 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
La ketamina es un antagonista de los receptores de N-metil-D-aspartato que ha sido utilizada como adyuvante en el manejo agudo del dolor postoperatorio debido a sus propiedades analgésicas. Sin embargo, su rol no está claramente determinado. Para aclarar esta interrogante utilizamos la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en multiples fuentes de información. Identificamos 19 revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 226 ensayos aleatorizados. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas, reanalizamos los datos de los estudios primarios y preparamos tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que el uso de ketamina endovenosa probablemente no produce una disminución del dolor postoperatorio, o esta es clínicamente irrelevante.
El manejo del dolor postoperatorio es un aspecto importante dentro de la práctica de la anestesiología. Entre las drogas más utilizadas para manejar el dolor agudo se encuentran los opioides, los cuales pese a ser muy efectivos, poseen efectos adversos como náuseas, vómitos, sedación y depresión respiratoria. Una de las estrategias para reducir estos efectos no deseados es utilizar analgésicos adyudantes que actúen a través de distintas vías involucradas en la respuesta al dolor.
El receptor de N-metil-D-aspartato (NMDA) es un receptor ionotrópico de glutamato que ha sido implicado en la modulación de mecanismos de dolor. La ketamina es un antagonista no competitivo de los receptores NMDA y se ha utilizado en dosis bajas como adyuvante en el manejo del dolor postoperatorio. Sin embargo, su uso clínico aún es controvertido debido a sus potenciales efectos adversos psicomiméticos como náuseas, mareos y alucinaciones.
Utilizamos la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples fuentes de información, para identificar revisiones sistemáticas y sus estudios primarios incluidos. Con esta información generamos un resumen estructurado, siguiendo un formato preestablecido, que incluye mensajes clave, un resumen del conjunto de evidencia (presentado como matriz de evidencia en Epistemonikos), metanálisis del total de los estudios, tablas de resumen de resultados con el método GRADE, y tabla de otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión.
|
Mensajes clave
|
|
Cuál es la evidencia. |
Encontramos 19 revisiones sistemáticas [1-19] que incluyen 226 [20-245] ensayos aleatorizados. De estos, hay 111 que incluyen el uso de ketamina endovenosa en pacientes adultos, que corresponde a la pregunta abordada por este resumen [20-130] |
|
Qué tipo de pacientes incluyeron los estudios* |
En 30 estudios se consideraron pacientes sometidos a cirugía abdominal [20],[21],[22],[23],[24],[25],[26],[27], |
|
Qué tipo de intervenciones incluyeron los estudios* |
Todos los estudios utilizaron ketamina de administración endovenosa. En 33 estudios se utilizó ketamina en bolo [21],[22],[25], En 16 estudios se administró ketamina durante el preoperatorio [21],[22],[25],[33],[40],[50],[54],[55],[59], Las dosis utilizadas cuando se administró ketamina en bolo variaron entre 0,05 mg/kg y 2 mg/kg. Las dosis utilizadas en infusión continua variaron entre: 0,002 mg/kg/hora y 1 mg/kg/hora. Treinta y tres estudios reportaron coadministración de opioides [22],[25],[27],[31],[32],[33],[35],[36],[38],[40], [58],[60],[61],[64],[66],[67],[68],[69],[70],[71],[72],[73], [74],[75],[76],[78],[79],[80],[81],[82],[84],[85],[89],[93], [94],[96],[98],[100],[102],[107],[112],[116],[119],[121], [122],[124],[125], 13 estudios compararon contra otras drogas, especialmente opioides [22],[33],[36],[40],[52], [54],[57],[59],[62],[63],[88],[91],[96] y en el resto de los estudios no fue reportado. |
|
Qué tipo de desenlaces midieron |
Los principales desenlaces analizados por las revisiones sistemáticas fueron: dolor postoperatorio, consumo perioperatorio de analgesia (opioides y otros), tiempo de solicitud de primera analgesia, tiempo de cirugía, tiempo de anestesia, náuseas y vómitos postoperatorios y otros efectos adversos (como sueños desagradables, efectos cognitivos y psicológicos, hipotensión y calofríos). |
* La información sobre los estudios primarios es extraída desde las revisiones sistemáticas identificadas, no directamente desde los estudios, a menos que se especifique lo contrario.
No fue posible extraer suficiente cantidad de información desde las revisiones identificadas como para reconstruir el metanálisis y la tabla de resumen de resultados. Por lo tanto, la información presentada se basa en las conclusiones por separado de las nueve revisiones sistemáticas que realizaron metanálisis para alguno de los desenlaces de interés [5],[6],[7],[10],[11],[14],[16],[19], es decir, dolor a las 24 horas del postoperatorio [5],[6],[7],[10],[11],[16], presencia de náuseas y vómitos postoperatorios [5],[6],[7],[10],[11],[16],[19] y sedación [9],[10],[14].
El resumen de los resultados es el siguiente:
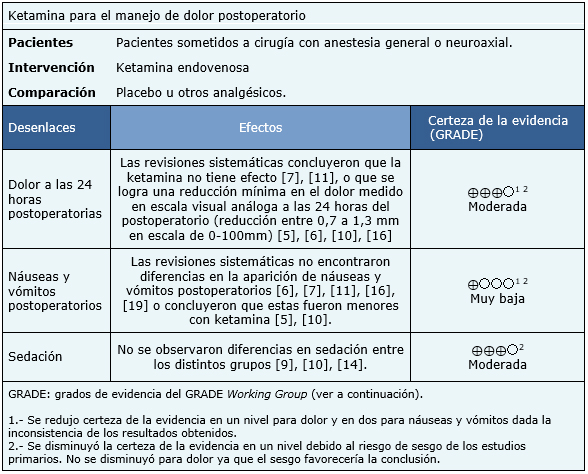

|
A quién se aplica y a quién no se aplica esta evidencia |
|
| Sobre los desenlaces incluidos en este resumen |
|
| Balance riesgo/beneficio y certeza de la evidencia |
|
| Qué piensan los pacientes y sus tratantes |
|
| Consideraciones de recursos |
|
| Diferencias entre este resumen y otras fuentes |
|
| ¿Puede que cambie esta información en el futuro? |
|
Mediante métodos automatizados y colaborativos recopilamos toda la evidencia relevante para la pregunta de interés y la presentamos en una matriz de evidencia.
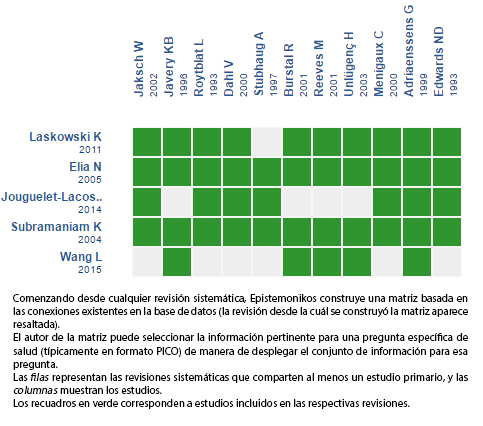
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva: Ketamina para el dolor postoperatorio
Si con posterioridad a la publicación de este resumen se publican nuevas revisiones sistemáticas sobre este tema, en la parte superior de la matriz se mostrará un aviso de “nueva evidencia”. Si bien el proyecto contempla la actualización periódica de estos resúmenes, los usuarios están invitados a comentar en Medwave o contactar a los autores mediante correo electrónico si creen que hay evidencia que motive una actualización más rápida.
Luego de crear una cuenta en Epistemonikos, al guardar las matrices recibirá notificaciones automáticas cada vez que exista nueva evidencia que potencialmente responda a esta pregunta. El detalle de los métodos para elaborar este resumen están descritos aquí: http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
La Fundación Epistemonikos es una organización que busca acercar la información a quienes toman decisiones en salud, mediante el uso de tecnologías. Su principal desarrollo es la base de datos Epistemonikos (www.epistemonikos.org).
Los resúmenes de evidencia siguen un riguroso proceso de revisión por pares interno.
Declaración de conflictos de intereses
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses con la materia de este artículo.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Ketamine is a N-Metil-D-Aspartate receptor antagonist that has been used as adjuvant in the acute postoperative pain management because of its analgesic properties. However, its role is not clearly determined. To answer this question, we searched in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources. We identified 19 systematic reviews including 226 randomized trials overall. We extracted data and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach. We concluded intravenous ketamine probably has little or no effect in reducing postoperative pain.
 Autores:
Camila Stuardo[1,2], Diego Lobos-Urbina[1,2], Fernando Altermatt[2,3]
Autores:
Camila Stuardo[1,2], Diego Lobos-Urbina[1,2], Fernando Altermatt[2,3]

Citación: Stuardo C, Lobos-Urbina D, Altermatt F. Is intravenous ketamine effective for postoperative pain management in adults? . Medwave2017;17(Suppl2):e6952 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2017.6952
Fecha de envío: 27/3/2015
Fecha de aceptación: 27/4/2016
Fecha de publicación: 17/5/2017

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Ansermino M, Basu R, Vandebeek C, Montgomery C. Nonopioid additives to local anaesthetics for caudal blockade in children: a systematic review. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Sep;13(7):561-73. | PubMed |
Ansermino M, Basu R, Vandebeek C, Montgomery C. Nonopioid additives to local anaesthetics for caudal blockade in children: a systematic review. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Sep;13(7):561-73. | PubMed | Carstensen M, Møller AM. Adding ketamine to morphine for intravenous patient-controlled analgesia for acute postoperative pain: a qualitative review of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth. 2010 Apr;104(4):401-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Carstensen M, Møller AM. Adding ketamine to morphine for intravenous patient-controlled analgesia for acute postoperative pain: a qualitative review of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth. 2010 Apr;104(4):401-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Cho HK, Kim KW, Jeong YM, Lee HS, Lee YJ, Hwang SH. Efficacy of ketamine in improving pain after tonsillectomy in children: meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014 Jun 30;9(6):e101259. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Cho HK, Kim KW, Jeong YM, Lee HS, Lee YJ, Hwang SH. Efficacy of ketamine in improving pain after tonsillectomy in children: meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014 Jun 30;9(6):e101259. | CrossRef | PubMed | Dahmani S, Michelet D, Abback PS, Wood C, Brasher C, Nivoche Y, et al. Ketamine for perioperative pain management in children: a meta-analysis of published studies. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011 Jun;21(6):636-52. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dahmani S, Michelet D, Abback PS, Wood C, Brasher C, Nivoche Y, et al. Ketamine for perioperative pain management in children: a meta-analysis of published studies. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011 Jun;21(6):636-52. | CrossRef | PubMed | Ding X, Jin S, Niu X, Wang T, Zhao X, Ren H, et al. Morphine with adjuvant ketamine versus higher dose of morphine alone for acute pain: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Sep 15;7(9):2504-10 | PubMed |
Ding X, Jin S, Niu X, Wang T, Zhao X, Ren H, et al. Morphine with adjuvant ketamine versus higher dose of morphine alone for acute pain: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Sep 15;7(9):2504-10 | PubMed | Elia N, Tramèr MR. Ketamine and postoperative pain--a quantitative systematic review of randomised trials. Pain. 2005 Jan;113(1-2):61-70 | PubMed |
Elia N, Tramèr MR. Ketamine and postoperative pain--a quantitative systematic review of randomised trials. Pain. 2005 Jan;113(1-2):61-70 | PubMed | Heesen M, Böhmer J, Brinck EC, Kontinen VK, Klöhr S, Rossaint R, et al. Intravenous ketamine during spinal and general anaesthesia for caesarean section: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2015 Apr;59(4):414-26. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Heesen M, Böhmer J, Brinck EC, Kontinen VK, Klöhr S, Rossaint R, et al. Intravenous ketamine during spinal and general anaesthesia for caesarean section: systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2015 Apr;59(4):414-26. | CrossRef | PubMed | Humble SR, Dalton AJ, Li L. A systematic review of therapeutic interventions to reduce acute and chronic post-surgical pain after amputation, thoracotomy or mastectomy. Eur J Pain. 2015 Apr;19(4):451-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Humble SR, Dalton AJ, Li L. A systematic review of therapeutic interventions to reduce acute and chronic post-surgical pain after amputation, thoracotomy or mastectomy. Eur J Pain. 2015 Apr;19(4):451-65 | CrossRef | PubMed | Jouguelet-Lacoste J, La Colla L, Schilling D, Chelly JE. The use of intravenous infusion or single dose of low-dose ketamine for postoperative analgesia: a review of the current literature. Pain Med. 2015 Feb;16(2):383-403 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Jouguelet-Lacoste J, La Colla L, Schilling D, Chelly JE. The use of intravenous infusion or single dose of low-dose ketamine for postoperative analgesia: a review of the current literature. Pain Med. 2015 Feb;16(2):383-403 | CrossRef | PubMed | Laskowski K, Stirling A, McKay WP, Lim HJ. A systematic review of intravenous ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Can J Anaesth. 2011 Oct;58(10):911-23 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Laskowski K, Stirling A, McKay WP, Lim HJ. A systematic review of intravenous ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Can J Anaesth. 2011 Oct;58(10):911-23 | CrossRef | PubMed | Liu Y, Zheng Y, Gu X, Ma Z. The efficacy of NMDA receptor antagonists for preventing remifentanil-induced increase in postoperative pain and analgesic requirement: a meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jun;78(6):653-67 | PubMed |
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Gu X, Ma Z. The efficacy of NMDA receptor antagonists for preventing remifentanil-induced increase in postoperative pain and analgesic requirement: a meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jun;78(6):653-67 | PubMed | McCartney CJ, Sinha A, Katz J. A qualitative systematic review of the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in preventive analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2004 May;98(5):1385-400 | PubMed |
McCartney CJ, Sinha A, Katz J. A qualitative systematic review of the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in preventive analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2004 May;98(5):1385-400 | PubMed | McNicol ED, Schumann R, Haroutounian S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of ketamine for the prevention of persistent post-surgical pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2014 Nov;58(10):1199-213 | CrossRef | PubMed |
McNicol ED, Schumann R, Haroutounian S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of ketamine for the prevention of persistent post-surgical pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2014 Nov;58(10):1199-213 | CrossRef | PubMed | Schmid RL, Sandler AN, Katz J. Use and efficacy of low-dose ketamine in the management of acute postoperative pain: a review of current techniques and outcomes. Pain. 1999 Aug;82(2):111-25 | PubMed |
Schmid RL, Sandler AN, Katz J. Use and efficacy of low-dose ketamine in the management of acute postoperative pain: a review of current techniques and outcomes. Pain. 1999 Aug;82(2):111-25 | PubMed | Schnabel A, Poepping DM, Kranke P, Zahn PK, Pogatzki-Zahn EM. Efficacy and adverse effects of ketamine as an additive for paediatric caudal anaesthesia: a quantitative systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Br J Anaesth. 2011 Oct;107(4):601-11 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Schnabel A, Poepping DM, Kranke P, Zahn PK, Pogatzki-Zahn EM. Efficacy and adverse effects of ketamine as an additive for paediatric caudal anaesthesia: a quantitative systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Br J Anaesth. 2011 Oct;107(4):601-11 | CrossRef | PubMed | Subramaniam K, Subramaniam B, Steinbrook RA. Ketamine as adjuvant analgesic to opioids: a quantitative and qualitative systematic review. Anesth Analg. 2004 Aug;99(2):482-95 | PubMed |
