 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Patients with brain tumors –primary or metastatic- have an increased risk of presenting seizures during the course of their disease. So, prophylactic antiepileptic drugs have been proposed. However, the effects of this intervention are not yet clear. To answer this question, we searched in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple databases. We identified 12 systematic reviews including 80 studies overall. Twelve corresponded to randomized trials, but only two answered the question of interest. We extracted data, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE method. We concluded primary prevention with antiepileptic drugs might not reduce the risk of seizures, and it is associated to frequent adverse effects.
Up to 60% of patients with brain tumors develop seizures. Various mechanisms have been proposed for this; neoplastic tissue could be the starting site of a seizure, especially if it is neural tissue, and on the other hand, intracranial lesions could alter both structurally and functionally the adjacent territory by causing edema, vascular insufficiency, inflammation or releasing metabolically active molecules that promote epileptic activity. It is proposed that the location of the lesions could also influence the onset of seizures, being the incidence higher in cortical lesions.
This summary seeks to answer if primary prevention with antiepileptic drugs is effective in patients that will not be subject to surgery.
We used Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple databases, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. With this information, we generated a structured summary using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
|
What is the evidence. |
We found 12 systematic reviews [1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6], [7],[8],[9],[10],[11],[12] that include 80 primary studies [13],[14],[15],[16],[17],[18],[19],[20],[21],[22],[23], [24],[25],[26],[27],[28],[29],[30],[31],[32],[33],[34], [35],[36],[37],[38],[39],[40],[41],[42],[43],[44],[45], [46],[47],[48],[49],[50],[51],[52],[53],[54],[55],[56], [57],[58],[59],[60],[61],[62],[63],[64],[65],[66],[67], [68],[69],[70],[71],[72],[73],[74],[75],[76],[77],[78], [79],[80],[81],[82],[83],[84],[85],[86],[87],[88],[89], [90],[91],[92], twelve of which are randomized controlled trials [13],[14],[17],[22],[23],[36],[42],[65],[84],[86],[91],[92]. Ten of the latter were not used for analyses in this summary because they evaluated patients that would be subject to surgery [17],[22],[23],[36],[42],[65],[84], [86],[91],[92], so only two randomized trials correspond to direct evidence and answer our question [13],[14]. |
|
What types of patients were included |
Both trials included patients older than 18 years of age, without any previous history of seizures, with diagnosis of primary brain tumor (28.2%) or cerebral metastases (71.8%) and who were not subject to surgery. None of the trials reported the location of the lesions. One trial [13] included people with less than a month from diagnosis, and the other trial [14] included patients with less than 14 days from the time of diagnosis. No trial reported the treatment for the underlying disease. |
|
What types of interventions were included |
One trial [13] administered for primary prevention 15 mg/kg of phenytoin orally as an initial dose, followed by 5mg/kg/day orally. They followed the patients for 5.4 months. One trial [14] used valproate with a target serum level of 50-100 μg/mL, and followed the patients for seven months. One trial compared the intervention against placebo [14] and the other did not give any treatment to the control group [13]. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The main outcome reported was the incidence of seizures. Other reported outcome was the incidence of adverse effects such as nausea, vertigo, myelosuppression, blurred vision, rash and ataxia. No trial evaluated quality of life or mortality. |
The information regarding the effects of antiepileptic drugs for primary prevention in brain tumors or brain metastases is based on two randomized trials [13],[14], which include 174 patients. Both trials measured the onset of seizures and the presence of adverse effects. No trial evaluated mortality or quality of life.
