 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
INTRODUCTION
Cannabinoids have been postulated as an alternative for anorexia nervosa. However, their actual clinical efficacy and safety are still discussed.
METHODS
To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified four systematic reviews including two primary studies, both corresponding to randomized trials. We concluded cannabinoids might not increase weight or improve symptoms in anorexia nervosa, and are probably associated to frequent adverse effects.
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by distortion in body image perception leading to weight loss and malnutrition. It causes important work, social and family dysfunction, and in severe cases it can be fatal.
Cannabinoids, by their effects as appetite stimulants would promote weight gain and so constitute a therapeutic alternative in anorexia nervosa. However, its clinical effects and safety still generate controversy among patients and clinicians.
To answer the question, we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We found four systematic reviews [1],[2],[3],[4] which included two primary studies that answered the question of interest, reported in three references [5],[6],[7]. Both studies correspond to randomized trials. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
One trial [5] included 11 women with a primary diagnosis of anorexia nervosa in a hospital setting. The average age was 23.6 years. The diagnosis of anorexia nervosa was made based on the Feighner criteria. All patients had amenorrhea and had lost at least 25% of their weight but were not below 15% of ideal weight **. The other trial [6] included 25 women aged over 18 years, diagnosed with DSM-IV anorexia nervosa for at least 5 years. Patients were considered in ambulatory and hospitalized setting. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
In one trial [5] THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) was used orally in doses between 2.5 and 10 mg three times daily. The control group received an active placebo (oral diazepam between 3 and 15 mg three times daily). In addition to the pharmacological treatment under study, patients received individual psychotherapy twice a week, group therapy once a week, and nasogastric tube feeding occasionally **. In another trial [6] dronabinol 2.5 mg twice daily was compared orally versus placebo.In both groups, the regular baseline treatment was maintained. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The main outcome used by systematic reviews was weight gain measured in kilograms [5],[6].
Other outcomes evaluated were the presence of adverse effects, such as sleep disturbance, paranoia and dysphoria. Follow-up was performed in one trial for 4 weeks [5] and for 8 weeks in the other trial [6]. |
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
** Information obtained directly from the primary study, because information provided by systematic reviews was incomplete.
The information on the effects of cannabinoids for anorexia nervosa is based on two trials that included a total of 36 patients [5],[6],[7].
The trials measured weight and symptoms based on clinical efficacy scales: HSCL-90, GAAQ, SDS, and PRS. The summary of findings is the following:
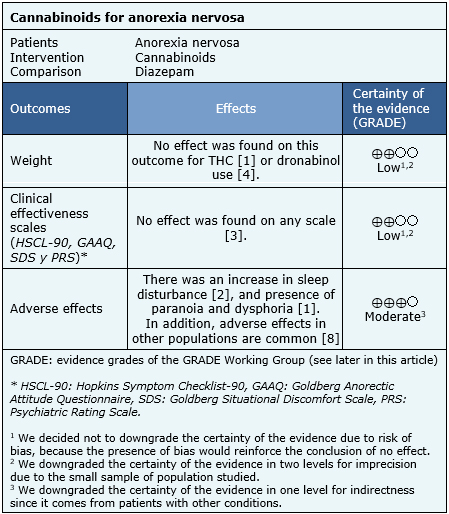
Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF)
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
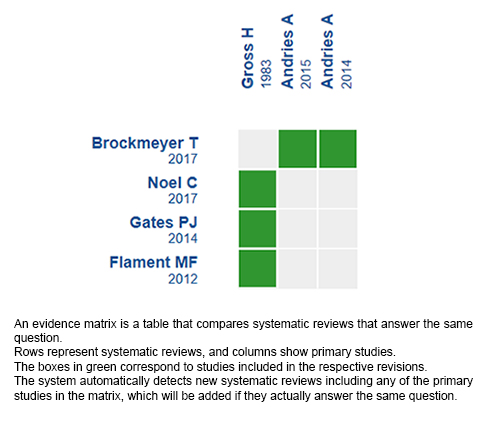
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Cannabinoids for anorexia nervosa
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