Subramaniam K, Subramaniam B, Steinbrook RA. Ketamine as adjuvant analgesic to opioids: a quantitative and qualitative systematic review. Anesth Analg. 2004 Aug;99(2):482-95 | PubMed | Tong Y, Ding XB, Wang X, Ren H, Chen ZX, Li Q. Ketamine peritonsillar infiltration during tonsillectomy in pediatric patients: An updated meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Oct;78(10):1735-41 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tong Y, Ding XB, Wang X, Ren H, Chen ZX, Li Q. Ketamine peritonsillar infiltration during tonsillectomy in pediatric patients: An updated meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014 Oct;78(10):1735-41 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wang L, Johnston B, Kaushal A, Cheng D, Zhu F, Martin J. Ketamine added to morphine or hydromorphone patient-controlled analgesia for acute postoperative pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Can J Anaesth. 2016 Mar;63(3):311-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Wang L, Johnston B, Kaushal A, Cheng D, Zhu F, Martin J. Ketamine added to morphine or hydromorphone patient-controlled analgesia for acute postoperative pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Can J Anaesth. 2016 Mar;63(3):311-25 | CrossRef | PubMed | Yang L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Zhao D, Li J. Preemptive analgesia effects of ketamine in patients undergoing surgery. A meta-analysis. Acta Cir Bras. 2014 Dec;29(12):819-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Yang L, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Zhao D, Li J. Preemptive analgesia effects of ketamine in patients undergoing surgery. A meta-analysis. Acta Cir Bras. 2014 Dec;29(12):819-25 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dualé C, Sibaud F, Guastella V, Vallet L, Gimbert YA, Taheri H, et al. Perioperative ketamine does not prevent chronic pain after thoracotomy. Eur J Pain. 2009 May;13(5):497-505 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dualé C, Sibaud F, Guastella V, Vallet L, Gimbert YA, Taheri H, et al. Perioperative ketamine does not prevent chronic pain after thoracotomy. Eur J Pain. 2009 May;13(5):497-505 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dullenkopf A, et al. “An Intraoperative Pre-Incision Single Dose of Intravenous Ketamine Does Not Have an Effect on Postoperative Analgesic Requirements under Clinical Conditions.”Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 37 (2007): 753–757 | Link |
Dullenkopf A, et al. “An Intraoperative Pre-Incision Single Dose of Intravenous Ketamine Does Not Have an Effect on Postoperative Analgesic Requirements under Clinical Conditions.”Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 37 (2007): 753–757 | Link | Papaziogas B, Argiriadou H, Papagiannopoulou P, Pavlidis T, Georgiou M, Sfyra E, et al. Preincisional intravenous low-dose ketamine and local infiltration with ropivacaine reduces postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc. 2001 Sep;15(9):1030-3 | PubMed |
Papaziogas B, Argiriadou H, Papagiannopoulou P, Pavlidis T, Georgiou M, Sfyra E, et al. Preincisional intravenous low-dose ketamine and local infiltration with ropivacaine reduces postoperative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc. 2001 Sep;15(9):1030-3 | PubMed | Parikh B, Maliwad J, Shah VR. Preventive analgesia: Effect of small dose of ketamine on morphine requirement after renal surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;27(4):485-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Parikh B, Maliwad J, Shah VR. Preventive analgesia: Effect of small dose of ketamine on morphine requirement after renal surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;27(4):485-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Pirim A, Karaman S, Uyar M, Certug A. [Addition of ketamine infusion to patient controlled analgesia with intravenous morphine after abdominal hysterectomy]. Agri. 2006 Jan;18(1):52-8 | PubMed |
Pirim A, Karaman S, Uyar M, Certug A. [Addition of ketamine infusion to patient controlled analgesia with intravenous morphine after abdominal hysterectomy]. Agri. 2006 Jan;18(1):52-8 | PubMed | Roytblat L, Korotkoruchko A, Katz J, Glazer M, Greemberg L, Fisher A. Postoperative pain: the effect of low-dose ketamine in addition to general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1993 Dec;77(6):1161-5 | PubMed |
Roytblat L, Korotkoruchko A, Katz J, Glazer M, Greemberg L, Fisher A. Postoperative pain: the effect of low-dose ketamine in addition to general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1993 Dec;77(6):1161-5 | PubMed | Safavi M, Honarmand A, Nematollahy Z. Pre-incisional analgesia with intravenous or subcutaneous infiltration of ketamine reduces postoperative pain in patients after open cholecystectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain Med. 2011 Sep;12(9):1418-26 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Safavi M, Honarmand A, Nematollahy Z. Pre-incisional analgesia with intravenous or subcutaneous infiltration of ketamine reduces postoperative pain in patients after open cholecystectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pain Med. 2011 Sep;12(9):1418-26 | CrossRef | PubMed | Sahin, A et al. “Bolus Ketamine Does Not Decrease Hyperalgesia after Remifentanil Infusion.” The Pain Clinic 16.4 (2004): 407–411 | Link |
Sahin, A et al. “Bolus Ketamine Does Not Decrease Hyperalgesia after Remifentanil Infusion.” The Pain Clinic 16.4 (2004): 407–411 | Link | Sami Mebazaa M, Mestiri T, Kaabi B, Ben Ammar MS. Clinical benefits related to the combination of ketamine with morphine for patient controlled analgesia after major abdominal surgery. Tunis Med. 2008 May;86(5):435-40 | PubMed |
Sami Mebazaa M, Mestiri T, Kaabi B, Ben Ammar MS. Clinical benefits related to the combination of ketamine with morphine for patient controlled analgesia after major abdominal surgery. Tunis Med. 2008 May;86(5):435-40 | PubMed | Sen H, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, Senol MG, Inangil G, Sücüllü I, Ozkan S, Dagli G. The effects of gabapentin on acute and chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009 Sep;26(9):772-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sen H, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, Senol MG, Inangil G, Sücüllü I, Ozkan S, Dagli G. The effects of gabapentin on acute and chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009 Sep;26(9):772-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Stessel B, Ovink JK, Theunissen HM, Kessels AG, Marcus MA, Gramke H. Is S-ketamine with or without magnesium sulphate an alternative for postoperative pain treatment? Randomised study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2013 Feb;30(2):91-3 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Stessel B, Ovink JK, Theunissen HM, Kessels AG, Marcus MA, Gramke H. Is S-ketamine with or without magnesium sulphate an alternative for postoperative pain treatment? Randomised study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2013 Feb;30(2):91-3 | CrossRef | PubMed | Stubhaug A, Breivik H, Eide PK, Kreunen M, Foss A. Mapping of punctuate hyperalgesia around a surgical incision demonstrates that ketamine is a powerful suppressor of central sensitization to pain following surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1997 Oct;41(9):1124-32 | PubMed |
Stubhaug A, Breivik H, Eide PK, Kreunen M, Foss A. Mapping of punctuate hyperalgesia around a surgical incision demonstrates that ketamine is a powerful suppressor of central sensitization to pain following surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1997 Oct;41(9):1124-32 | PubMed | Suzuki M, Tsueda K, Lansing PS, Tolan MM, Fuhrman TM, Ignacio CI, et. Small-dose ketamine enhances morphine-induced analgesia after outpatient surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999 Jul;89(1):98-103 | PubMed |
Suzuki M, Tsueda K, Lansing PS, Tolan MM, Fuhrman TM, Ignacio CI, et. Small-dose ketamine enhances morphine-induced analgesia after outpatient surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999 Jul;89(1):98-103 | PubMed | Tverskoy M, Oz Y, Isakson A, Finger J, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I. Preemptive effect of fentanyl and ketamine on postoperative pain and wound hyperalgesia. Anesth Analg. 1994 Feb;78(2):205-9 | PubMed |
Tverskoy M, Oz Y, Isakson A, Finger J, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I. Preemptive effect of fentanyl and ketamine on postoperative pain and wound hyperalgesia. Anesth Analg. 1994 Feb;78(2):205-9 | PubMed | Webb AR, Skinner BS, Leong S, Kolawole H, Crofts T, Taverner M, et al. The addition of a small-dose ketamine infusion to tramadol for postoperative analgesia: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized trial after abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2007 Apr;104(4):912-7 | PubMed |
Webb AR, Skinner BS, Leong S, Kolawole H, Crofts T, Taverner M, et al. The addition of a small-dose ketamine infusion to tramadol for postoperative analgesia: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomized trial after abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2007 Apr;104(4):912-7 | PubMed | Weinbroum AA. A single small dose of postoperative ketamine provides rapid and sustained improvement in morphine analgesia in the presence of morphine-resistant pain. Anesth Analg. 2003 Mar;96(3):789-95 | PubMed |
Weinbroum AA. A single small dose of postoperative ketamine provides rapid and sustained improvement in morphine analgesia in the presence of morphine-resistant pain. Anesth Analg. 2003 Mar;96(3):789-95 | PubMed | Wilder-Smith OH, Arendt-Nielsen L, Gäumann D, Tassonyi E, Rifat KR. Sensory changes and pain after abdominal hysterectomy: a comparison of anesthetic supplementation with fentanyl versus magnesium or ketamine. Anesth Analg. 1998 Jan;86(1):95-101 | PubMed |
Wilder-Smith OH, Arendt-Nielsen L, Gäumann D, Tassonyi E, Rifat KR. Sensory changes and pain after abdominal hysterectomy: a comparison of anesthetic supplementation with fentanyl versus magnesium or ketamine. Anesth Analg. 1998 Jan;86(1):95-101 | PubMed | Zakine J, Samarcq D, Lorne E, Moubarak M, Montravers P, Beloucif S, et al. Postoperative ketamine administration decreases morphine consumption in major abdominal surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2008 Jun;106(6):1856-61 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zakine J, Samarcq D, Lorne E, Moubarak M, Montravers P, Beloucif S, et al. Postoperative ketamine administration decreases morphine consumption in major abdominal surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2008 Jun;106(6):1856-61 | CrossRef | PubMed | Mathisen LC, Aasbø V, Raeder J. Lack of pre-emptive analgesic effect of (R)-ketamine in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1999 Feb;43(2):220-4 | PubMed |
Mathisen LC, Aasbø V, Raeder J. Lack of pre-emptive analgesic effect of (R)-ketamine in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1999 Feb;43(2):220-4 | PubMed | Nesek-Adam V, Grizelj-Stojcic E, Mršic V, Rašic Z, Schwarz D. Preemptive use of diclofenac in combination with ketamine in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012 Jun;22(3):232-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nesek-Adam V, Grizelj-Stojcic E, Mršic V, Rašic Z, Schwarz D. Preemptive use of diclofenac in combination with ketamine in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012 Jun;22(3):232-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Owen H, Reekie RM, Clements JA, Watson R, Nimmo WS. Analgesia from morphine and ketamine. A comparison of infusions of morphine and ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia. 1987 Oct;42(10):1051-6 | PubMed |
Owen H, Reekie RM, Clements JA, Watson R, Nimmo WS. Analgesia from morphine and ketamine. A comparison of infusions of morphine and ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia. 1987 Oct;42(10):1051-6 | PubMed | Kafali H, Aldemir B, Kaygusuz K, Gürsoy S, Kunt N. Small-dose ketamine decreases postoperative morphine requirements. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004 Nov;21(11):916-7 | PubMed |
Kafali H, Aldemir B, Kaygusuz K, Gürsoy S, Kunt N. Small-dose ketamine decreases postoperative morphine requirements. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004 Nov;21(11):916-7 | PubMed | Karaman S, Kocabas S, Zincircioglu C, Firat V. [Has ketamine preemptive analgesic effect in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy?]. Agri. 2006 Jul;18(3):36-44 | PubMed |
Karaman S, Kocabas S, Zincircioglu C, Firat V. [Has ketamine preemptive analgesic effect in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy?]. Agri. 2006 Jul;18(3):36-44 | PubMed | Kararmaz A, Kaya S, Karaman H, Turhanoglu S, Ozyilmaz MA. Intraoperative intravenous ketamine in combination with epidural analgesia: postoperative analgesia after renal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003 Oct;97(4):1092-6 | PubMed |
Kararmaz A, Kaya S, Karaman H, Turhanoglu S, Ozyilmaz MA. Intraoperative intravenous ketamine in combination with epidural analgesia: postoperative analgesia after renal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003 Oct;97(4):1092-6 | PubMed | Launo C, Bassi C, Spagnolo L, Badano S, Ricci C, Lizzi A, et. Preemptive ketamine during general anesthesia for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Minerva Anestesiol. 2004 Oct;70(10):727-34; 734-8 | PubMed |
Launo C, Bassi C, Spagnolo L, Badano S, Ricci C, Lizzi A, et. Preemptive ketamine during general anesthesia for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Minerva Anestesiol. 2004 Oct;70(10):727-34; 734-8 | PubMed | Joachimsson PO, Hedstrand U, Eklund A. Low-dose ketamine infusion for analgesia during postoperative ventilator treatment. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1986 Nov;30(8):697-702 | PubMed |
Joachimsson PO, Hedstrand U, Eklund A. Low-dose ketamine infusion for analgesia during postoperative ventilator treatment. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1986 Nov;30(8):697-702 | PubMed | Ilkjaer S, Nikolajsen L, Hansen TM, Wernberg M, Brennum J, Dahl JB. Effect of i.v. ketamine in combination with epidural bupivacaine or epidural morphine on postoperative pain and wound tenderness after renal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1998 Nov;81(5):707-12 | PubMed |
Ilkjaer S, Nikolajsen L, Hansen TM, Wernberg M, Brennum J, Dahl JB. Effect of i.v. ketamine in combination with epidural bupivacaine or epidural morphine on postoperative pain and wound tenderness after renal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1998 Nov;81(5):707-12 | PubMed | Joly V, Richebe P, Guignard B, Fletcher D, Maurette P, Sessler DI, et al. Remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia and its prevention with small-dose ketamine. Anesthesiology. 2005 Jul;103(1):147-55 | PubMed |
Joly V, Richebe P, Guignard B, Fletcher D, Maurette P, Sessler DI, et al. Remifentanil-induced postoperative hyperalgesia and its prevention with small-dose ketamine. Anesthesiology. 2005 Jul;103(1):147-55 | PubMed | Fu ES, Miguel R, Scharf JE. Preemptive ketamine decreases postoperative narcotic requirements in patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 1997 May;84(5):1086-90 | PubMed |
Fu ES, Miguel R, Scharf JE. Preemptive ketamine decreases postoperative narcotic requirements in patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 1997 May;84(5):1086-90 | PubMed | Guillou N, Tanguy M, Seguin P, Branger B, Campion JP, Mallédant Y. The effects of small-dose ketamine on morphine consumption in surgical intensive care unit patients after major abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003 Sep;97(3):843-7 | PubMed |