The summary of findings is:
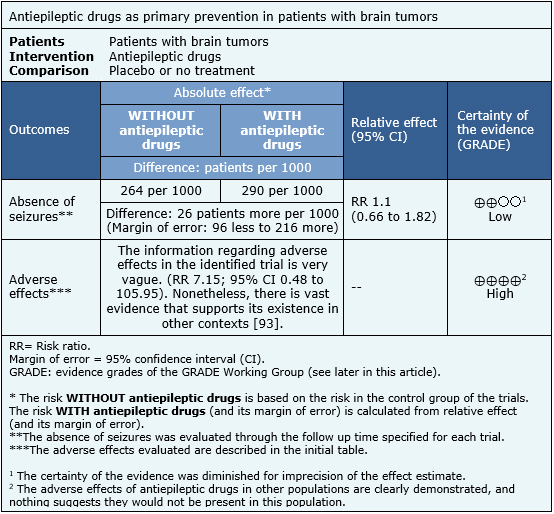

|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
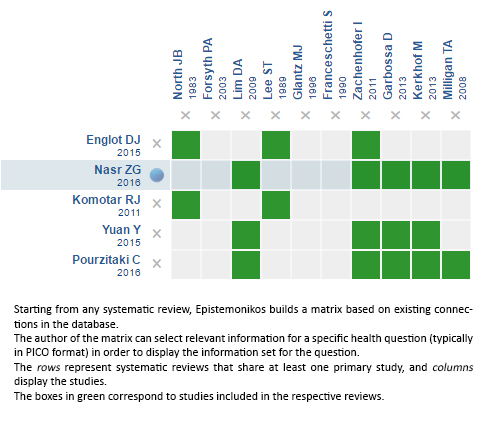
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Antiepileptic drugs for patients with brain tumors
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier. After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
The details about the methods used to produce these summaries are described here http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
These summaries follow a rigorous process of internal peer review.
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Patients with brain tumors –primary or metastatic- have an increased risk of presenting seizures during the course of their disease. So, prophylactic antiepileptic drugs have been proposed. However, the effects of this intervention are not yet clear. To answer this question, we searched in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple databases. We identified 12 systematic reviews including 80 studies overall. Twelve corresponded to randomized trials, but only two answered the question of interest. We extracted data, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE method. We concluded primary prevention with antiepileptic drugs might not reduce the risk of seizures, and it is associated to frequent adverse effects.
 Autores:
Diego Lobos-Urbina[1,2], Lucas Kittsteiner-Manubens[1,2], José Peña[2,3,4]
Autores:
Diego Lobos-Urbina[1,2], Lucas Kittsteiner-Manubens[1,2], José Peña[2,3,4]

Citación: Lobos-Urbina D, Kittsteiner-Manubens L, Peña J. Is primary prevention with antiepileptic drugs effective in brain tumors or brain metastases?. Medwave2017;17(Suppl1):e6871 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2017.6871
Fecha de envío: 28/12/2016
Fecha de aceptación: 28/12/2016
Fecha de publicación: 21/3/2017

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Tremont-Lukats IW, Ratilal BO, Armstrong T, Gilbert MR. Antiepileptic drugs for preventing seizures in people with brain tumors. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Apr 16;(2):CD004424 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tremont-Lukats IW, Ratilal BO, Armstrong T, Gilbert MR. Antiepileptic drugs for preventing seizures in people with brain tumors. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Apr 16;(2):CD004424 | CrossRef | PubMed | Sirven JI, Wingerchuk DM, Drazkowski JF, Lyons MK, Zimmerman RS. Seizure prophylaxis in patients with brain tumors: a meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004 Dec;79(12):1489-94 | PubMed |
Sirven JI, Wingerchuk DM, Drazkowski JF, Lyons MK, Zimmerman RS. Seizure prophylaxis in patients with brain tumors: a meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004 Dec;79(12):1489-94 | PubMed | Mikkelsen T, Paleologos NA, Robinson PD, Ammirati M, Andrews DW, Asher AL, et al. The role of prophylactic anticonvulsants in the management of brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol. 2010 Jan;96(1):97-102 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Mikkelsen T, Paleologos NA, Robinson PD, Ammirati M, Andrews DW, Asher AL, et al. The role of prophylactic anticonvulsants in the management of brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol. 2010 Jan;96(1):97-102 | CrossRef | PubMed | Perry J, Zinman L, Chambers A, Spithoff K, Lloyd N, Laperriere N; Neuro-oncology Disease Site Group; Cancer Care Ontario’s Program in Evidence-Based Care. The use of prophylactic anticonvulsants in patients with brain tumours-a systematic review. Curr Oncol. 2006 Dec;13(6):222-9. | PubMed |
