Moon SK, Park JM, Ko CN, Cho KH, Park SU. Effectiveness of acupuncture and bee venom acupuncture in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2012 Sep;18(8):948-52. | CrossRef | PubMed | Cristian A, Katz M, Cutrone E, Walker RH. Evaluation of acupuncture in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: a double-blind pilot study. Mov Disord. 2005 Sep;20(9):1185-8. | PubMed |
Cristian A, Katz M, Cutrone E, Walker RH. Evaluation of acupuncture in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: a double-blind pilot study. Mov Disord. 2005 Sep;20(9):1185-8. | PubMed | Danhong Y, Huade C. The principle of acupuncture with drugs on the rehabilitation of Parkinson's disease. Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2006. | Link |
Danhong Y, Huade C. The principle of acupuncture with drugs on the rehabilitation of Parkinson's disease. Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2006. | Link | Danhong Y, Yin S, Jia Shengmin. Acupuncture combined with drug therapy to improve the symptoms of Parkinson's disease And the impact on the antioxidant system of blood. Chinese clinical rehabilitation 2006. | Link |
Danhong Y, Yin S, Jia Shengmin. Acupuncture combined with drug therapy to improve the symptoms of Parkinson's disease And the impact on the antioxidant system of blood. Chinese clinical rehabilitation 2006. | Link | Feng C, Ying Y. Clinical Observation on treating Parkinson's disease by "the Seven Acupoints of the Cranial Base". (Chinese Journal of Basic Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine) 2008;14(9):680-682. | Link |
Feng C, Ying Y. Clinical Observation on treating Parkinson's disease by "the Seven Acupoints of the Cranial Base". (Chinese Journal of Basic Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine) 2008;14(9):680-682. | Link | Fu B, Lun X, Rong L. Electroacupuncture at head and du plus acupoints for treatment of Parkinson disease: randomized controlled observation. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;8(22):4524-4525. | Link |
Fu B, Lun X, Rong L. Electroacupuncture at head and du plus acupoints for treatment of Parkinson disease: randomized controlled observation. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;8(22):4524-4525. | Link | Gu K, Liu K, Lu ZY. Clinical observations on combined treatment of Parkinson's disease using acupuncture and medicine. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link |
Gu K, Liu K, Lu ZY. Clinical observations on combined treatment of Parkinson's disease using acupuncture and medicine. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link | Han TW, Liu JM, Li YJ. Clinical observation of using “Xingnaokaiqiao” acupuncture method to improve tremor paralysis. J North Sichuan Med College 2011. | Link |
Han TW, Liu JM, Li YJ. Clinical observation of using “Xingnaokaiqiao” acupuncture method to improve tremor paralysis. J North Sichuan Med College 2011. | Link | Huang Y, Jiang X, Zhuo Y, Tang A, Wik G. Complementary acupuncture treatment increases cerebral metabolism in patients with Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 2009;119(8):1190-7. | PubMed |
Huang Y, Jiang X, Zhuo Y, Tang A, Wik G. Complementary acupuncture treatment increases cerebral metabolism in patients with Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 2009;119(8):1190-7. | PubMed | Huang Y, Jiang X, Zhuo Y, Wik G. Complementary acupuncture in Parkinson's disease: a spect study. Int J Neurosci. 2010 Feb;120(2):150-4. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Huang Y, Jiang X, Zhuo Y, Wik G. Complementary acupuncture in Parkinson's disease: a spect study. Int J Neurosci. 2010 Feb;120(2):150-4. | CrossRef | PubMed | Jiang XM, Huang Y, Li DJ, Tang AW, Wang SX, Zhuo Y, Li QS, Chen J, Gao YP. [Effect of electro-scalp acupuncture on cerebral dopamine transporter in the striatum area of the patient of Parkinson's disease by means of single photon emission computer tomography]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006 Jun;26(6):427-30. Chinese. | PubMed |
Jiang XM, Huang Y, Li DJ, Tang AW, Wang SX, Zhuo Y, Li QS, Chen J, Gao YP. [Effect of electro-scalp acupuncture on cerebral dopamine transporter in the striatum area of the patient of Parkinson's disease by means of single photon emission computer tomography]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006 Jun;26(6):427-30. Chinese. | PubMed | Jiang XM, Huang Y, Zhuo Y, Gao YP. [Therapeutic effect of scalp electroacupuncture on Parkinson disease]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):114-6. Chinese. | PubMed |