Guillou N, Tanguy M, Seguin P, Branger B, Campion JP, Mallédant Y. The effects of small-dose ketamine on morphine consumption in surgical intensive care unit patients after major abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003 Sep;97(3):843-7 | PubMed | Lehmann KA, Klaschik M. [Lack of pre-emptive analgesic effect of low-dose ketamine in postoperative patients. A prospective, randomised double-blind study]. Schmerz. 2001 Aug;15(4):248-53 | PubMed |
Lehmann KA, Klaschik M. [Lack of pre-emptive analgesic effect of low-dose ketamine in postoperative patients. A prospective, randomised double-blind study]. Schmerz. 2001 Aug;15(4):248-53 | PubMed | Lenzmeier B, Moore RL, Cordts P, Garrett N. Menstrual cycle-related variations in postoperative analgesia with the preemptive use of N-methyl D-aspartate antagonist ketamine: a pilot study. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. 2008 Nov-Dec;27(6):271-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lenzmeier B, Moore RL, Cordts P, Garrett N. Menstrual cycle-related variations in postoperative analgesia with the preemptive use of N-methyl D-aspartate antagonist ketamine: a pilot study. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. 2008 Nov-Dec;27(6):271-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Maurset A, Skoglund LA, Hustveit O, Oye I. Comparison of ketamine and pethidine in experimental and postoperative pain. Pain. 1989 Jan;36(1):37-41 | PubMed |
Maurset A, Skoglund LA, Hustveit O, Oye I. Comparison of ketamine and pethidine in experimental and postoperative pain. Pain. 1989 Jan;36(1):37-41 | PubMed | Menkiti ID, Desalu I, Kushimo OT. Low-dose intravenous ketamine improves postoperative analgesia after caesarean delivery with spinal bupivacaine in African parturients. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2012 Jul;21(3):217-21 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Menkiti ID, Desalu I, Kushimo OT. Low-dose intravenous ketamine improves postoperative analgesia after caesarean delivery with spinal bupivacaine in African parturients. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2012 Jul;21(3):217-21 | CrossRef | PubMed | Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Ma ML, Mainland PA, Gin T. Postoperative analgesic requirement after cesarean section: a comparison of anesthetic induction with ketamine or thiopental. Anesth Analg. 1997 Dec;85(6):1294-8 | PubMed |
Ngan Kee WD, Khaw KS, Ma ML, Mainland PA, Gin T. Postoperative analgesic requirement after cesarean section: a comparison of anesthetic induction with ketamine or thiopental. Anesth Analg. 1997 Dec;85(6):1294-8 | PubMed | Reza FM, Zahra F, Esmaeel F, Hossein A. Preemptive analgesic effect of ketamine in patients undergoing elective cesarean section. Clin J Pain. 2010 Mar-Apr;26(3):223-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Reza FM, Zahra F, Esmaeel F, Hossein A. Preemptive analgesic effect of ketamine in patients undergoing elective cesarean section. Clin J Pain. 2010 Mar-Apr;26(3):223-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Katz J, Schmid R, Snijdelaar DG, Coderre TJ, McCartney CJ, Wowk A. Pre-emptive analgesia using intravenous fentanyl plus low-dose ketamine for radical prostatectomy under general anesthesia does not produce short-term or long-term reductions in pain or analgesic use. Pain. 2004 Aug;110(3):707-18 | PubMed |
Katz J, Schmid R, Snijdelaar DG, Coderre TJ, McCartney CJ, Wowk A. Pre-emptive analgesia using intravenous fentanyl plus low-dose ketamine for radical prostatectomy under general anesthesia does not produce short-term or long-term reductions in pain or analgesic use. Pain. 2004 Aug;110(3):707-18 | PubMed | Sen S, Ozmert G, Aydin ON, Baran N, Caliskan E. The persisting analgesic effect of low-dose intravenous ketamine after spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005 Jul;22(7):518-23 | PubMed |
Sen S, Ozmert G, Aydin ON, Baran N, Caliskan E. The persisting analgesic effect of low-dose intravenous ketamine after spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005 Jul;22(7):518-23 | PubMed | Suppa E, Valente A, Catarci S, Zanfini BA, Draisci G. A study of low-dose S-ketamine infusion as "preventive" pain treatment for cesarean section with spinal anesthesia: benefits and side effects. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jul;78(7):774-81 | PubMed |
Suppa E, Valente A, Catarci S, Zanfini BA, Draisci G. A study of low-dose S-ketamine infusion as "preventive" pain treatment for cesarean section with spinal anesthesia: benefits and side effects. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jul;78(7):774-81 | PubMed | Wanna O, Werawatganon T, Piriyakitphaiboon S, Taesiri B. A comparison of propofol and ketamine as induction agents for cesarean section. J Med Assoc Thai. 2004 Jul;87 (7):774-9 | PubMed |
Wanna O, Werawatganon T, Piriyakitphaiboon S, Taesiri B. A comparison of propofol and ketamine as induction agents for cesarean section. J Med Assoc Thai. 2004 Jul;87 (7):774-9 | PubMed | Kose EA, Honca M, Dal D, Akinci SB, Aypar U. Prophylactic ketamine to prevent shivering in parturients undergoing Cesarean delivery during spinal anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 2013 Jun;25(4):275-80 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kose EA, Honca M, Dal D, Akinci SB, Aypar U. Prophylactic ketamine to prevent shivering in parturients undergoing Cesarean delivery during spinal anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 2013 Jun;25(4):275-80 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kwok RF, Lim J, Chan MT, Gin T, Chiu WK. Preoperative ketamine improves postoperative analgesia after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004 Apr;98 (4):1044-9 | PubMed |
Kwok RF, Lim J, Chan MT, Gin T, Chiu WK. Preoperative ketamine improves postoperative analgesia after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004 Apr;98 (4):1044-9 | PubMed | Lauretti GR, Azevedo VM. Intravenous ketamine or fentanyl prolongs postoperative analgesia after intrathecal neostigmine. Anesth Analg. 1996 Oct;83(4):766-70 | PubMed |
Lauretti GR, Azevedo VM. Intravenous ketamine or fentanyl prolongs postoperative analgesia after intrathecal neostigmine. Anesth Analg. 1996 Oct;83(4):766-70 | PubMed | Heinke W, Grimm D. [Preemptive effects caused by co-analgesia with ketamine in gynecological laparotomies?]. Anaesthesiol Reanim. 1999;24(3):60-4 | PubMed |
Heinke W, Grimm D. [Preemptive effects caused by co-analgesia with ketamine in gynecological laparotomies?]. Anaesthesiol Reanim. 1999;24(3):60-4 | PubMed | Hajipour, A. “Effects of Preemptive Ketamine on Post-Cesarean Analgesic Requirement.” Acta Medica Iranica 40.2 (2002): 100–103 | Link |
Hajipour, A. “Effects of Preemptive Ketamine on Post-Cesarean Analgesic Requirement.” Acta Medica Iranica 40.2 (2002): 100–103 | Link | Han SY, Jin HC, Yang WD, Lee JH, Cho SH, Chae WS, Lee JS, Kim YI. The Effect of Low-dose Ketamine on Post-caesarean Delivery Analgesia after Spinal Anesthesia. Korean J Pain. 2013 Jul;26(3):270-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Han SY, Jin HC, Yang WD, Lee JH, Cho SH, Chae WS, Lee JS, Kim YI. The Effect of Low-dose Ketamine on Post-caesarean Delivery Analgesia after Spinal Anesthesia. Korean J Pain. 2013 Jul;26(3):270-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kudoh A, Takahira Y, Katagai H, Takazawa T. Small-dose ketamine improves the postoperative state of depressed patients. Anesth Analg. 2002 Jul;95(1):114-8 | PubMed |
Kudoh A, Takahira Y, Katagai H, Takazawa T. Small-dose ketamine improves the postoperative state of depressed patients. Anesth Analg. 2002 Jul;95(1):114-8 | PubMed | Menigaux C, Fletcher D, Dupont X, Guignard B, Guirimand F, Chauvin M. The benefits of intraoperative small-dose ketamine on postoperative pain after anterior cruciate ligament repair. Anesth Analg. 2000 Jan;90(1):129-35 | PubMed |
Menigaux C, Fletcher D, Dupont X, Guignard B, Guirimand F, Chauvin M. The benefits of intraoperative small-dose ketamine on postoperative pain after anterior cruciate ligament repair. Anesth Analg. 2000 Jan;90(1):129-35 | PubMed | Menigaux C, Guignard B, Fletcher D, Sessler DI, Dupont X, Chauvin M. Intraoperative small-dose ketamine enhances analgesia after outpatient knee arthroscopy. Anesth Analg. 2001 Sep;93(3):606-12 | PubMed |
Menigaux C, Guignard B, Fletcher D, Sessler DI, Dupont X, Chauvin M. Intraoperative small-dose ketamine enhances analgesia after outpatient knee arthroscopy. Anesth Analg. 2001 Sep;93(3):606-12 | PubMed | Subramaniam K, Akhouri V, Glazer PA, Rachlin J, Kunze L, Cronin M, et al. Intra- and postoperative very low dose intravenous ketamine infusion does not increase pain relief after major spine surgery in patients with preoperative narcotic analgesic intake. Pain Med. 2011 Aug;12(8):1276-83 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Subramaniam K, Akhouri V, Glazer PA, Rachlin J, Kunze L, Cronin M, et al. Intra- and postoperative very low dose intravenous ketamine infusion does not increase pain relief after major spine surgery in patients with preoperative narcotic analgesic intake. Pain Med. 2011 Aug;12(8):1276-83 | CrossRef | PubMed | Urban MK, Ya Deau JT, Wukovits B, Lipnitsky JY. Ketamine as an adjunct to postoperative pain management in opioid tolerant patients after spinal fusions: a prospective randomized trial. HSS J. 2008 Feb;4(1):62-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Urban MK, Ya Deau JT, Wukovits B, Lipnitsky JY. Ketamine as an adjunct to postoperative pain management in opioid tolerant patients after spinal fusions: a prospective randomized trial. HSS J. 2008 Feb;4(1):62-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Jaksch W, Lang S, Reichhalter R, Raab G, Dann K, Fitzal S. Perioperative small-dose S(+)-ketamine has no incremental beneficial effects on postoperative pain when standard-practice opioid infusions are used. Anesth Analg. 2002 Apr;94(4):981-6 | PubMed |
Jaksch W, Lang S, Reichhalter R, Raab G, Dann K, Fitzal S. Perioperative small-dose S(+)-ketamine has no incremental beneficial effects on postoperative pain when standard-practice opioid infusions are used. Anesth Analg. 2002 Apr;94(4):981-6 | PubMed | Kim SH, Kim SI, Ok SY, Park SY, Kim MG, Lee SJ, Noh JI, Chun HR, Suh H. Opioid sparing effect of low dose ketamine in patients with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia using fentanyl after lumbar spinal fusion surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013 Jun;64(6):524-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kim SH, Kim SI, Ok SY, Park SY, Kim MG, Lee SJ, Noh JI, Chun HR, Suh H. Opioid sparing effect of low dose ketamine in patients with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia using fentanyl after lumbar spinal fusion surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013 Jun;64(6):524-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Hayes C, Armstrong-Brown A, Burstal R. Perioperative intravenous ketamine infusion for the prevention of persistent post-amputation pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004 Jun;32(3):330-8 | PubMed |
Hayes C, Armstrong-Brown A, Burstal R. Perioperative intravenous ketamine infusion for the prevention of persistent post-amputation pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2004 Jun;32(3):330-8 | PubMed | Joseph C, Gaillat F, Duponq R, Lieven R, Baumstarck K, Thomas P, et al. Is there any benefit to adding intravenous ketamine to patient-controlled epidural analgesia after thoracic surgery? A randomized double-blind study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Oct;42(4):e58-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Joseph C, Gaillat F, Duponq R, Lieven R, Baumstarck K, Thomas P, et al. Is there any benefit to adding intravenous ketamine to patient-controlled epidural analgesia after thoracic surgery? A randomized double-blind study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012 Oct;42(4):e58-65 | CrossRef | PubMed | Lahtinen P, Kokki H, Hakala T, Hynynen M. S(+)-ketamine as an analgesic adjunct reduces opioid consumption after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004 Nov;99(5):1295-301 | PubMed |
Lahtinen P, Kokki H, Hakala T, Hynynen M. S(+)-ketamine as an analgesic adjunct reduces opioid consumption after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2004 Nov;99(5):1295-301 | PubMed | Mendola C, Cammarota G, Netto R, Cecci G, Pisterna A, Ferrante D, et al. S+ -ketamine for control of perioperative pain and prevention of post thoracotomy pain syndrome: a randomized, double-blind study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jul;78(7):757-66 | PubMed |
Mendola C, Cammarota G, Netto R, Cecci G, Pisterna A, Ferrante D, et al. S+ -ketamine for control of perioperative pain and prevention of post thoracotomy pain syndrome: a randomized, double-blind study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Jul;78(7):757-66 | PubMed | Ögün CÖ, Duman A, Ökesli S. “The Comparison of Postoperative Analgesic Effects of Preemptive Ketamine and Fentanyl Use in Mastectomy Operations.” The journal of the Turkish Society of Algology 13.2 (2001): 31–40. Web. 7 May 2016 | Link |
Ögün CÖ, Duman A, Ökesli S. “The Comparison of Postoperative Analgesic Effects of Preemptive Ketamine and Fentanyl Use in Mastectomy Operations.” The journal of the Turkish Society of Algology 13.2 (2001): 31–40. Web. 7 May 2016 | Link | Edwards ND, Fletcher A, Cole JR, Peacock JE. Combined infusions of morphine and ketamine for postoperative pain in elderly patients. Anaesthesia. 1993 Feb;48(2):124-7 | PubMed |
Edwards ND, Fletcher A, Cole JR, Peacock JE. Combined infusions of morphine and ketamine for postoperative pain in elderly patients. Anaesthesia. 1993 Feb;48(2):124-7 | PubMed | Ganne O, Abisseror M, Menault P, Malhière S, Chambost V, Charpiat B, Ganne C, Viale JP. Low-dose ketamine failed to spare morphine after a remifentanil-based anaesthesia for ear, nose and throat surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005 Jun;22(6):426-30. | PubMed |
Ganne O, Abisseror M, Menault P, Malhière S, Chambost V, Charpiat B, Ganne C, Viale JP. Low-dose ketamine failed to spare morphine after a remifentanil-based anaesthesia for ear, nose and throat surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005 Jun;22(6):426-30. | PubMed | Guignard B, Coste C, Costes H, Sessler DI, Lebrault C, Morris W, Simonnet G, Chauvin M. Supplementing desflurane-remifentanil anesthesia with small-dose ketamine reduces perioperative opioid analgesic requirements. Anesth Analg. 2002 Jul;95(1):103-8, table of contents | PubMed |
Guignard B, Coste C, Costes H, Sessler DI, Lebrault C, Morris W, Simonnet G, Chauvin M. Supplementing desflurane-remifentanil anesthesia with small-dose ketamine reduces perioperative opioid analgesic requirements. Anesth Analg. 2002 Jul;95(1):103-8, table of contents | PubMed | Hadi BA, Daas R, Zelkó R. “A Randomized, Controlled Trial of a Clinical Pharmacist Intervention in Microdiscectomy Surgery - Low Dose Intravenous Ketamine as an Adjunct to Standard Therapy.” Saudi pharmaceutical journal : SPJ : the official publication of the Saudi Pharmaceutical Society 21.2 (2013): 169–175 | Link |
Hadi BA, Daas R, Zelkó R. “A Randomized, Controlled Trial of a Clinical Pharmacist Intervention in Microdiscectomy Surgery - Low Dose Intravenous Ketamine as an Adjunct to Standard Therapy.” Saudi pharmaceutical journal : SPJ : the official publication of the Saudi Pharmaceutical Society 21.2 (2013): 169–175 | Link | Van Elstraete AC, Lebrun T, Sandefo I, Polin B. Ketamine does not decrease postoperative pain after remifentanil-based anaesthesia for tonsillectomy in adults. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004 Jul;48(6):756-60 | PubMed |