Perry J, Zinman L, Chambers A, Spithoff K, Lloyd N, Laperriere N; Neuro-oncology Disease Site Group; Cancer Care Ontario’s Program in Evidence-Based Care. The use of prophylactic anticonvulsants in patients with brain tumours-a systematic review. Curr Oncol. 2006 Dec;13(6):222-9. | PubMed | Kong X, Guan J, Yang Y, Li Y, Ma W, Wang R. A meta-analysis: Do prophylactic antiepileptic drugs in patients with brain tumors decrease the incidence of seizures? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015 Jul;134:98-103 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kong X, Guan J, Yang Y, Li Y, Ma W, Wang R. A meta-analysis: Do prophylactic antiepileptic drugs in patients with brain tumors decrease the incidence of seizures? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015 Jul;134:98-103 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kerrigan S, Grant R. Antiepileptic drugs for treating seizures in adults with brain tumours. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Aug 10;(8):CD008586 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kerrigan S, Grant R. Antiepileptic drugs for treating seizures in adults with brain tumours. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Aug 10;(8):CD008586 | CrossRef | PubMed | Komotar RJ, Raper DM, Starke RM, Iorgulescu JB, Gutin PH. Prophylactic antiepileptic drug therapy in patients undergoing supratentorial meningioma resection: a systematic analysis of efficacy. J Neurosurg. 2011 Sep;115(3):483-90 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Komotar RJ, Raper DM, Starke RM, Iorgulescu JB, Gutin PH. Prophylactic antiepileptic drug therapy in patients undergoing supratentorial meningioma resection: a systematic analysis of efficacy. J Neurosurg. 2011 Sep;115(3):483-90 | CrossRef | PubMed | Yuan Y, Yunhe M, Xiang W, Yanhui L, Yanwu Y, Shuang L, et al. P450 enzyme-inducing and non-enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs for seizure prophylaxis after glioma resection surgery: a meta-analysis. Seizure. 2014 Sep;23(8):616-21 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Yuan Y, Yunhe M, Xiang W, Yanhui L, Yanwu Y, Shuang L, et al. P450 enzyme-inducing and non-enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs for seizure prophylaxis after glioma resection surgery: a meta-analysis. Seizure. 2014 Sep;23(8):616-21 | CrossRef | PubMed | Yuan Y, Peizhi Z, Maling G, Wu L, Yunhe M, Xiang W, Qing M, Yanhui L, Ruofei L, Jiewen L. The efficacy of levetiracetam for patients with supratentorial brain tumors. J Clin Neurosci. 2015 Aug;22(8):1227-31 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Yuan Y, Peizhi Z, Maling G, Wu L, Yunhe M, Xiang W, Qing M, Yanhui L, Ruofei L, Jiewen L. The efficacy of levetiracetam for patients with supratentorial brain tumors. J Clin Neurosci. 2015 Aug;22(8):1227-31 | CrossRef | PubMed | Englot DJ, Magill ST, Han SJ, Chang EF, Berger MS, McDermott MW. Seizures in supratentorial meningioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2016 Jun;124(6):1552-61 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Englot DJ, Magill ST, Han SJ, Chang EF, Berger MS, McDermott MW. Seizures in supratentorial meningioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 2016 Jun;124(6):1552-61 | CrossRef | PubMed | Nasr ZG, Paravattil B, Wilby KJ. Levetiracetam for seizure prevention in brain tumor patients: a systematic review. J Neurooncol. 2016 Aug;129(1):1-13 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nasr ZG, Paravattil B, Wilby KJ. Levetiracetam for seizure prevention in brain tumor patients: a systematic review. J Neurooncol. 2016 Aug;129(1):1-13 | CrossRef | PubMed | Pourzitaki C, Tsaousi G, Apostolidou E, Karakoulas K, Kouvelas D, Amaniti E. Efficacy and safety of prophylactic levetiracetam in supratentorial brain tumour surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;82(1):315-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Pourzitaki C, Tsaousi G, Apostolidou E, Karakoulas K, Kouvelas D, Amaniti E. Efficacy and safety of prophylactic levetiracetam in supratentorial brain tumour surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;82(1):315-25 | CrossRef | PubMed | Forsyth PA, Weaver S, Fulton D, Brasher PM, Sutherland G, Stewart D, et al. Prophylactic anticonvulsants in patients with brain tumour. Can J Neurol Sci. 2003 May;30(2):106-12 | PubMed |