Jiang XM, Huang Y, Zhuo Y, Gao YP. [Therapeutic effect of scalp electroacupuncture on Parkinson disease]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):114-6. Chinese. | PubMed | Jung JC, Kim KH, Park YC. The study on the effect of acupuncture on UPDRS and heart rate variability in the patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s diseas. J Korean Acupunct Moxibust Soc 2006. | Link |
Jung JC, Kim KH, Park YC. The study on the effect of acupuncture on UPDRS and heart rate variability in the patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s diseas. J Korean Acupunct Moxibust Soc 2006. | Link | Lei H, Toosizadeh N, Schwenk M. Objective assessment of electro-acupuncture benefit for improving balance and gait in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2014. | Link |
Lei H, Toosizadeh N, Schwenk M. Objective assessment of electro-acupuncture benefit for improving balance and gait in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2014. | Link | Li X. Clinical analysis on treatment of Parkinson’s disease by acupuncture of points on the governor vessel. Chinese Acupunct Moxibu 2003. | Link |
Li X. Clinical analysis on treatment of Parkinson’s disease by acupuncture of points on the governor vessel. Chinese Acupunct Moxibu 2003. | Link | Lifen Y, Xinghua C, Zhuang Lixing. Acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease clinical research. Journal of Medicine, 2007. | Link |
Lifen Y, Xinghua C, Zhuang Lixing. Acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease clinical research. Journal of Medicine, 2007. | Link | Liu XY, Jiang ZK, Xiang Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture for Parkinson's disease. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link |
Liu XY, Jiang ZK, Xiang Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture for Parkinson's disease. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link | Park Y, Chang D, Lee Yh, Park Ds. The study on the effect of acupunture Treatment in Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson`s Disease. The Journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 2007;24(4):43-43. | Link |
Park Y, Chang D, Lee Yh, Park Ds. The study on the effect of acupunture Treatment in Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson`s Disease. The Journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 2007;24(4):43-43. | Link | Ren XM, Shi YS, Shuang L. Clinical study on acupuncture tonifying liver and kidney in the treatment of Parkinson disease. Chin Archi Tradit Chin Med 2011. | Link |
Ren XM, Shi YS, Shuang L. Clinical study on acupuncture tonifying liver and kidney in the treatment of Parkinson disease. Chin Archi Tradit Chin Med 2011. | Link | Sun HN. Observations on combined treatment of Parkinson's disease using acupuncture and medicine—a report of 29 cases. Mongolia Tradit Chin Med 2014. | Link |
Sun HN. Observations on combined treatment of Parkinson's disease using acupuncture and medicine—a report of 29 cases. Mongolia Tradit Chin Med 2014. | Link | Wang L, He C, Liu Y, Zhu L. Effect of acupuncture on the auditory evoked brain stem potential in Parkinson's disease. J Tradit Chin Med. 2002 Mar;22(1):15-7. | PubMed |
Wang L, He C, Liu Y, Zhu L. Effect of acupuncture on the auditory evoked brain stem potential in Parkinson's disease. J Tradit Chin Med. 2002 Mar;22(1):15-7. | PubMed | Wang S, Cai YY, Shang YJ, Jin-rong L. [Effects of head point-through-point electroacupuncture on SOD and LPO in the patient of Parkinson's disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006 Apr;26(4):240-2. Chinese. | PubMed |
Wang S, Cai YY, Shang YJ, Jin-rong L. [Effects of head point-through-point electroacupuncture on SOD and LPO in the patient of Parkinson's disease]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2006 Apr;26(4):240-2. Chinese. | PubMed | Wang S, Zhou ZK, Hu BC. Clinical study on head point- through-point electroacupuncture for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion 2003. | Link |
Wang S, Zhou ZK, Hu BC. Clinical study on head point- through-point electroacupuncture for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Chin Acupunct Moxibustion 2003. | Link | Wén Xìng, Ying L. reatment of 30 cases of tetanus hyperactivity Parkinson's disease with abdominal acupuncture combined with moxibustion. Journal of Guangzhou Medical College 2008. | Link |
Wén Xìng, Ying L. reatment of 30 cases of tetanus hyperactivity Parkinson's disease with abdominal acupuncture combined with moxibustion. Journal of Guangzhou Medical College 2008. | Link | Wu Lingyun. Clinical and Experimental Study on the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. Doctoral Dissertation 2006. | Link |