Van Elstraete AC, Lebrun T, Sandefo I, Polin B. Ketamine does not decrease postoperative pain after remifentanil-based anaesthesia for tonsillectomy in adults. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004 Jul;48(6):756-60 | PubMed | Abu-Shahwan I. Ketamine does not reduce postoperative morphine consumption after tonsillectomy in children. Clin J Pain. 2008 Jun;24(5):395-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Abu-Shahwan I. Ketamine does not reduce postoperative morphine consumption after tonsillectomy in children. Clin J Pain. 2008 Jun;24(5):395-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Adam F, Chauvin M, Du Manoir B, Langlois M, Sessler DI, Fletcher D. Small-dose ketamine infusion improves postoperative analgesia and rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2005 Feb;100(2):475-80 | PubMed |
Adam F, Chauvin M, Du Manoir B, Langlois M, Sessler DI, Fletcher D. Small-dose ketamine infusion improves postoperative analgesia and rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2005 Feb;100(2):475-80 | PubMed | Adriaenssens G, Vermeyen KM, Hoffmann VL, Mertens E, Adriaensen HF. Postoperative analgesia with i.v. patient-controlled morphine: effect of adding ketamine. Br J Anaesth. 1999 Sep;83(3):393-6 | PubMed |
Adriaenssens G, Vermeyen KM, Hoffmann VL, Mertens E, Adriaensen HF. Postoperative analgesia with i.v. patient-controlled morphine: effect of adding ketamine. Br J Anaesth. 1999 Sep;83(3):393-6 | PubMed | Aida S, Yamakura T, Baba H, Taga K, Fukuda S, Shimoji K. Preemptive analgesia by intravenous low-dose ketamine and epidural morphine in gastrectomy: a randomized double-blind study. Anesthesiology. 2000 Jun;92(6):1624-30 | PubMed |
Aida S, Yamakura T, Baba H, Taga K, Fukuda S, Shimoji K. Preemptive analgesia by intravenous low-dose ketamine and epidural morphine in gastrectomy: a randomized double-blind study. Anesthesiology. 2000 Jun;92(6):1624-30 | PubMed | Argiriadou H, Himmelseher S, Papagiannopoulou P, Georgiou M, Kanakoudis F, Giala M, et al. Improvement of pain treatment after major abdominal surgery by intravenous S+-ketamine. Anesth Analg. 2004 May;98(5):1413-8 | PubMed |
Argiriadou H, Himmelseher S, Papagiannopoulou P, Georgiou M, Kanakoudis F, Giala M, et al. Improvement of pain treatment after major abdominal surgery by intravenous S+-ketamine. Anesth Analg. 2004 May;98(5):1413-8 | PubMed | Arroyo-Novoa CM, Figueroa-Ramos MI, Miaskowski C, Padilla G, Paul SM, Rodríguez-Ortiz P, et al. Efficacy of small doses of ketamine with morphine to decrease procedural pain responses during open wound care. Clin J Pain. 2011 Sep;27(7):561-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Arroyo-Novoa CM, Figueroa-Ramos MI, Miaskowski C, Padilla G, Paul SM, Rodríguez-Ortiz P, et al. Efficacy of small doses of ketamine with morphine to decrease procedural pain responses during open wound care. Clin J Pain. 2011 Sep;27(7):561-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Aubrun F, Gaillat C, Rosenthal D, Dupuis M, Mottet P, Marchetti F, et al. Effect of a low-dose ketamine regimen on pain, mood, cognitive function and memory after major gynaecological surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Feb;25(2):97-105 | PubMed |
Aubrun F, Gaillat C, Rosenthal D, Dupuis M, Mottet P, Marchetti F, et al. Effect of a low-dose ketamine regimen on pain, mood, cognitive function and memory after major gynaecological surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Feb;25(2):97-105 | PubMed | Aveline C, Hetet HL, Vautier P, Gautier JF, Bonnet F. Peroperative ketamine and morphine for postoperative pain control after lumbar disk surgery. Eur J Pain. 2006 Oct;10(7):653-8 | PubMed |
Aveline C, Hetet HL, Vautier P, Gautier JF, Bonnet F. Peroperative ketamine and morphine for postoperative pain control after lumbar disk surgery. Eur J Pain. 2006 Oct;10(7):653-8 | PubMed | Aveline C, Gautier JF, Vautier P, Cognet F, Hetet HL, Attali JY, et al. Postoperative analgesia and early rehabilitation after total knee replacement: a comparison of continuous low-dose intravenous ketamine versus nefopam. Eur J Pain. 2009 Jul;13(6):613-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Aveline C, Gautier JF, Vautier P, Cognet F, Hetet HL, Attali JY, et al. Postoperative analgesia and early rehabilitation after total knee replacement: a comparison of continuous low-dose intravenous ketamine versus nefopam. Eur J Pain. 2009 Jul;13(6):613-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Ayoglu H , Karadeniz U , Kunduracilar Z , Ayoglu FN , Erdemli O. “The Analgesic Effect of Magnesium Sulfate and Ketamine in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.” The Pain Clinic 17.1 (2005): 45–53 | Link |
Ayoglu H , Karadeniz U , Kunduracilar Z , Ayoglu FN , Erdemli O. “The Analgesic Effect of Magnesium Sulfate and Ketamine in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.” The Pain Clinic 17.1 (2005): 45–53 | Link | Barreveld AM, Correll DJ, Liu X, Max B, McGowan JA, Shovel L, et al. Ketamine decreases postoperative pain scores in patients taking opioids for chronic pain: results of a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Pain Med. 2013 Jun;14(6):925-34 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Barreveld AM, Correll DJ, Liu X, Max B, McGowan JA, Shovel L, et al. Ketamine decreases postoperative pain scores in patients taking opioids for chronic pain: results of a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Pain Med. 2013 Jun;14(6):925-34 | CrossRef | PubMed | Bauchat JR, Higgins N, Wojciechowski KG, McCarthy RJ, Toledo P, Wong CA. Low-dose ketamine with multimodal postcesarean delivery analgesia: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2011 Jan;20(1):3-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bauchat JR, Higgins N, Wojciechowski KG, McCarthy RJ, Toledo P, Wong CA. Low-dose ketamine with multimodal postcesarean delivery analgesia: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2011 Jan;20(1):3-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Becke K, Albrecht S, Schmitz B, Rech D, Koppert W, Schüttler J, et al. Intraoperative low-dose S-ketamine has no preventive effects on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after major urological surgery in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Jun;15(6):484-90 | PubMed |
Becke K, Albrecht S, Schmitz B, Rech D, Koppert W, Schüttler J, et al. Intraoperative low-dose S-ketamine has no preventive effects on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after major urological surgery in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Jun;15(6):484-90 | PubMed | Behdad A, Hosseinpour M, Khorasani P. Preemptive use of ketamine on post operative pain of appendectomy. Korean J Pain. 2011 Sep;24(3):137-40 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Behdad A, Hosseinpour M, Khorasani P. Preemptive use of ketamine on post operative pain of appendectomy. Korean J Pain. 2011 Sep;24(3):137-40 | CrossRef | PubMed | Behdad S, Hajiesmaeili MR, Abbasi HR, Ayatollahi V, Khadiv Z, Sedaghat A. Analgesic Effects of Intravenous Ketamine during Spinal Anesthesia in Pregnant Women Undergone Caesarean Section; A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Pain Med. 2013 Sep;3(2):230-3 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Behdad S, Hajiesmaeili MR, Abbasi HR, Ayatollahi V, Khadiv Z, Sedaghat A. Analgesic Effects of Intravenous Ketamine during Spinal Anesthesia in Pregnant Women Undergone Caesarean Section; A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Pain Med. 2013 Sep;3(2):230-3 | CrossRef | PubMed | Bilgen S, Köner O, Türe H, Menda F, Fiçicioglu C, Aykaç B. Effect of three different doses of ketamine prior to general anaesthesia on postoperative pain following Caesarean delivery: a prospective randomized study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Apr;78(4):442-9 | PubMed |
Bilgen S, Köner O, Türe H, Menda F, Fiçicioglu C, Aykaç B. Effect of three different doses of ketamine prior to general anaesthesia on postoperative pain following Caesarean delivery: a prospective randomized study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012 Apr;78(4):442-9 | PubMed | Butkovic D, Kralik S, Matolic M, Jakobovic J, Zganjer M, Radesic L. Comparison of a preincisional and postincisional small dose of ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2007;108(4-5):184-8 | PubMed |
Butkovic D, Kralik S, Matolic M, Jakobovic J, Zganjer M, Radesic L. Comparison of a preincisional and postincisional small dose of ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2007;108(4-5):184-8 | PubMed | Clausen L, Sinclair DM, Van Hasselt CH. “Intravenous Ketamine for Postoperative Analgesia.” South African medical journal 49.35 (1975): 1437–1440 | Link |
Clausen L, Sinclair DM, Van Hasselt CH. “Intravenous Ketamine for Postoperative Analgesia.” South African medical journal 49.35 (1975): 1437–1440 | Link | Colombani S, Kabbani Y, Mathoulin-Pélissier S, Gékière JP, Dixmérias F, Monnin D, et al. [Administration of ketamine during induction and maintenance of anaesthesia in postoperative pain prevention]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2008 Mar;27(3):202-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Colombani S, Kabbani Y, Mathoulin-Pélissier S, Gékière JP, Dixmérias F, Monnin D, et al. [Administration of ketamine during induction and maintenance of anaesthesia in postoperative pain prevention]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2008 Mar;27(3):202-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dahl V, Ernoe PE, Steen T, Raeder JC, White PF. Does ketamine have preemptive effects in women undergoing abdominal hysterectomy procedures? Anesth Analg. 2000 Jun;90(6):1419-22 | PubMed |
Dahl V, Ernoe PE, Steen T, Raeder JC, White PF. Does ketamine have preemptive effects in women undergoing abdominal hysterectomy procedures? Anesth Analg. 2000 Jun;90(6):1419-22 | PubMed | Dal D, Celebi N, Elvan EG, Celiker V, Aypar U. The efficacy of intravenous or peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007 Mar;17(3):263-9 | PubMed |
Dal D, Celebi N, Elvan EG, Celiker V, Aypar U. The efficacy of intravenous or peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007 Mar;17(3):263-9 | PubMed | Dal D, Kose A, Honca M, Akinci SB, Basgul E, Aypar U. Efficacy of prophylactic ketamine in preventing postoperative shivering. Br J Anaesth. 2005 Aug;95(2):189-92 | PubMed |
Dal D, Kose A, Honca M, Akinci SB, Basgul E, Aypar U. Efficacy of prophylactic ketamine in preventing postoperative shivering. Br J Anaesth. 2005 Aug;95(2):189-92 | PubMed | Darabi ME , Mireskandari SM , Sadeghi M , Salamati P , Rahimi E. “Ketamine Has No Pre-Emptive Analgesic Effect in Children Undergoing Inguinal Hernia Repair.” Acta Medica Iranica 46.6 (2008): 451–456 | Link |
Darabi ME , Mireskandari SM , Sadeghi M , Salamati P , Rahimi E. “Ketamine Has No Pre-Emptive Analgesic Effect in Children Undergoing Inguinal Hernia Repair.” Acta Medica Iranica 46.6 (2008): 451–456 | Link | Darwish HM , Marzouk S , El Kholy G , El-Din WS. “Low Dose Ketamine Prevents Acute Opioid Tolerance Induced by Remifentanil Infusion.” Egyptian Journal Of Anaesthesia 21.3 (2005): 259–266 | Link |
Darwish HM , Marzouk S , El Kholy G , El-Din WS. “Low Dose Ketamine Prevents Acute Opioid Tolerance Induced by Remifentanil Infusion.” Egyptian Journal Of Anaesthesia 21.3 (2005): 259–266 | Link | De Kock M, Lavand'homme P, Waterloos H. 'Balanced analgesia' in the perioperative period: is there a place for ketamine? Pain. 2001 Jun;92(3):373-80 | PubMed |
De Kock M, Lavand'homme P, Waterloos H. 'Balanced analgesia' in the perioperative period: is there a place for ketamine? Pain. 2001 Jun;92(3):373-80 | PubMed | Deng GF, Zheng JP, Wang S, Tian B, Zhang SG. Remifentanil combined with low-dose ketamine for postoperative analgesia of lower limb fracture: a double-blind, controlled study. Chin J Traumatol. 2009 Aug;12(4):223-7 | PubMed |
Deng GF, Zheng JP, Wang S, Tian B, Zhang SG. Remifentanil combined with low-dose ketamine for postoperative analgesia of lower limb fracture: a double-blind, controlled study. Chin J Traumatol. 2009 Aug;12(4):223-7 | PubMed | Gilabert Morell A, Sánchez Pérez C. [Effect of low-dose intravenous ketamine in postoperative analgesia for hysterectomy and adnexectomy]. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2002 May;49(5):247-53 | PubMed |
Gilabert Morell A, Sánchez Pérez C. [Effect of low-dose intravenous ketamine in postoperative analgesia for hysterectomy and adnexectomy]. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2002 May;49(5):247-53 | PubMed | Gillies A, Lindholm D, Angliss M, Orr A. The use of ketamine as rescue analgesia in the recovery room following morphine administration--a double-blind randomised controlled trial in postoperative patients. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007 Apr;35(2):199-203 | PubMed |
Gillies A, Lindholm D, Angliss M, Orr A. The use of ketamine as rescue analgesia in the recovery room following morphine administration--a double-blind randomised controlled trial in postoperative patients. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007 Apr;35(2):199-203 | PubMed | Hadi BA, Al Ramadani R, Daas R, Naylor I, Zelkó R. Remifentanil in combination with ketamine versus remifentanil in spinal fusion surgery--a double blind study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;48(8):542-8 | PubMed |
Hadi BA, Al Ramadani R, Daas R, Naylor I, Zelkó R. Remifentanil in combination with ketamine versus remifentanil in spinal fusion surgery--a double blind study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;48(8):542-8 | PubMed | Jahangir SM, Islam F, Aziz L. Ketamine infusion for postoperative analgesia in asthmatics: a comparison with intermittent meperidine. Anesth Analg. 1993 Jan;76(1):45-9 | PubMed |
Jahangir SM, Islam F, Aziz L. Ketamine infusion for postoperative analgesia in asthmatics: a comparison with intermittent meperidine. Anesth Analg. 1993 Jan;76(1):45-9 | PubMed | Kapfer B, Alfonsi P, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M. Nefopam and ketamine comparably enhance postoperative analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2005 Jan;100(1):169-74 | PubMed |
Kapfer B, Alfonsi P, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M. Nefopam and ketamine comparably enhance postoperative analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2005 Jan;100(1):169-74 | PubMed | Lak M , Foroozanmehr MJ , Ramazani MA. “Assessment of Ketamine Effect as Adjuvant to Morphine in Post-Operative Pain Reduction in Donor Kidney Transplanted.” Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 12.1 (2010): 38–44. Web. 5 May 2016 | Link |
Lak M , Foroozanmehr MJ , Ramazani MA. “Assessment of Ketamine Effect as Adjuvant to Morphine in Post-Operative Pain Reduction in Donor Kidney Transplanted.” Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 12.1 (2010): 38–44. Web. 5 May 2016 | Link | Lebrun T, Van Elstraete AC, Sandefo I, Polin B, Pierre-Louis L. Lack of a pre-emptive effect of low-dose ketamine on postoperative pain following oral surgery. Can J Anaesth. 2006 Feb;53(2):146-52 | PubMed |