Forsyth PA, Weaver S, Fulton D, Brasher PM, Sutherland G, Stewart D, et al. Prophylactic anticonvulsants in patients with brain tumour. Can J Neurol Sci. 2003 May;30(2):106-12 | PubMed | Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Friedberg MH, Lathi E, Choy H, Furie K, et al. A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of divalproex sodium prophylaxis in adults with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Neurology. 1996 Apr;46(4):985-91 | PubMed |
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Friedberg MH, Lathi E, Choy H, Furie K, et al. A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of divalproex sodium prophylaxis in adults with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Neurology. 1996 Apr;46(4):985-91 | PubMed | Findler G, Lavy S. Transient hemiparesis: a rare manifestation of diphenylhydantoin toxicity. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1979 May;50(5):685-7 | PubMed |
Findler G, Lavy S. Transient hemiparesis: a rare manifestation of diphenylhydantoin toxicity. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1979 May;50(5):685-7 | PubMed | Ramamurthi B, Ravi B, Ramachandran V. Convulsions with meningiomas: incidence and significance. Surg Neurol. 1980 Dec;14(6):415-6 | PubMed |
Ramamurthi B, Ravi B, Ramachandran V. Convulsions with meningiomas: incidence and significance. Surg Neurol. 1980 Dec;14(6):415-6 | PubMed | North JB, Penhall RK, Hanieh A, Frewin DB, Taylor WB. Phenytoin and postoperative epilepsy. A double-blind study. J Neurosurg. 1983 May;58(5):672-7 | PubMed |
North JB, Penhall RK, Hanieh A, Frewin DB, Taylor WB. Phenytoin and postoperative epilepsy. A double-blind study. J Neurosurg. 1983 May;58(5):672-7 | PubMed | Giombini S, Solero CL, Lasio G, Morello G. Immediate and late outcome of operations for Parasagittal and falx meningiomas. Report of 342 cases. SurgNeurol. 1984 May;21(5):427-35 | PubMed |
Giombini S, Solero CL, Lasio G, Morello G. Immediate and late outcome of operations for Parasagittal and falx meningiomas. Report of 342 cases. SurgNeurol. 1984 May;21(5):427-35 | PubMed | Chan RC, Thompson GB. Morbidity, mortality, and quality of life following surgery for intracranial meningiomas. A retrospective study in 257 cases. JNeurosurg. 1984 Jan;60(1):52-60 | PubMed |
Chan RC, Thompson GB. Morbidity, mortality, and quality of life following surgery for intracranial meningiomas. A retrospective study in 257 cases. JNeurosurg. 1984 Jan;60(1):52-60 | PubMed | Andrews BT, Wilson CB. Suprasellar meningiomas: the effect of tumor location on postoperative visual outcome. J Neurosurg. 1988 Oct;69(4):523-8 | PubMed |
Andrews BT, Wilson CB. Suprasellar meningiomas: the effect of tumor location on postoperative visual outcome. J Neurosurg. 1988 Oct;69(4):523-8 | PubMed | Ferrante L, Acqui M, Artico M, Mastronardi L, Rocchi G, Fortuna A. Cerebral meningiomas in children. Childs Nerv Syst. 1989 Apr;5(2):83-6 | PubMed |
Ferrante L, Acqui M, Artico M, Mastronardi L, Rocchi G, Fortuna A. Cerebral meningiomas in children. Childs Nerv Syst. 1989 Apr;5(2):83-6 | PubMed | Lee ST, Lui TN, Chang CN, Cheng WC, Wang DJ, Heimburger RF, et al. Prophylactic anticonvulsants for prevention of immediate and early postcraniotomy seizures. Surg Neurol. 1989 May;31(5):361-4 | PubMed |
Lee ST, Lui TN, Chang CN, Cheng WC, Wang DJ, Heimburger RF, et al. Prophylactic anticonvulsants for prevention of immediate and early postcraniotomy seizures. Surg Neurol. 1989 May;31(5):361-4 | PubMed | Franceschetti S, Binelli S, Casazza M, Lodrini S, Panzica F, Pluchino F, et al. Influence of surgery and antiepileptic drugs on seizures symptomatic of cerebral tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1990;103(1-2):47-51 | PubMed |
Franceschetti S, Binelli S, Casazza M, Lodrini S, Panzica F, Pluchino F, et al. Influence of surgery and antiepileptic drugs on seizures symptomatic of cerebral tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1990;103(1-2):47-51 | PubMed | Howng SL, Kwan AL. Intracranial meningioma. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi. 1992 Jun;8(6):312-9 | PubMed |