Wu Lingyun. Clinical and Experimental Study on the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. Doctoral Dissertation 2006. | Link | Xia Y, Wang HD, Ding Y, Kang B, Liu WG. Parkinson’s disease combined with depression treated with electroacupuncture and medication and its effect on serum BDNF. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2012. | Link |
Xia Y, Wang HD, Ding Y, Kang B, Liu WG. Parkinson’s disease combined with depression treated with electroacupuncture and medication and its effect on serum BDNF. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2012. | Link | Xu B, Shen MH, Chen GZ. Effects of acupuncture and point-injection on central neuropeptide and nitric oxide in patients with primary Parkinson disease. Chin J Clin Rehabil 2004. | Link |
Xu B, Shen MH, Chen GZ. Effects of acupuncture and point-injection on central neuropeptide and nitric oxide in patients with primary Parkinson disease. Chin J Clin Rehabil 2004. | Link | Yan Y, Hongtao C. Clinical observation of 30 cases of Parkinson's disease treated with scalp acupuncture. Chi 2004. | Link |
Yan Y, Hongtao C. Clinical observation of 30 cases of Parkinson's disease treated with scalp acupuncture. Chi 2004. | Link | Yang DH, Chen H, Fang Z. Observations on the efficacy of acupuncture plus western drug on rehabilitation treatment of Parkinson’s diease. J Clin Acupunc Med 2006. | Link |
Yang DH, Chen H, Fang Z. Observations on the efficacy of acupuncture plus western drug on rehabilitation treatment of Parkinson’s diease. J Clin Acupunc Med 2006. | Link | Yang DH, Chen HD, Fang Z. Clinical observation of the efficacy of acupuncture plus drug in treatment of Parkinson disease. J Altern Complement Med 2006. | Link |
Yang DH, Chen HD, Fang Z. Clinical observation of the efficacy of acupuncture plus drug in treatment of Parkinson disease. J Altern Complement Med 2006. | Link | Yang DH, Chen HD, Fang Z. Efficacy of rehabilitation on acupuncture and Parkinson's disease drugs. JCAM 2006. | Link |
Yang DH, Chen HD, Fang Z. Efficacy of rehabilitation on acupuncture and Parkinson's disease drugs. JCAM 2006. | Link | Yang DH, Shi Y, Jia YM. Influence of acupuncture plus drug in the amelioration of symptoms and blood antioxidant system of patients with Parkinson disease. Chin J Clinic Rehabil 2006;10:14–6.
Yang DH, Shi Y, Jia YM. Influence of acupuncture plus drug in the amelioration of symptoms and blood antioxidant system of patients with Parkinson disease. Chin J Clinic Rehabil 2006;10:14–6.  Yang Y, Chen HT. Clinical observation on the treatment of parkinson’s disease by scalp. JCAM 2004. | Link |
Yang Y, Chen HT. Clinical observation on the treatment of parkinson’s disease by scalp. JCAM 2004. | Link | Yao LF, Chen XH, Zhuan LX, Bai DY. Clinical research of acupuncture in treatment of Parkinson disease. China Foreign Med J 2007. | Link |
Yao LF, Chen XH, Zhuan LX, Bai DY. Clinical research of acupuncture in treatment of Parkinson disease. China Foreign Med J 2007. | Link | Zhang Wenge. Head acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease in 32 cases. Bright Chinese medicine 2002. | Link |
Zhang Wenge. Head acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease in 32 cases. Bright Chinese medicine 2002. | Link | Zhang WG, Wang GB, Qing Y. Scalp acupuncture for treat- ment of Parkinson disease: 32 cases. Guang Ming Chi Med 2000. | Link |
Zhang WG, Wang GB, Qing Y. Scalp acupuncture for treat- ment of Parkinson disease: 32 cases. Guang Ming Chi Med 2000. | Link | Zhang XL, Feng WJ, Chen YL. Observations on combined use of acupuncture and medicine in treating Parkinson disease with mild cognitive impairment. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link |
Zhang XL, Feng WJ, Chen YL. Observations on combined use of acupuncture and medicine in treating Parkinson disease with mild cognitive impairment. Shanghai J Acu-mox 2013. | Link | Zhong P, Xu F, Hou YR, Fu WB. Clinical effect of moxibustion plus drug therapy of Parkinson's disease of liver-kidney deficiency syndrome. Chinese Journal of Gerontology. 2012. | Link |
Zhong P, Xu F, Hou YR, Fu WB. Clinical effect of moxibustion plus drug therapy of Parkinson's disease of liver-kidney deficiency syndrome. Chinese Journal of Gerontology. 2012. | Link | Zhuang X, Wang L. Acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease--a report of 29 cases. J Tradit Chin Med. 2000 Dec;20(4):265-7. | PubMed |
Zhuang X, Wang L. Acupuncture treatment of Parkinson's disease--a report of 29 cases. J Tradit Chin Med. 2000 Dec;20(4):265-7. | PubMed | Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Lim SY, Ravina B, Seppi K, Coelho M et al. (2015). The movement disorder society evidence‐based medicine review update: Treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders, 26(S3), S2-S41.
Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Lim SY, Ravina B, Seppi K, Coelho M et al. (2015). The movement disorder society evidence‐based medicine review update: Treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Movement Disorders, 26(S3), S2-S41.  Grimes D, Gordon J, Snelgrove B, Lim-Carter I, Fon E, Martin W, Wieler M, Suchowersky O, Rajput A, Lafontaine AL, Stoessl J, Moro E, Schoffer K, Miyasaki J, Hobson D, Mahmoudi M, Fox S, Postuma R, Kumar H, Jog M; Canadian Nourological Sciences Federation. Canadian Guidelines on Parkinson's Disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012 Jul;39(4 Suppl 4):S1-30. | PubMed |
Grimes D, Gordon J, Snelgrove B, Lim-Carter I, Fon E, Martin W, Wieler M, Suchowersky O, Rajput A, Lafontaine AL, Stoessl J, Moro E, Schoffer K, Miyasaki J, Hobson D, Mahmoudi M, Fox S, Postuma R, Kumar H, Jog M; Canadian Nourological Sciences Federation. Canadian Guidelines on Parkinson's Disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 2012 Jul;39(4 Suppl 4):S1-30. | PubMed | Huang Yong. Effect of Jin three-needle therapy on quality of life in patients of Parkinson Disease: a multicenter randomized controlled study. ChiCTR-INR-17013201 | Link |
Huang Yong. Effect of Jin three-needle therapy on quality of life in patients of Parkinson Disease: a multicenter randomized controlled study. ChiCTR-INR-17013201 | Link | Chao Hsien Hung. Acupuncture for Management of Balance Impairment in Patients with Parkinson's Disease. NCT03178175. | Link |
Chao Hsien Hung. Acupuncture for Management of Balance Impairment in Patients with Parkinson's Disease. NCT03178175. | Link | Harutsugu Tatebe. Examination of the acupuncture for the neurologic disease with muscle tone abnormalities including the Parkinson's syndrome. JPRN-UMIN000025559. | Link |
Harutsugu Tatebe. Examination of the acupuncture for the neurologic disease with muscle tone abnormalities including the Parkinson's syndrome. JPRN-UMIN000025559. | Link | Shimpei Fukuda. Effects of acupuncture treatment on stress in patients with Parkinson's disease. JPRN-UMIN000023856. | Link |
Shimpei Fukuda. Effects of acupuncture treatment on stress in patients with Parkinson's disease. JPRN-UMIN000023856. | Link | NADJA ASANO. Acupuncture as Adjuvant Therapy for Sleep Disorders in Parkinson's Disease. NCT02731677. | Link |
NADJA ASANO. Acupuncture as Adjuvant Therapy for Sleep Disorders in Parkinson's Disease. NCT02731677. | Link | Masato Egawa. Effects of acupuncture treatment on gait disturbance in patients with Parkinson's disease. JPRN-UMIN000010139. | Link |
Masato Egawa. Effects of acupuncture treatment on gait disturbance in patients with Parkinson's disease. JPRN-UMIN000010139. | Link | Masato Egawa. The Clinical Effects of Acupuncture in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JPRN-UMIN000007773. | Link |
Masato Egawa. The Clinical Effects of Acupuncture in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JPRN-UMIN000007773. | Link | Benzi Kluger. Acupuncture as a Symptomatic Treatment for Fatigue in Parkinson's Disease. NCT01360229. | Link |
Benzi Kluger. Acupuncture as a Symptomatic Treatment for Fatigue in Parkinson's Disease. NCT01360229. | Link |