Lebrun T, Van Elstraete AC, Sandefo I, Polin B, Pierre-Louis L. Lack of a pre-emptive effect of low-dose ketamine on postoperative pain following oral surgery. Can J Anaesth. 2006 Feb;53(2):146-52 | PubMed | Loftus RW, Yeager MP, Clark JA, Brown JR, Abdu WA, Sengupta DK, et al. Intraoperative ketamine reduces perioperative opiate consumption in opiate-dependent patients with chronic back pain undergoing back surgery. Anesthesiology. 2010 Sep;113(3):639-46 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Loftus RW, Yeager MP, Clark JA, Brown JR, Abdu WA, Sengupta DK, et al. Intraoperative ketamine reduces perioperative opiate consumption in opiate-dependent patients with chronic back pain undergoing back surgery. Anesthesiology. 2010 Sep;113(3):639-46 | CrossRef | PubMed | McKay WP, Donais P. Bowel function after bowel surgery: morphine with ketamine or placebo; a randomized controlled trial pilot study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007 Oct;51(9):1166-71 | PubMed |
McKay WP, Donais P. Bowel function after bowel surgery: morphine with ketamine or placebo; a randomized controlled trial pilot study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007 Oct;51(9):1166-71 | PubMed | Michelet P, Guervilly C, Hélaine A, Avaro JP, Blayac D, Gaillat F, et al. Adding ketamine to morphine for patient-controlled analgesia after thoracic surgery: influence on morphine consumption, respiratory function, and nocturnal desaturation. Br J Anaesth. 2007 Sep;99(3):396-403 | PubMed |
Michelet P, Guervilly C, Hélaine A, Avaro JP, Blayac D, Gaillat F, et al. Adding ketamine to morphine for patient-controlled analgesia after thoracic surgery: influence on morphine consumption, respiratory function, and nocturnal desaturation. Br J Anaesth. 2007 Sep;99(3):396-403 | PubMed | Mortero RF, Clark LD, Tolan MM, Metz RJ, Tsueda K, Sheppard RA. The effects of small-dose ketamine on propofol sedation: respiration, postoperative mood, perception, cognition, and pain. Anesth Analg. 2001 Jun;92(6):1465-9 | PubMed |
Mortero RF, Clark LD, Tolan MM, Metz RJ, Tsueda K, Sheppard RA. The effects of small-dose ketamine on propofol sedation: respiration, postoperative mood, perception, cognition, and pain. Anesth Analg. 2001 Jun;92(6):1465-9 | PubMed | Ozgun S, Ugur B , Aydin ON , Eyigor H , Erpek G. “The Effect of Preemptive Ketamine on Analgesia and Analgesic Consumption after Tonsillectomy.” TURK ANESTEZIYOLOJI VE REANIMASYON DERNEGI DERGISI 31.5 (2003): 247-52 | Link |
Ozgun S, Ugur B , Aydin ON , Eyigor H , Erpek G. “The Effect of Preemptive Ketamine on Analgesia and Analgesic Consumption after Tonsillectomy.” TURK ANESTEZIYOLOJI VE REANIMASYON DERNEGI DERGISI 31.5 (2003): 247-52 | Link | Perrin SB, Purcell AN. Intraoperative ketamine may influence persistent pain following knee arthroplasty under combined general and spinal anaesthesia: a pilot study. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009 Mar;37(2):248-53 | PubMed |
Perrin SB, Purcell AN. Intraoperative ketamine may influence persistent pain following knee arthroplasty under combined general and spinal anaesthesia: a pilot study. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009 Mar;37(2):248-53 | PubMed | Remérand F, Le Tendre C, Baud A, Couvret C, Pourrat X, Favard L, et al. The early and delayed analgesic effects of ketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Analg. 2009 Dec;109(6):1963-71 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Remérand F, Le Tendre C, Baud A, Couvret C, Pourrat X, Favard L, et al. The early and delayed analgesic effects of ketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Analg. 2009 Dec;109(6):1963-71 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wu YQ, Li H, Xiong JC, Xu ZM, Ma LY, Huang XM, Zhang DT, et al. [Effects of patient-controlled analgesia with small dose ketamine combined with morphine and the influence thereof on plasma beta-endorphin level in patients after radical operation for esophageal carcinoma]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Feb 10;89(5):314-7 | PubMed |
Wu YQ, Li H, Xiong JC, Xu ZM, Ma LY, Huang XM, Zhang DT, et al. [Effects of patient-controlled analgesia with small dose ketamine combined with morphine and the influence thereof on plasma beta-endorphin level in patients after radical operation for esophageal carcinoma]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Feb 10;89(5):314-7 | PubMed | Xie H, Wang X, Liu G, Wang G. Analgesic effects and pharmacokinetics of a low dose of ketamine preoperatively administered epidurally or intravenously. Clin J Pain. 2003 Sep-Oct;19(5):317-22 | PubMed |
Xie H, Wang X, Liu G, Wang G. Analgesic effects and pharmacokinetics of a low dose of ketamine preoperatively administered epidurally or intravenously. Clin J Pain. 2003 Sep-Oct;19(5):317-22 | PubMed | Yamauchi M, Asano M, Watanabe M, Iwasaki S, Furuse S, Namiki A. Continuous low-dose ketamine improves the analgesic effects of fentanyl patient-controlled analgesia after cervical spine surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008 Sep;107(3):1041-4 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Yamauchi M, Asano M, Watanabe M, Iwasaki S, Furuse S, Namiki A. Continuous low-dose ketamine improves the analgesic effects of fentanyl patient-controlled analgesia after cervical spine surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008 Sep;107(3):1041-4 | CrossRef | PubMed | Yentur EA, Topçu I, Keles G, Tasyüz T, Civi M. Subanalgesic Dose of Ketamine Added to Tramadol Does Not Reduce Analgesic Demand. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2004; 32(2): 106–112. | Link |
Yentur EA, Topçu I, Keles G, Tasyüz T, Civi M. Subanalgesic Dose of Ketamine Added to Tramadol Does Not Reduce Analgesic Demand. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2004; 32(2): 106–112. | Link | Ong E Osborne GA. Ketamine for Co-Induction of Anaesthesia in Oral Surgery. Ambul Surg. 2001 Oct;9(3): 131–135 | CrossRef |
Ong E Osborne GA. Ketamine for Co-Induction of Anaesthesia in Oral Surgery. Ambul Surg. 2001 Oct;9(3): 131–135 | CrossRef | Badrinath S, Avramov MN, Shadrick M, Witt TR, Ivankovich AD. The use of a ketamine-propofol combination during monitored anesthesia care. Anesth Analg. 2000 Apr;90(4):858-62 | PubMed |
Badrinath S, Avramov MN, Shadrick M, Witt TR, Ivankovich AD. The use of a ketamine-propofol combination during monitored anesthesia care. Anesth Analg. 2000 Apr;90(4):858-62 | PubMed | Frey K, Sukhani R, Pawlowski J, Pappas AL, Mikat-Stevens M, Slogoff S. Propofol versus propofol-ketamine sedation for retrobulbar nerve block: comparison of sedation quality, intraocular pressure changes, and recovery profiles. Anesth Analg. 1999 Aug;89(2):317-21 | PubMed |
Frey K, Sukhani R, Pawlowski J, Pappas AL, Mikat-Stevens M, Slogoff S. Propofol versus propofol-ketamine sedation for retrobulbar nerve block: comparison of sedation quality, intraocular pressure changes, and recovery profiles. Anesth Analg. 1999 Aug;89(2):317-21 | PubMed | Gorgias NK, Maidatsi PG, Kyriakidis AM, Karakoulas KA, Alvanos DN, Giala MM. Clonidine versus ketamine to prevent tourniquet pain during intravenous regional anesthesia with lidocaine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001 Nov-Dec;26(6):512-7 | PubMed |
Gorgias NK, Maidatsi PG, Kyriakidis AM, Karakoulas KA, Alvanos DN, Giala MM. Clonidine versus ketamine to prevent tourniquet pain during intravenous regional anesthesia with lidocaine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001 Nov-Dec;26(6):512-7 | PubMed | Choudhuri AH, Dharmani P, Kumarl N, Prakash A. Comparison of caudal epidural bupivacaine with bupivacaine plus tramadol and bupivacaine plus ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2008 Mar;36(2):174-9 | PubMed |
Choudhuri AH, Dharmani P, Kumarl N, Prakash A. Comparison of caudal epidural bupivacaine with bupivacaine plus tramadol and bupivacaine plus ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2008 Mar;36(2):174-9 | PubMed | Akbas M, Akbas H, Yegin A, Sahin N, Titiz TA. Comparison of the effects of clonidine and ketamine added to ropivacaine on stress hormone levels and the duration of caudal analgesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Jul;15(7):580-5 | PubMed |
Akbas M, Akbas H, Yegin A, Sahin N, Titiz TA. Comparison of the effects of clonidine and ketamine added to ropivacaine on stress hormone levels and the duration of caudal analgesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Jul;15(7):580-5 | PubMed | Akbas M, Titiz TA, Ertugrul F, Akbas H, Melikoglu M. Comparison of the effect of ketamine added to bupivacaine and ropivacaine, on stress hormone levels and the duration of caudal analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005 Nov;49(10):1520-6 | PubMed |
Akbas M, Titiz TA, Ertugrul F, Akbas H, Melikoglu M. Comparison of the effect of ketamine added to bupivacaine and ropivacaine, on stress hormone levels and the duration of caudal analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005 Nov;49(10):1520-6 | PubMed | Moustafa AM, Negmi HH, Rabie ME. The combined effect of ketamine and remifentanil infusions as total intravenous anesthesia for scoliosis surgery in children. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Jun;19(5):1151-68 | PubMed |
Moustafa AM, Negmi HH, Rabie ME. The combined effect of ketamine and remifentanil infusions as total intravenous anesthesia for scoliosis surgery in children. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Jun;19(5):1151-68 | PubMed | Siddiqui AS, Raees US, Siddiqui SZ, Raza SA. Efficacy of pre-incisional peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for post-tonsillectomy analgesia in children. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013 Aug;23(8):533-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Siddiqui AS, Raees US, Siddiqui SZ, Raza SA. Efficacy of pre-incisional peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for post-tonsillectomy analgesia in children. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013 Aug;23(8):533-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Atangana R, Ngowe Ngowe M, Binam F, Sosso MA. Morphine versus morphine-ketamine association in the management of post operative pain in thoracic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2007;58(2):125-7 | PubMed |
Atangana R, Ngowe Ngowe M, Binam F, Sosso MA. Morphine versus morphine-ketamine association in the management of post operative pain in thoracic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2007;58(2):125-7 | PubMed | Ayatollahi V, Behdad S, Hatami M, Moshtaghiun H, Baghianimoghadam B. Comparison of peritonsillar infiltration effects of ketamine and tramadol on post tonsillectomy pain: a double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Croat Med J. 2012 Apr;53(2):155-61 | PubMed |
Ayatollahi V, Behdad S, Hatami M, Moshtaghiun H, Baghianimoghadam B. Comparison of peritonsillar infiltration effects of ketamine and tramadol on post tonsillectomy pain: a double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Croat Med J. 2012 Apr;53(2):155-61 | PubMed | Bazin V, Bollot J, Asehnoune K, Roquilly A, Guillaud C, De Windt A, et al. Effects of perioperative intravenous low dose of ketamine on postoperative analgesia in children. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010 Jan;27(1):47-52 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bazin V, Bollot J, Asehnoune K, Roquilly A, Guillaud C, De Windt A, et al. Effects of perioperative intravenous low dose of ketamine on postoperative analgesia in children. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2010 Jan;27(1):47-52 | CrossRef | PubMed | Locatelli BG, Frawley G, Spotti A, Ingelmo P, Kaplanian S, Rossi B, et al. Analgesic effectiveness of caudal levobupivacaine and ketamine. Br J Anaesth. 2008 May;100(5):701-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Locatelli BG, Frawley G, Spotti A, Ingelmo P, Kaplanian S, Rossi B, et al. Analgesic effectiveness of caudal levobupivacaine and ketamine. Br J Anaesth. 2008 May;100(5):701-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Burstal R, Danjoux G, Hayes C, Lantry G. PCA ketamine and morphine after abdominal hysterectomy. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2001 Jun;29(3):246-51 | PubMed |
Burstal R, Danjoux G, Hayes C, Lantry G. PCA ketamine and morphine after abdominal hysterectomy. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2001 Jun;29(3):246-51 | PubMed | Canbay O, Celebi N, Uzun S, Sahin A, Celiker V, Aypar U. Topical ketamine and morphine for post-tonsillectomy pain. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Apr;25(4):287-92 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Canbay O, Celebi N, Uzun S, Sahin A, Celiker V, Aypar U. Topical ketamine and morphine for post-tonsillectomy pain. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2008 Apr;25(4):287-92 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chazan S, Buda I, Nesher N, Paz J, Weinbroum AA. Low-dose ketamine via intravenous patient-controlled analgesia device after various transthoracic procedures improves analgesia and patient and family satisfaction. Pain Manag Nurs. 2010 Sep;11(3):169-76 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Chazan S, Buda I, Nesher N, Paz J, Weinbroum AA. Low-dose ketamine via intravenous patient-controlled analgesia device after various transthoracic procedures improves analgesia and patient and family satisfaction. Pain Manag Nurs. 2010 Sep;11(3):169-76 | CrossRef | PubMed | Choe H, Choi YS, Kim YH, Ko SH, Choi HG, Han YJ, et al. Epidural morphine plus ketamine for upper abdominal surgery: improved analgesia from preincisional versus postincisional administration. Anesth Analg. 1997 Mar;84(3):560-3 | PubMed |
Choe H, Choi YS, Kim YH, Ko SH, Choi HG, Han YJ, et al. Epidural morphine plus ketamine for upper abdominal surgery: improved analgesia from preincisional versus postincisional administration. Anesth Analg. 1997 Mar;84(3):560-3 | PubMed | Murdoch CJ, Crooks BA, Miller CD. Effect of the addition of ketamine to morphine in patient-controlled analgesia. Anaesthesia. 2002 May;57(5):484-8 | PubMed |
Murdoch CJ, Crooks BA, Miller CD. Effect of the addition of ketamine to morphine in patient-controlled analgesia. Anaesthesia. 2002 May;57(5):484-8 | PubMed | Cook B, Grubb DJ, Aldridge LA, Doyle E. Comparison of the effects of adrenaline, clonidine and ketamine on the duration of caudal analgesia produced by bupivacaine in children. Br J Anaesth. 1995 Dec;75(6):698-701 | PubMed |
Cook B, Grubb DJ, Aldridge LA, Doyle E. Comparison of the effects of adrenaline, clonidine and ketamine on the duration of caudal analgesia produced by bupivacaine in children. Br J Anaesth. 1995 Dec;75(6):698-701 | PubMed | Crousier M, Cognet V, Khaled M, Gueugniaud PY, Piriou V. [Effect of ketamine on prevention of postmastectomy chronic pain. A pilot study]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2008 Dec;27(12):987-93 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Crousier M, Cognet V, Khaled M, Gueugniaud PY, Piriou V. [Effect of ketamine on prevention of postmastectomy chronic pain. A pilot study]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2008 Dec;27(12):987-93 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wong CS, Lu CC, Cherng CH, Ho ST. Pre-emptive analgesia with ketamine, morphine and epidural lidocaine prior to total knee replacement. Can J Anaesth. 1997 Jan;44(1):31-7 | PubMed |
Wong CS, Lu CC, Cherng CH, Ho ST. Pre-emptive analgesia with ketamine, morphine and epidural lidocaine prior to total knee replacement. Can J Anaesth. 1997 Jan;44(1):31-7 | PubMed | Wong CS, Liaw WJ, Tung CS, Su YF, Ho ST. Ketamine potentiates analgesic effect of morphine in postoperative epidural pain control. Reg Anesth. 1996 Nov-Dec;21(6):534-41 | PubMed |