Howng SL, Kwan AL. Intracranial meningioma. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi. 1992 Jun;8(6):312-9 | PubMed | Tsuji M, Shinomiya S, Inoue R, Sato K. Prospective study of postoperative seizure in intracranial meningioma. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol. 1993 Jun;47(2):331-4 | PubMed |
Tsuji M, Shinomiya S, Inoue R, Sato K. Prospective study of postoperative seizure in intracranial meningioma. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol. 1993 Jun;47(2):331-4 | PubMed | Agbi CB, Bernstein M. Seizure prophylaxis for brain tumour patients. Brief review and guide for family physicians. Can Fam Physician. 1993 May;39:1153-6 | PubMed |
Agbi CB, Bernstein M. Seizure prophylaxis for brain tumour patients. Brief review and guide for family physicians. Can Fam Physician. 1993 May;39:1153-6 | PubMed | de Vries J, Wakhloo AK. Cerebral oedema associated with WHO-I, WHO-II, and WHO-III-meningiomas: correlation of clinical, computed tomographic, operative and histological findings. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993;125(1-4):34-40 | PubMed |
de Vries J, Wakhloo AK. Cerebral oedema associated with WHO-I, WHO-II, and WHO-III-meningiomas: correlation of clinical, computed tomographic, operative and histological findings. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993;125(1-4):34-40 | PubMed | Kilpatrick C, Kaye A, Dohrmann P, Gonzales M, Hopper J. Epilepsy and primary cerebral tumours. J Clin Neurosci. 1994 Jul;1(3):178-81 | PubMed |
Kilpatrick C, Kaye A, Dohrmann P, Gonzales M, Hopper J. Epilepsy and primary cerebral tumours. J Clin Neurosci. 1994 Jul;1(3):178-81 | PubMed | Germano IM, Edwards MS, Davis RL, Schiffer D. Intracranial meningiomas of the first two decades of life. J Neurosurg. 1994 Mar;80(3):447-53 | PubMed |
Germano IM, Edwards MS, Davis RL, Schiffer D. Intracranial meningiomas of the first two decades of life. J Neurosurg. 1994 Mar;80(3):447-53 | PubMed | Chow SY et al. “Epilepsy and Intracranial Meningiomas.” Zhonghua yi xue za zhi= Chinese medical journal; Free China ed 55.2 (1995): 151–155 | Link |
Chow SY et al. “Epilepsy and Intracranial Meningiomas.” Zhonghua yi xue za zhi= Chinese medical journal; Free China ed 55.2 (1995): 151–155 | Link | Chozick BS, Reinert SE, Greenblatt SH. Incidence of seizures after surgery for supratentorial meningiomas: a modern analysis. J Neurosurg. 1996 Mar;84(3):382-6 | PubMed |
Chozick BS, Reinert SE, Greenblatt SH. Incidence of seizures after surgery for supratentorial meningiomas: a modern analysis. J Neurosurg. 1996 Mar;84(3):382-6 | PubMed | Meixensberger J, Meister T, Janka M, Haubitz B, Bushe KA, Roosen K. Factors influencing morbidity and mortality after cranial meningioma surgery—a multivariate analysis. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1996;65:99-101 | PubMed |
Meixensberger J, Meister T, Janka M, Haubitz B, Bushe KA, Roosen K. Factors influencing morbidity and mortality after cranial meningioma surgery—a multivariate analysis. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1996;65:99-101 | PubMed | Lobato RD, Alday R, Gómez PA, Rivas JJ, Domínguez J, Cabrera A, et al. Brain oedema in patients with intracranial meningioma. Correlation between clinical, radiological, and histological factors and the presence and intensity of oedema. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996;138(5):485-93; discussion 493-4 | PubMed |
Lobato RD, Alday R, Gómez PA, Rivas JJ, Domínguez J, Cabrera A, et al. Brain oedema in patients with intracranial meningioma. Correlation between clinical, radiological, and histological factors and the presence and intensity of oedema. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996;138(5):485-93; discussion 493-4 | PubMed | Kawaguchi T, Kameyama S, Tanaka R. Peritumoral edema and seizure in patients with cerebral convexity and parasagittal meningiomas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1996 Aug;36(8):568-73; discussion 573-4 | PubMed |