INTRODUCTION
Cannabinoids have been postulated as an alternative for anorexia nervosa. However, their actual clinical efficacy and safety are still discussed.
METHODS
To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified four systematic reviews including two primary studies, both corresponding to randomized trials. We concluded cannabinoids might not increase weight or improve symptoms in anorexia nervosa, and are probably associated to frequent adverse effects.
 Autores:
Tania Contreras[1,2], Gonzalo A Bravo-Soto[2,4], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]
Autores:
Tania Contreras[1,2], Gonzalo A Bravo-Soto[2,4], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]

Citación: Contreras T, Bravo-Soto GA, Rada G. Do cannabinoids constitute a therapeutic alternative for anorexia nervosa? . Medwave 2017 Nov-Dic;17(9):e7095 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2017.09.7095
Fecha de envío: 14/8/2017
Fecha de aceptación: 24/11/2017
Fecha de publicación: 1/12/2017
Origen: Este artículo es producto del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project de la Fundación Epistemonikos, en colaboración con Medwave para su publicación.
Tipo de revisión: Con revisión por pares sin ciego por parte del equipo metodológico del Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project.

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Flament MF, Bissada H, Spettigue W. Evidence-based pharmacotherapy of eating disorders. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;15(2):189-207. | Link |
Flament MF, Bissada H, Spettigue W. Evidence-based pharmacotherapy of eating disorders. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;15(2):189-207. | Link | Gates PJ, Albertella L, Copeland J. The effects of cannabinoid administration on sleep: a systematic review of human studies. Sleep medicine reviews. 2014;18(6):477-487. | Link |
Gates PJ, Albertella L, Copeland J. The effects of cannabinoid administration on sleep: a systematic review of human studies. Sleep medicine reviews. 2014;18(6):477-487. | Link | Noel C. Evidence for the use of “medical marijuana” in psychiatric and neurologic disorders. Mental Health Clinician. 2017;7(1):29-38. | Link |
Noel C. Evidence for the use of “medical marijuana” in psychiatric and neurologic disorders. Mental Health Clinician. 2017;7(1):29-38. | Link | Brockmeyer T, Friederich HC, Schmidt U. Advances in the treatment of anorexia
nervosa: a review of established and emerging interventions. Psychol Med. 2017
Sep 11:1-37
| CrossRef | PubMed |
Brockmeyer T, Friederich HC, Schmidt U. Advances in the treatment of anorexia
nervosa: a review of established and emerging interventions. Psychol Med. 2017
Sep 11:1-37
| CrossRef | PubMed | Gross H, Ebert MH, Faden VB, Goldberg SC, Kaye WH, Caine ED, Hawks R, Zinberg N. A double-blind trial of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in primary anorexia nervosa. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1983 Jun;3(3):165-71 | PubMed |
Gross H, Ebert MH, Faden VB, Goldberg SC, Kaye WH, Caine ED, Hawks R, Zinberg N. A double-blind trial of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in primary anorexia nervosa. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1983 Jun;3(3):165-71 | PubMed | Andries A, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Støving RK. Dronabinol in severe, enduring anorexia nervosa: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Eat Disord. 2014 Jan;47(1):18-23. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Andries A, Frystyk J, Flyvbjerg A, Støving RK. Dronabinol in severe, enduring anorexia nervosa: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Eat Disord. 2014 Jan;47(1):18-23. | CrossRef | PubMed | Andries A, Gram B, Støving RK. Effect of dronabinol therapy on physical
activity in anorexia nervosa: a randomised, controlled trial. Eat Weight Disord.
2015 Mar;20(1):13-21
| CrossRef | PubMed |
Andries A, Gram B, Støving RK. Effect of dronabinol therapy on physical
activity in anorexia nervosa: a randomised, controlled trial. Eat Weight Disord.
2015 Mar;20(1):13-21
| CrossRef | PubMed | Whiting PF, Wolff RF, Deshpande S, Di Nisio M, Duffy S, Hernandez AV, et al. Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2015 Jun 23-30;313(24):2456-73 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Whiting PF, Wolff RF, Deshpande S, Di Nisio M, Duffy S, Hernandez AV, et al. Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA. 2015 Jun 23-30;313(24):2456-73 | CrossRef | PubMed | National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. 2017. | CrossRef |
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. 2017. | CrossRef |