Wong CS, Liaw WJ, Tung CS, Su YF, Ho ST. Ketamine potentiates analgesic effect of morphine in postoperative epidural pain control. Reg Anesth. 1996 Nov-Dec;21(6):534-41 | PubMed | Dahi-Taleghani M, Fazli B, Ghasemi M, Vosoughian M, Dabbagh A. Effect of intravenous patient controlled ketamine analgesiaon postoperative pain in opium abusers. Anesth Pain Med. 2014 Feb 15;4(1):e14129 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dahi-Taleghani M, Fazli B, Ghasemi M, Vosoughian M, Dabbagh A. Effect of intravenous patient controlled ketamine analgesiaon postoperative pain in opium abusers. Anesth Pain Med. 2014 Feb 15;4(1):e14129 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dang X, Su S, Sun L, He L, Wu J. Analgesic Effect of Ketamine Adding to Morphine in Patient-Controlled Analgesia for Patients after Surgery for Femur Fracture. Guangdong Yi Xue. 2013;34(4): 608–611 | Link |
Dang X, Su S, Sun L, He L, Wu J. Analgesic Effect of Ketamine Adding to Morphine in Patient-Controlled Analgesia for Patients after Surgery for Femur Fracture. Guangdong Yi Xue. 2013;34(4): 608–611 | Link | Snijdelaar DG, Cornelisse HB, Schmid RL, Katz J. A randomised, controlled study of peri-operative low dose s(+)-ketamine in combination with postoperative patient-controlled s(+)-ketamine and morphine after radical prostatectomy. Anaesthesia. 2004 Mar;59(3):222-8 | PubMed |
Snijdelaar DG, Cornelisse HB, Schmid RL, Katz J. A randomised, controlled study of peri-operative low dose s(+)-ketamine in combination with postoperative patient-controlled s(+)-ketamine and morphine after radical prostatectomy. Anaesthesia. 2004 Mar;59(3):222-8 | PubMed | Dix P, Martindale S, Stoddart PA. Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of the effect of ketamine on postoperative morphine consumption in children following appendicectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Jun;13(5):422-6 | PubMed |
Dix P, Martindale S, Stoddart PA. Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of the effect of ketamine on postoperative morphine consumption in children following appendicectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Jun;13(5):422-6 | PubMed | Elhakim M, Khalafallah Z, El-Fattah HA, Farouk S, Khattab A. Ketamine reduces swallowing-evoked pain after paediatric tonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003 May;47(5):604-9 | PubMed |
Elhakim M, Khalafallah Z, El-Fattah HA, Farouk S, Khattab A. Ketamine reduces swallowing-evoked pain after paediatric tonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003 May;47(5):604-9 | PubMed | Elshammaa N, Chidambaran V, Housny W, Thomas J, Zhang X, Michael R. Ketamine as an adjunct to fentanyl improves postoperative analgesia and hastens discharge in children following tonsillectomy - a prospective, double-blinded, randomized study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011 Oct;21(10):1009-14 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Elshammaa N, Chidambaran V, Housny W, Thomas J, Zhang X, Michael R. Ketamine as an adjunct to fentanyl improves postoperative analgesia and hastens discharge in children following tonsillectomy - a prospective, double-blinded, randomized study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2011 Oct;21(10):1009-14 | CrossRef | PubMed | Engelhardt T, Zaarour C, Naser B, Pehora C, de Ruiter J, Howard A, et al. Intraoperative low-dose ketamine does not prevent a remifentanil-induced increase in morphine requirement after pediatric scoliosis surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008 Oct;107(4):1170-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Engelhardt T, Zaarour C, Naser B, Pehora C, de Ruiter J, Howard A, et al. Intraoperative low-dose ketamine does not prevent a remifentanil-induced increase in morphine requirement after pediatric scoliosis surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008 Oct;107(4):1170-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zahra FA, Abudallah HM, Shabana RI, Abdulmageed WM, Abdulrazik SI, Nassar AM. Intramuscular ketamine for prevention of postanesthesia shivering in children. Saudi Med J. 2008 Sep;29(9):1255-9 | PubMed |
Zahra FA, Abudallah HM, Shabana RI, Abdulmageed WM, Abdulrazik SI, Nassar AM. Intramuscular ketamine for prevention of postanesthesia shivering in children. Saudi Med J. 2008 Sep;29(9):1255-9 | PubMed | Huang GS, Yeh CC, Kong SS, Lin TC, Ho ST, Wong CS. Intra-articular ketamine for pain control following arthroscopic knee surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2000 Sep;38(3):131-6 | PubMed |
Huang GS, Yeh CC, Kong SS, Lin TC, Ho ST, Wong CS. Intra-articular ketamine for pain control following arthroscopic knee surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2000 Sep;38(3):131-6 | PubMed | Günes Y, Seçen M, Ozcengiz D, Gündüz M, Balcioglu O, Isik G. Comparison of caudal ropivacaine, ropivacaine plus ketamine and ropivacaine plus tramadol administration for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jul;14(7):557-63 | PubMed |
Günes Y, Seçen M, Ozcengiz D, Gündüz M, Balcioglu O, Isik G. Comparison of caudal ropivacaine, ropivacaine plus ketamine and ropivacaine plus tramadol administration for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jul;14(7):557-63 | PubMed | Hagelin A, Lundberg D. Ketamine for postoperative analgesia after upper abdominal surgery. Clin Ther. 1981;4(3):229-33 | PubMed |
Hagelin A, Lundberg D. Ketamine for postoperative analgesia after upper abdominal surgery. Clin Ther. 1981;4(3):229-33 | PubMed | Hasnain F, Janbaz KH, Qureshi MA. Analgesic effect of ketamine and morphine after tonsillectomy in children. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012 Jul;25(3):599-606 | PubMed |
Hasnain F, Janbaz KH, Qureshi MA. Analgesic effect of ketamine and morphine after tonsillectomy in children. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012 Jul;25(3):599-606 | PubMed | Hercock T, Gillham MJ, Sleigh J, Jones SF. The Addition of Ketamine to Patient Controlled Morphine Analgesia Does Not Improve Quality of Analgesia after Total Abdominal Hysterectomy. Acute Pain. 1999 Jun;2(2): 68–72 | CrossRef |
Hercock T, Gillham MJ, Sleigh J, Jones SF. The Addition of Ketamine to Patient Controlled Morphine Analgesia Does Not Improve Quality of Analgesia after Total Abdominal Hysterectomy. Acute Pain. 1999 Jun;2(2): 68–72 | CrossRef | Ryu HG, Lee CJ, Kim YT, Bahk JH. Preemptive low-dose epidural ketamine for preventing chronic postthoracotomy pain: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, clinical trial. Clin J Pain. 2011 May;27(4):304-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ryu HG, Lee CJ, Kim YT, Bahk JH. Preemptive low-dose epidural ketamine for preventing chronic postthoracotomy pain: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized, clinical trial. Clin J Pain. 2011 May;27(4):304-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Himmelseher S, Ziegler-Pithamitsis D, Argiriadou H, Martin J, Jelen-Esselborn S, Kochs E. Small-dose S(+)-ketamine reduces postoperative pain when applied with ropivacaine in epidural anesthesia for total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2001 May;92(5):1290-5 | PubMed |
Himmelseher S, Ziegler-Pithamitsis D, Argiriadou H, Martin J, Jelen-Esselborn S, Kochs E. Small-dose S(+)-ketamine reduces postoperative pain when applied with ropivacaine in epidural anesthesia for total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2001 May;92(5):1290-5 | PubMed | Lee HM, Sanders GM. Caudal ropivacaine and ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Anaesthesia. 2000 Aug;55(8):806-10 | PubMed |
Lee HM, Sanders GM. Caudal ropivacaine and ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Anaesthesia. 2000 Aug;55(8):806-10 | PubMed | Honarmand A, Safavi MR, Jamshidi M. The preventative analgesic effect of preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of two low doses of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008 Jun;18(6):508-14 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Honarmand A, Safavi MR, Jamshidi M. The preventative analgesic effect of preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of two low doses of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008 Jun;18(6):508-14 | CrossRef | PubMed | Honarmand A, Safavi M, Kashefi P, Hosseini B, Badiei S. Comparison of effect of intravenous ketamine, peritonsillar infiltration of tramadol and their combination on pediatric posttonsillectomy pain: A double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Res Pharm Sci. 2013 Jul;8(3):177-83 | PubMed |
Honarmand A, Safavi M, Kashefi P, Hosseini B, Badiei S. Comparison of effect of intravenous ketamine, peritonsillar infiltration of tramadol and their combination on pediatric posttonsillectomy pain: A double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Res Pharm Sci. 2013 Jul;8(3):177-83 | PubMed | Inanoglu K, Ozbakis Akkurt BC, Turhanoglu S, Okuyucu S, Akoglu E. Intravenous ketamine and local bupivacaine infiltration are effective as part of a multimodal regime for reducing post-tonsillectomy pain. Med Sci Monit. 2009 Oct;15(10):CR539-543 | PubMed |
Inanoglu K, Ozbakis Akkurt BC, Turhanoglu S, Okuyucu S, Akoglu E. Intravenous ketamine and local bupivacaine infiltration are effective as part of a multimodal regime for reducing post-tonsillectomy pain. Med Sci Monit. 2009 Oct;15(10):CR539-543 | PubMed | Wilson JA, Nimmo AF, Fleetwood-Walker SM, Colvin LA. A randomised double blind trial of the effect of pre-emptive epidural ketamine on persistent pain after lower limb amputation. Pain. 2008 Mar;135(1-2):108-18 | PubMed |
Wilson JA, Nimmo AF, Fleetwood-Walker SM, Colvin LA. A randomised double blind trial of the effect of pre-emptive epidural ketamine on persistent pain after lower limb amputation. Pain. 2008 Mar;135(1-2):108-18 | PubMed | O'Flaherty JE, Lin CX. Does ketamine or magnesium affect osttonsillectomy pain in children? Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Jun;13(5):413-21 | PubMed |
O'Flaherty JE, Lin CX. Does ketamine or magnesium affect osttonsillectomy pain in children? Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Jun;13(5):413-21 | PubMed | Dich-Nielsen JO, Svendsen LB, Berthelsen P. Intramuscular low-dose ketamine versus pethidine for postoperative pain treatment after thoracic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1992 Aug;36(6):583-7 | PubMed |
Dich-Nielsen JO, Svendsen LB, Berthelsen P. Intramuscular low-dose ketamine versus pethidine for postoperative pain treatment after thoracic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1992 Aug;36(6):583-7 | PubMed | Kamal, Hanan Mahmoud. Ketamine as an Adjuvant to Morphine for Patient Controlled Analgesia in Morbidly Obese Patients. J Med Sci. 2008;8(4): 364–370. | CrossRef |
Kamal, Hanan Mahmoud. Ketamine as an Adjuvant to Morphine for Patient Controlled Analgesia in Morbidly Obese Patients. J Med Sci. 2008;8(4): 364–370. | CrossRef | Kararmaz A, Kaya S, Turhanoglu S, Ozyilmaz MA. Oral ketamine premedication can prevent emergence agitation in children after desflurane anaesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jun;14(6):477-82 | PubMed |
Kararmaz A, Kaya S, Turhanoglu S, Ozyilmaz MA. Oral ketamine premedication can prevent emergence agitation in children after desflurane anaesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jun;14(6):477-82 | PubMed | Kathirvel S, Sadhasivam S, Saxena A, Kannan TR, Ganjoo P. Effects of intrathecal ketamine added to bupivacaine for spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2000 Sep;55(9):899-904 | PubMed |
Kathirvel S, Sadhasivam S, Saxena A, Kannan TR, Ganjoo P. Effects of intrathecal ketamine added to bupivacaine for spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2000 Sep;55(9):899-904 | PubMed | Javery KB, Ussery TW, Steger HG, Colclough GW. Comparison of morphine and morphine with ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Can J Anaesth. 1996 Mar;43(3):212-5 | PubMed |
Javery KB, Ussery TW, Steger HG, Colclough GW. Comparison of morphine and morphine with ketamine for postoperative analgesia. Can J Anaesth. 1996 Mar;43(3):212-5 | PubMed | Khademi S, Ghaffarpasand F, Heiran HR, Yavari MJ, Motazedian S, Dehghankhalili M. Intravenous and peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for postoperative pain after adenotonsillectomy: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Med Princ Pract. 2011;20(5):433-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Khademi S, Ghaffarpasand F, Heiran HR, Yavari MJ, Motazedian S, Dehghankhalili M. Intravenous and peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine for postoperative pain after adenotonsillectomy: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Med Princ Pract. 2011;20(5):433-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kirdemir P, Ozkoçak I, Demir T, Gögüs N. Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of preemptively used epidural ketamine and neostigmine. J Clin Anesth. 2000 Nov;12(7):543-8 | PubMed |
Kirdemir P, Ozkoçak I, Demir T, Gögüs N. Comparison of postoperative analgesic effects of preemptively used epidural ketamine and neostigmine. J Clin Anesth. 2000 Nov;12(7):543-8 | PubMed | Kollender Y, Bickels J, Stocki D, Maruoani N, Chazan S, Nirkin A, et al. Subanaesthetic ketamine spares postoperative morphine and controls pain better than standard morphine does alone in orthopaedic-oncological patients. Eur J Cancer. 2008 May;44(7):954-62 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kollender Y, Bickels J, Stocki D, Maruoani N, Chazan S, Nirkin A, et al. Subanaesthetic ketamine spares postoperative morphine and controls pain better than standard morphine does alone in orthopaedic-oncological patients. Eur J Cancer. 2008 May;44(7):954-62 | CrossRef | PubMed | Ugur KS, Karabayirli S, Demircioglu RI, Ark N, Kurtaran H, Muslu B, et al. The comparison of preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine and tramadol for postoperative pain relief on children following adenotonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Nov;77(11):1825-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ugur KS, Karabayirli S, Demircioglu RI, Ark N, Kurtaran H, Muslu B, et al. The comparison of preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of ketamine and tramadol for postoperative pain relief on children following adenotonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Nov;77(11):1825-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kumar P, Rudra A, Pan AK, Acharya A. Caudal additives in pediatrics: a comparison among midazolam, ketamine, and neostigmine coadministered with bupivacaine. Anesth Analg. 2005 Jul;101(1):69-73 | PubMed |
Kumar P, Rudra A, Pan AK, Acharya A. Caudal additives in pediatrics: a comparison among midazolam, ketamine, and neostigmine coadministered with bupivacaine. Anesth Analg. 2005 Jul;101(1):69-73 | PubMed | Mathisen LC, Skjelbred P, Skoglund LA, Oye I. Effect of ketamine, an NMDA receptor inhibitor, in acute and chronic orofacial pain. Pain. 1995 May;61(2):215-20 | PubMed |
Mathisen LC, Skjelbred P, Skoglund LA, Oye I. Effect of ketamine, an NMDA receptor inhibitor, in acute and chronic orofacial pain. Pain. 1995 May;61(2):215-20 | PubMed | Levänen J. Ketamine and oxycodone in the management of postoperative pain. Mil Med. 2000 Jun;165(6):450-5 | PubMed |
Levänen J. Ketamine and oxycodone in the management of postoperative pain. Mil Med. 2000 Jun;165(6):450-5 | PubMed | Liu G, Huang Y, Luo A. Patient-Controlled Intravenous Morphine and Ketamine for Postoperative Analgesia. Chinese Journal of Anesthesiology. 2003;23(6): 416–418 | Link |
Liu G, Huang Y, Luo A. Patient-Controlled Intravenous Morphine and Ketamine for Postoperative Analgesia. Chinese Journal of Anesthesiology. 2003;23(6): 416–418 | Link | Jensen LL, Handberg G, Helbo-Hansen HS, Skaarup I, Lohse T, Munk T, Lund N. No morphine sparing effect of ketamine added to morphine for patient-controlled intravenous analgesia after uterine artery embolization. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008 Apr;52(4):479-86 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Jensen LL, Handberg G, Helbo-Hansen HS, Skaarup I, Lohse T, Munk T, Lund N. No morphine sparing effect of ketamine added to morphine for patient-controlled intravenous analgesia after uterine artery embolization. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008 Apr;52(4):479-86 | CrossRef | PubMed | Lo A, Macpherson N, Spiwak R. “Prospective Randomized Trial of Patient-Controlled Analgesia with Ketamine and Morphine or Morphine Alone after Hysterectomy. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2008 Sep;61(5): 334–339 | CrossRef |
Lo A, Macpherson N, Spiwak R. “Prospective Randomized Trial of Patient-Controlled Analgesia with Ketamine and Morphine or Morphine Alone after Hysterectomy. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2008 Sep;61(5): 334–339 | CrossRef | Martinez V, Cymerman A, Ben Ammar S, Fiaud JF, Rapon C, Poindessous F, et al. The analgesic efficiency of combined pregabalin and ketamine for total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, double-blind, controlled study. Anaesthesia. 2014 Jan;69(1):46-52 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Martinez V, Cymerman A, Ben Ammar S, Fiaud JF, Rapon C, Poindessous F, et al. The analgesic efficiency of combined pregabalin and ketamine for total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, double-blind, controlled study. Anaesthesia. 2014 Jan;69(1):46-52 | CrossRef | PubMed | Abdel-Ghaffar ME, Abdulatif MA, al-Ghamdi A, Mowafi H, Anwar A. Epidural ketamine reduces post-operative epidural PCA consumption of fentanyl/bupivacaine. Can J Anaesth. 1998 Feb;45(2):103-9 | PubMed |
Abdel-Ghaffar ME, Abdulatif MA, al-Ghamdi A, Mowafi H, Anwar A. Epidural ketamine reduces post-operative epidural PCA consumption of fentanyl/bupivacaine. Can J Anaesth. 1998 Feb;45(2):103-9 | PubMed | Eghbal MH, Taregh S, Amin A, Sahmeddini MA. Ketamine improves postoperative pain and emergence agitation following adenotonsillectomy in children. A randomized clinical trial. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2013 Jun;22(2):155-60 | PubMed |
Eghbal MH, Taregh S, Amin A, Sahmeddini MA. Ketamine improves postoperative pain and emergence agitation following adenotonsillectomy in children. A randomized clinical trial. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2013 Jun;22(2):155-60 | PubMed | El Sonbaty MI, Abo el Dahab H, Mostafa A, Abo Shanab O. Preemptive peritonsillar ketamine infiltration: postoperative analgesic efficacy versus meperidine. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011 Feb;21(1):43-51 | PubMed |
El Sonbaty MI, Abo el Dahab H, Mostafa A, Abo Shanab O. Preemptive peritonsillar ketamine infiltration: postoperative analgesic efficacy versus meperidine. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011 Feb;21(1):43-51 | PubMed | DA Conceição MJ, Bruggemann DA Conceição D, Carneiro Leão C. Effect of an intravenous single dose of ketamine on postoperative pain in tonsillectomy patients. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006 Sep;16(9):962-7 | PubMed |
DA Conceição MJ, Bruggemann DA Conceição D, Carneiro Leão C. Effect of an intravenous single dose of ketamine on postoperative pain in tonsillectomy patients. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006 Sep;16(9):962-7 | PubMed | Sadove MS, Shulman M, Hatano S, Fevold N. Analgesic effects of ketamine administered in subdissociative doses. Anesth Analg. 1971 May-Jun;50(3):452-7 | PubMed |
Sadove MS, Shulman M, Hatano S, Fevold N. Analgesic effects of ketamine administered in subdissociative doses. Anesth Analg. 1971 May-Jun;50(3):452-7 | PubMed | Grady MV, Mascha E, Sessler DI, Kurz A. The effect of perioperative intravenous lidocaine and ketamine on recovery after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2012 Nov;115(5):1078-84 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Grady MV, Mascha E, Sessler DI, Kurz A. The effect of perioperative intravenous lidocaine and ketamine on recovery after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2012 Nov;115(5):1078-84 | CrossRef | PubMed | Naguib M, Sharif AM, Seraj M, el Gammal M, Dawlatly AA. Ketamine for caudal analgesia in children: comparison with caudal bupivacaine. Br J Anaesth. 1991 Nov;67(5):559-64 | PubMed |
Naguib M, Sharif AM, Seraj M, el Gammal M, Dawlatly AA. Ketamine for caudal analgesia in children: comparison with caudal bupivacaine. Br J Anaesth. 1991 Nov;67(5):559-64 | PubMed | Nesher N, Ekstein MP, Paz Y, Marouani N, Chazan S, Weinbroum AA. Morphine with adjuvant ketamine vs higher dose of morphine alone for immediate postthoracotomy analgesia. Chest. 2009 Jul;136(1):245-52 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nesher N, Ekstein MP, Paz Y, Marouani N, Chazan S, Weinbroum AA. Morphine with adjuvant ketamine vs higher dose of morphine alone for immediate postthoracotomy analgesia. Chest. 2009 Jul;136(1):245-52 | CrossRef | PubMed | Nesher N, Serovian I, Marouani N, Chazan S, Weinbroum AA. Ketamine spares morphine consumption after transthoracic lung and heart surgery without adverse hemodynamic effects. Pharmacol Res. 2008 Jul;58(1):38-44 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nesher N, Serovian I, Marouani N, Chazan S, Weinbroum AA. Ketamine spares morphine consumption after transthoracic lung and heart surgery without adverse hemodynamic effects. Pharmacol Res. 2008 Jul;58(1):38-44 | CrossRef | PubMed | Nitta R, Goyagi T, Nishikawa T. Combination of oral clonidine and intravenous low-dose ketamine reduces the consumption of postoperative patient-controlled analgesia morphine after spine surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2013 Mar;51(1):14-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nitta R, Goyagi T, Nishikawa T. Combination of oral clonidine and intravenous low-dose ketamine reduces the consumption of postoperative patient-controlled analgesia morphine after spine surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2013 Mar;51(1):14-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Erhan OL, Göksu H, Alpay C, Bestas A. Ketamine in post-tonsillectomy pain. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007 May;71(5):735-9 | PubMed |
Erhan OL, Göksu H, Alpay C, Bestas A. Ketamine in post-tonsillectomy pain. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007 May;71(5):735-9 | PubMed | Aydin ON, Ugur B, Ozgun S, Eyigör H, Copcu O. Pain prevention with intraoperative ketamine in outpatient children undergoing tonsillectomy or tonsillectomy and adenotomy. J Clin Anesth. 2007 Mar;19(2):115-9 | PubMed |
Aydin ON, Ugur B, Ozgun S, Eyigör H, Copcu O. Pain prevention with intraoperative ketamine in outpatient children undergoing tonsillectomy or tonsillectomy and adenotomy. J Clin Anesth. 2007 Mar;19(2):115-9 | PubMed | Nafiu OO, Kolawole IK, Salam RA, Elegbe EO. Comparison of caudal ketamine with or without bupivacaine in pediatric subumbilical surgery. J Natl Med Assoc. 2007 Jun;99(6):670-3 | PubMed |
Nafiu OO, Kolawole IK, Salam RA, Elegbe EO. Comparison of caudal ketamine with or without bupivacaine in pediatric subumbilical surgery. J Natl Med Assoc. 2007 Jun;99(6):670-3 | PubMed | Ozbek H, Bilen A, Ozcengiz D, Günes Y, Ozalevli M, Akman H. The comparison of caudal ketamine, alfentanil and ketamine plus alfentanil administration for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2002 Sep;12(7):610-6 | PubMed |
Ozbek H, Bilen A, Ozcengiz D, Günes Y, Ozalevli M, Akman H. The comparison of caudal ketamine, alfentanil and ketamine plus alfentanil administration for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2002 Sep;12(7):610-6 | PubMed | De Negri P, Ivani G, Visconti C, De Vivo P. How to prolong postoperative analgesia after caudal anaesthesia with ropivacaine in children: S-ketamine versus clonidine. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001 Nov;11(6):679-83 | PubMed |
De Negri P, Ivani G, Visconti C, De Vivo P. How to prolong postoperative analgesia after caudal anaesthesia with ropivacaine in children: S-ketamine versus clonidine. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001 Nov;11(6):679-83 | PubMed | Pan AK, Rudra A. Caudal Analgesia in Paediatrics: Comparison between Bupivacaine Alone and in Combination with Ketamine, Midazolam and Ketamine-Midazolam. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Oct:21(4): 401
Pan AK, Rudra A. Caudal Analgesia in Paediatrics: Comparison between Bupivacaine Alone and in Combination with Ketamine, Midazolam and Ketamine-Midazolam. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Oct:21(4): 401  Parkhouse J, Marriott G. Postoperative analgesia with ketamine and pethidine. Anaesthesia. 1977 Mar;32(3):285-9
Parkhouse J, Marriott G. Postoperative analgesia with ketamine and pethidine. Anaesthesia. 1977 Mar;32(3):285-9  Pathania J, Sodhi SS, Thakur JR. Comparison of Efficacy and Duration of Caudal Analgesia Produced by Bupivacaine Alone and in Combination with Adrenaline and Ketamine in Children. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;19(2): 207–2011 | Link |
Pathania J, Sodhi SS, Thakur JR. Comparison of Efficacy and Duration of Caudal Analgesia Produced by Bupivacaine Alone and in Combination with Adrenaline and Ketamine in Children. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;19(2): 207–2011 | Link | Tan PH, Kuo MC, Kao PF, Chia YY, Liu K. Patient-controlled epidural analgesia with morphine or morphine plus ketamine for post-operative pain relief. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999 Dec;16(12):820-5 | PubMed |
Tan PH, Kuo MC, Kao PF, Chia YY, Liu K. Patient-controlled epidural analgesia with morphine or morphine plus ketamine for post-operative pain relief. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999 Dec;16(12):820-5 | PubMed | Pirzadeh A, Mohammadi MA, Allaf-Akbari S, Entezariasl M. The effect of ketamine on posttonsillectomy pain in children: a clinical trial. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Winter;24(66):23-8 | PubMed |
Pirzadeh A, Mohammadi MA, Allaf-Akbari S, Entezariasl M. The effect of ketamine on posttonsillectomy pain in children: a clinical trial. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Winter;24(66):23-8 | PubMed | Reeves M, Lindholm DE, Myles PS, Fletcher H, Hunt JO. Adding ketamine to morphine for patient-controlled analgesia after major abdominal surgery: a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2001 Jul;93(1):116-20 | PubMed |
Reeves M, Lindholm DE, Myles PS, Fletcher H, Hunt JO. Adding ketamine to morphine for patient-controlled analgesia after major abdominal surgery: a double-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2001 Jul;93(1):116-20 | PubMed | Marcus RJ, Victoria BA, Rushman SC, Thompson JP. Comparison of ketamine and morphine for analgesia after tonsillectomy in children. Br J Anaesth. 2000 Jun;84(6):739-42 | PubMed |
Marcus RJ, Victoria BA, Rushman SC, Thompson JP. Comparison of ketamine and morphine for analgesia after tonsillectomy in children. Br J Anaesth. 2000 Jun;84(6):739-42 | PubMed | Aspinall RL, Mayor A. A prospective randomized controlled study of the efficacy of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children after adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001 May;11(3):333-6 | PubMed |
Aspinall RL, Mayor A. A prospective randomized controlled study of the efficacy of ketamine for postoperative pain relief in children after adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001 May;11(3):333-6 | PubMed | Safavi M, Honarmand A, Habibabady MR, Baraty S, Aghadavoudi O. Assessing intravenous ketamine and intravenous dexamethasone separately and in combination for early oral intake, vomiting and postoperative pain relief in children following tonsillectomy. Med Arh. 2012;66(2):111-5 | PubMed |
Safavi M, Honarmand A, Habibabady MR, Baraty S, Aghadavoudi O. Assessing intravenous ketamine and intravenous dexamethasone separately and in combination for early oral intake, vomiting and postoperative pain relief in children following tonsillectomy. Med Arh. 2012;66(2):111-5 | PubMed | Santawat U, Pongraweewan O, Lertakayamanee J, Rushatamukayanunt P, Phalakornkule N, Svasdi-Xuto O. Can ketamine potentiate the analgesic effect of epidural morphine, preincisional or postincisional administration? J Med Assoc Thai. 2002 Sep;85 Suppl 3:S1024-30 | PubMed |
Santawat U, Pongraweewan O, Lertakayamanee J, Rushatamukayanunt P, Phalakornkule N, Svasdi-Xuto O. Can ketamine potentiate the analgesic effect of epidural morphine, preincisional or postincisional administration? J Med Assoc Thai. 2002 Sep;85 Suppl 3:S1024-30 | PubMed | Semple D, Findlow D, Aldridge LM, Doyle E. The optimal dose of ketamine for caudal epidural blockade in children. Anaesthesia. 1996 Dec;51(12):1170-2 | PubMed |
Semple D, Findlow D, Aldridge LM, Doyle E. The optimal dose of ketamine for caudal epidural blockade in children. Anaesthesia. 1996 Dec;51(12):1170-2 | PubMed | Sen H, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, Emirkadi H, Ozkan S, Dagli G, et al. A comparison of gabapentin and ketamine in acute and chronic pain after hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2009 Nov;109(5):1645-50 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sen H, Sizlan A, Yanarates O, Emirkadi H, Ozkan S, Dagli G, et al. A comparison of gabapentin and ketamine in acute and chronic pain after hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2009 Nov;109(5):1645-50 | CrossRef | PubMed | Peat SJ, Bras P, Hanna MH. A double-blind comparison of epidural ketamine and diamorphine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia. 1989 Jul;44(7):555-8 | PubMed |
Peat SJ, Bras P, Hanna MH. A double-blind comparison of epidural ketamine and diamorphine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia. 1989 Jul;44(7):555-8 | PubMed | Somasundaran S, Garasia M. A Comparative Study of Ketamine and Tramadol as Additives to Plain Bupivacaine in Caudal Anaesthesia in Children. Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 2008;17(2) | Link |
Somasundaran S, Garasia M. A Comparative Study of Ketamine and Tramadol as Additives to Plain Bupivacaine in Caudal Anaesthesia in Children. Internet Journal of Anesthesiology. 2008;17(2) | Link | Spreng UJ, Dahl V, Ræder J. Effects of Perioperative S (+) Ketamine Infusion Added to Multimodal Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Haemorrhoidectomy. Scand J Pain. 2010 Apr;1(2): 100–105 | CrossRef |
Spreng UJ, Dahl V, Ræder J. Effects of Perioperative S (+) Ketamine Infusion Added to Multimodal Analgesia in Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Haemorrhoidectomy. Scand J Pain. 2010 Apr;1(2): 100–105 | CrossRef | Subramaniam B, Subramaniam K, Pawar DK, Sennaraj B. Preoperative epidural ketamine in combination with morphine does not have a clinically relevant intra- and postoperative opioid-sparing effect. Anesth Analg. 2001 Nov;93(5):1321-6 | PubMed |
Subramaniam B, Subramaniam K, Pawar DK, Sennaraj B. Preoperative epidural ketamine in combination with morphine does not have a clinically relevant intra- and postoperative opioid-sparing effect. Anesth Analg. 2001 Nov;93(5):1321-6 | PubMed | Subramaniam K, Subramaniam B, Pawar DK, Kumar L. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of epidural ketamine combined with morphine for postoperative analgesia after major upper abdominal surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2001 Aug;13(5):339-44 | PubMed |
Subramaniam K, Subramaniam B, Pawar DK, Kumar L. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of epidural ketamine combined with morphine for postoperative analgesia after major upper abdominal surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2001 Aug;13(5):339-44 | PubMed | Suzuki M, Haraguti S, Sugimoto K, Kikutani T, Shimada Y, Sakamoto A. Low-dose intravenous ketamine potentiates epidural analgesia after thoracotomy. Anesthesiology. 2006 Jul;105(1):111-9 | PubMed |
Suzuki M, Haraguti S, Sugimoto K, Kikutani T, Shimada Y, Sakamoto A. Low-dose intravenous ketamine potentiates epidural analgesia after thoracotomy. Anesthesiology. 2006 Jul;105(1):111-9 | PubMed | Sveticic G, Farzanegan F, Zmoos P, Zmoos S, Eichenberger U, Curatolo M. Is the combination of morphine with ketamine better than morphine alone for postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia? Anesth Analg. 2008 Jan;106(1):287-93 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sveticic G, Farzanegan F, Zmoos P, Zmoos S, Eichenberger U, Curatolo M. Is the combination of morphine with ketamine better than morphine alone for postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia? Anesth Analg. 2008 Jan;106(1):287-93 | CrossRef | PubMed | Taheri R, Seyedhejazi M, Ghojazadeh M, Ghabili K, Shayeghi S. Comparison of ketamine and fentanyl for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. Pak J Biol Sci. 2011 May 15;14(10):572-7 | PubMed |
Taheri R, Seyedhejazi M, Ghojazadeh M, Ghabili K, Shayeghi S. Comparison of ketamine and fentanyl for postoperative pain relief in children following adenotonsillectomy. Pak J Biol Sci. 2011 May 15;14(10):572-7 | PubMed | Tanaka M, Sato M, Saito A, Nishikawa T. Reevaluation of rectal ketamine premedication in children: comparison with rectal midazolam. Anesthesiology. 2000 Nov;93(5):1217-24 | PubMed |
Tanaka M, Sato M, Saito A, Nishikawa T. Reevaluation of rectal ketamine premedication in children: comparison with rectal midazolam. Anesthesiology. 2000 Nov;93(5):1217-24 | PubMed | Tarkkila P, Viitanen H, Mennander S, Annila P. Comparison of remifentanil versus ketamine for paediatric day case adenoidectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2003;54(3):217-22 | PubMed |
Tarkkila P, Viitanen H, Mennander S, Annila P. Comparison of remifentanil versus ketamine for paediatric day case adenoidectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2003;54(3):217-22 | PubMed | Taurá P, Fuster J, Blasi A, Martinez-Ocon J, Anglada T, Beltran J, et al. Postoperative pain relief after hepatic resection in cirrhotic patients: the efficacy of a single small dose of ketamine plus morphine epidurally. Anesth Analg. 2003 Feb;96(2):475-80 | PubMed |
Taurá P, Fuster J, Blasi A, Martinez-Ocon J, Anglada T, Beltran J, et al. Postoperative pain relief after hepatic resection in cirrhotic patients: the efficacy of a single small dose of ketamine plus morphine epidurally. Anesth Analg. 2003 Feb;96(2):475-80 | PubMed | Tverskoy M, Oren M, Vaskovich M, Dashkovsky I, Kissin I. Ketamine enhances local anesthetic and analgesic effects of bupivacaine by peripheral mechanism: a study in postoperative patients. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Aug 30;215(1):5-8 | PubMed |
Tverskoy M, Oren M, Vaskovich M, Dashkovsky I, Kissin I. Ketamine enhances local anesthetic and analgesic effects of bupivacaine by peripheral mechanism: a study in postoperative patients. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Aug 30;215(1):5-8 | PubMed | Umuroglu T, Eti Z, Ciftçi H, Yilmaz Gögüs F. Analgesia for adenotonsillectomy in children: a comparison of morphine, ketamine and tramadol. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jul;14(7):568-73 | PubMed |
Umuroglu T, Eti Z, Ciftçi H, Yilmaz Gögüs F. Analgesia for adenotonsillectomy in children: a comparison of morphine, ketamine and tramadol. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004 Jul;14(7):568-73 | PubMed | Unlügenç H, Gündüz M, Ozalevli M, Akman H. A comparative study on the analgesic effect of tramadol, tramadol plus magnesium, and tramadol plus ketamine for postoperative pain management after major abdominal surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Sep;46(8):1025-30 | PubMed |
Unlügenç H, Gündüz M, Ozalevli M, Akman H. A comparative study on the analgesic effect of tramadol, tramadol plus magnesium, and tramadol plus ketamine for postoperative pain management after major abdominal surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Sep;46(8):1025-30 | PubMed | Unlügenç H, Ozalevli M, Güler T, Isik G. Postoperative pain management with intravenous patient-controlled morphine: comparison of the effect of adding magnesium or ketamine. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2003 May;20(5):416-21 | PubMed |
Unlügenç H, Ozalevli M, Güler T, Isik G. Postoperative pain management with intravenous patient-controlled morphine: comparison of the effect of adding magnesium or ketamine. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2003 May;20(5):416-21 | PubMed | Tekelioglu UY, Apuhan T, Akkaya A, Demirhan A, Yildiz I, Simsek T, et al. Comparison of topical tramadol and ketamine in pain treatment after tonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013 Jun;23(6):496-501 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tekelioglu UY, Apuhan T, Akkaya A, Demirhan A, Yildiz I, Simsek T, et al. Comparison of topical tramadol and ketamine in pain treatment after tonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013 Jun;23(6):496-501 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wang Q, Wang Z, Wang B. Continuous Intravenous Infusion of Low Dose of Ketamine Combined with Morphine Used for Postoperative Analgesia in Patients with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice. 2007;13(1): 86–88 | Link |
Wang Q, Wang Z, Wang B. Continuous Intravenous Infusion of Low Dose of Ketamine Combined with Morphine Used for Postoperative Analgesia in Patients with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Theory and Practice. 2007;13(1): 86–88 | Link | Murray WB, Yankelowitz SM, le Roux M, Bester HF. Prevention of post-tonsillectomy pain with analgesic doses of ketamine. S Afr Med J. 1987 Dec 19;72(12):839-42 | PubMed |
Murray WB, Yankelowitz SM, le Roux M, Bester HF. Prevention of post-tonsillectomy pain with analgesic doses of ketamine. S Afr Med J. 1987 Dec 19;72(12):839-42 | PubMed | Weber F, Wulf H. Caudal bupivacaine and s(+)-ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Mar;13(3):244-8 | PubMed |
Weber F, Wulf H. Caudal bupivacaine and s(+)-ketamine for postoperative analgesia in children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2003 Mar;13(3):244-8 | PubMed | Batra YK, Shamsah M, Al-Khasti MJ, Rawdhan HJ, Al-Qattan AR, Belani KG. Intraoperative small-dose ketamine does not reduce pain or analgesic consumption during perioperative opioid analgesia in children after tonsillectomy. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Mar;45(3):155-60 | PubMed |
Batra YK, Shamsah M, Al-Khasti MJ, Rawdhan HJ, Al-Qattan AR, Belani KG. Intraoperative small-dose ketamine does not reduce pain or analgesic consumption during perioperative opioid analgesia in children after tonsillectomy. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Mar;45(3):155-60 | PubMed | Chia YY, Liu K, Liu YC, Chang HC, Wong CS. Adding ketamine in a multimodal patient-controlled epidural regimen reduces postoperative pain and analgesic consumption. Anesth Analg. 1998 Jun;86(6):1245-9 | PubMed |
Chia YY, Liu K, Liu YC, Chang HC, Wong CS. Adding ketamine in a multimodal patient-controlled epidural regimen reduces postoperative pain and analgesic consumption. Anesth Analg. 1998 Jun;86(6):1245-9 | PubMed | Siddiqui Q, Chowdhury E. Caudal Analgesia in Paediatrics: A Comparison between Bupivacaine and Ketamine. Internet J Anesthesiol. 2006; 11 | Link |
Siddiqui Q, Chowdhury E. Caudal Analgesia in Paediatrics: A Comparison between Bupivacaine and Ketamine. Internet J Anesthesiol. 2006; 11 | Link | Azevedo VM, Lauretti GR, Pereira NL, Reis MP. Transdermal ketamine as an adjuvant for postoperative analgesia after abdominal gynecological surgery using lidocaine epidural blockade. Anesth Analg. 2000 Dec;91(6):1479-82 | PubMed |
Azevedo VM, Lauretti GR, Pereira NL, Reis MP. Transdermal ketamine as an adjuvant for postoperative analgesia after abdominal gynecological surgery using lidocaine epidural blockade. Anesth Analg. 2000 Dec;91(6):1479-82 | PubMed | Kakinohana M, Hasegawa A, Taira Y, Okuda Y. [Pre-emptive analgesia with intravenous ketamine reduces postoperative pain in young patients after appendicectomy: a randomized conrol study]. Masui. 2000 Oct;49(10):1092-6 | PubMed |
Kakinohana M, Hasegawa A, Taira Y, Okuda Y. [Pre-emptive analgesia with intravenous ketamine reduces postoperative pain in young patients after appendicectomy: a randomized conrol study]. Masui. 2000 Oct;49(10):1092-6 | PubMed | Kawana Y, Sato H, Shimada H, Fujita N, Ueda Y, Hayashi A, Araki Y. Epidural ketamine for postoperative pain relief after gynecologic operations: a double-blind study and comparison with epidural morphine. Anesth Analg. 1987 Aug;66(8):735-8 | PubMed |
Kawana Y, Sato H, Shimada H, Fujita N, Ueda Y, Hayashi A, Araki Y. Epidural ketamine for postoperative pain relief after gynecologic operations: a double-blind study and comparison with epidural morphine. Anesth Analg. 1987 Aug;66(8):735-8 | PubMed | Lauretti GR, Oliveira AP, Rodrigues AM, Paccola CA. The effect of transdermal nitroglycerin on spinal S(+)-ketamine antinociception following orthopedic surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2001 Dec;13(8):576-81 | PubMed |
Lauretti GR, Oliveira AP, Rodrigues AM, Paccola CA. The effect of transdermal nitroglycerin on spinal S(+)-ketamine antinociception following orthopedic surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2001 Dec;13(8):576-81 | PubMed | Lee IO, Kim WK, Kong MH, Lee MK, Kim NS, Choi YS, Lim SH. No enhancement of sensory and motor blockade by ketamine added to ropivacaine interscalene brachial plexus blockade. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Aug;46(7):821-6 | PubMed |
Lee IO, Kim WK, Kong MH, Lee MK, Kim NS, Choi YS, Lim SH. No enhancement of sensory and motor blockade by ketamine added to ropivacaine interscalene brachial plexus blockade. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002 Aug;46(7):821-6 | PubMed | Qureshi FA, Mellis PT, McFadden MA. Efficacy of oral ketamine for providing sedation and analgesia to children requiring laceration repair. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1995 Apr;11(2):93-7 | PubMed |
Qureshi FA, Mellis PT, McFadden MA. Efficacy of oral ketamine for providing sedation and analgesia to children requiring laceration repair. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1995 Apr;11(2):93-7 | PubMed | Rosseland LA, Stubhaug A, Sandberg L, Breivik H. Intra-articular (IA) catheter administration of postoperative analgesics. A new trial design allows evaluation of baseline pain, demonstrates large variation in need of analgesics, and finds no analgesic effect of IA ketamine compared with IA saline. Pain. 2003 Jul;104(1-2):25-34 | PubMed |
Rosseland LA, Stubhaug A, Sandberg L, Breivik H. Intra-articular (IA) catheter administration of postoperative analgesics. A new trial design allows evaluation of baseline pain, demonstrates large variation in need of analgesics, and finds no analgesic effect of IA ketamine compared with IA saline. Pain. 2003 Jul;104(1-2):25-34 | PubMed | Weir PS, Fee JP. Double-blind comparison of extradural block with three bupivacaine-ketamine mixtures in knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1998 Mar;80(3):299-301 | PubMed |
Weir PS, Fee JP. Double-blind comparison of extradural block with three bupivacaine-ketamine mixtures in knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1998 Mar;80(3):299-301 | PubMed | Zohar E, Luban I, Zunser I, Shapiro A, Jedeikin R, Fredman B. Patient-controlled bupivacaine wound instillation following cesarean section: the lack of efficacy of adjuvant ketamine. J Clin Anesth. 2002 Nov;14(7):505-11 | PubMed |
Zohar E, Luban I, Zunser I, Shapiro A, Jedeikin R, Fredman B. Patient-controlled bupivacaine wound instillation following cesarean section: the lack of efficacy of adjuvant ketamine. J Clin Anesth. 2002 Nov;14(7):505-11 | PubMed | Yanli Y, Eren A. The effect of extradural ketamine on onset time and sensory block in extradural anaesthesia with bupivacaine. Anaesthesia. 1996 Jan;51(1):84-6 | PubMed |
Yanli Y, Eren A. The effect of extradural ketamine on onset time and sensory block in extradural anaesthesia with bupivacaine. Anaesthesia. 1996 Jan;51(1):84-6 | PubMed | Wu M, Xing C, Ren Y, Dong L, Liu B, Jiang H. Peri-Operative Low Dose Ketamine to Reduce Postoperative Morphine Consumption. Journal of the Fourth Military Medical University. 2004;25(23): 2161 | Link |
Wu M, Xing C, Ren Y, Dong L, Liu B, Jiang H. Peri-Operative Low Dose Ketamine to Reduce Postoperative Morphine Consumption. Journal of the Fourth Military Medical University. 2004;25(23): 2161 | Link | American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Practice guidelines for acute pain management in the perioperative setting: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Anesthesiology. 2012 Feb;116(2):248-73 | CrossRef | PubMed |
American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Practice guidelines for acute pain management in the perioperative setting: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Anesthesiology. 2012 Feb;116(2):248-73 | CrossRef | PubMed | Schug SA, Palmer GM, Scott DA, Halliwell R, Trinca J. Acute pain management: scientific evidence, fourth edition, 2015. Med J Aust. 2016 May 2;204(8):315-7 | PubMed |
Schug SA, Palmer GM, Scott DA, Halliwell R, Trinca J. Acute pain management: scientific evidence, fourth edition, 2015. Med J Aust. 2016 May 2;204(8):315-7 | PubMed | Wang N, Fu Y, Ma H, Wang J. Clinical research regarding preemptive analgesic effect of preoperative ketamine after transurethral resection of prostate. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2015 Oct;23(3):295-300 | PubMed |
Wang N, Fu Y, Ma H, Wang J. Clinical research regarding preemptive analgesic effect of preoperative ketamine after transurethral resection of prostate. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2015 Oct;23(3):295-300 | PubMed | Garg N, Panda NB, Gandhi KA, Bhagat H, Batra YK, Grover VK, et al. Comparison of Small Dose Ketamine and Dexmedetomidine Infusion for Postoperative Analgesia in Spine Surgery--A Prospective Randomized Double-blind Placebo Controlled Study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2016 Jan;28(1):27-31 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Garg N, Panda NB, Gandhi KA, Bhagat H, Batra YK, Grover VK, et al. Comparison of Small Dose Ketamine and Dexmedetomidine Infusion for Postoperative Analgesia in Spine Surgery--A Prospective Randomized Double-blind Placebo Controlled Study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2016 Jan;28(1):27-31 | CrossRef | PubMed |