Kawaguchi T, Kameyama S, Tanaka R. Peritumoral edema and seizure in patients with cerebral convexity and parasagittal meningiomas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1996 Aug;36(8):568-73; discussion 573-4 | PubMed | Puchner MJ, Fischer-Lampsatis RC, Herrmann HD, Freckmann N. Suprasellar meningiomas--neurological and visual outcome at long-term follow-up in a homogeneous series of patients treated microsurgically. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998;140(12):1231-8 | PubMed |
Puchner MJ, Fischer-Lampsatis RC, Herrmann HD, Freckmann N. Suprasellar meningiomas--neurological and visual outcome at long-term follow-up in a homogeneous series of patients treated microsurgically. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998;140(12):1231-8 | PubMed | Beenen LF, Lindeboom J, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité DG, Heimans JJ, Snoek FJ, Touw DJ, et al. Comparative double blind clinical trial of phenytoin and sodium valproate as anticonvulsant prophylaxis after craniotomy: efficacy, tolerability, and cognitive effects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999 Oct;67(4):474-80 | PubMed |
Beenen LF, Lindeboom J, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité DG, Heimans JJ, Snoek FJ, Touw DJ, et al. Comparative double blind clinical trial of phenytoin and sodium valproate as anticonvulsant prophylaxis after craniotomy: efficacy, tolerability, and cognitive effects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999 Oct;67(4):474-80 | PubMed | Lieu AS, Howng SL. Intracranial meningiomas and epilepsy: incidence, prognosis and influencing factors. Epilepsy Res. 2000 Jan;38(1):45-52 | PubMed |
Lieu AS, Howng SL. Intracranial meningiomas and epilepsy: incidence, prognosis and influencing factors. Epilepsy Res. 2000 Jan;38(1):45-52 | PubMed | Amirjamshidi A, Mehrazin M, Abbassioun K. Meningiomas of the central nervous system occurring below the age of 17: report of 24 cases not associated with neurofibromatosis and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2000 Jul;16(7):406-16 | PubMed |
Amirjamshidi A, Mehrazin M, Abbassioun K. Meningiomas of the central nervous system occurring below the age of 17: report of 24 cases not associated with neurofibromatosis and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2000 Jul;16(7):406-16 | PubMed | Im SH, Wang KC, Kim SK, Oh CW, Kim DG, Hong SK, et al. Childhood meningioma: unusual location, atypical radiological findings, and favorable treatment outcome. Childs Nerv Syst. 2001 Nov;17(11):656-62 | PubMed |
Im SH, Wang KC, Kim SK, Oh CW, Kim DG, Hong SK, et al. Childhood meningioma: unusual location, atypical radiological findings, and favorable treatment outcome. Childs Nerv Syst. 2001 Nov;17(11):656-62 | PubMed | Ohigashi Y, Tanabe A. A huge frontal meningioma associated with intraoperative massive bleeding and severe brain swelling--case report. J Clin Neurosci. 2001 May;8 Suppl 1:54-8 | PubMed |
Ohigashi Y, Tanabe A. A huge frontal meningioma associated with intraoperative massive bleeding and severe brain swelling--case report. J Clin Neurosci. 2001 May;8 Suppl 1:54-8 | PubMed | Jallo GI, Benjamin V. Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: microsurgical anatomy and surgical technique. Neurosurgery. 2002 Dec;51(6):1432-39; discussion 1439-40 | PubMed |
Jallo GI, Benjamin V. Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: microsurgical anatomy and surgical technique. Neurosurgery. 2002 Dec;51(6):1432-39; discussion 1439-40 | PubMed | De Santis A, Villani R, Sinisi M, Stocchetti N, Perucca E. Add-on phenytoin fails to prevent early seizures after surgery for supratentorial brain tumors: a randomized controlled study. Epilepsia. 2002 Feb;43(2):175-82 | PubMed |
De Santis A, Villani R, Sinisi M, Stocchetti N, Perucca E. Add-on phenytoin fails to prevent early seizures after surgery for supratentorial brain tumors: a randomized controlled study. Epilepsia. 2002 Feb;43(2):175-82 | PubMed | Zwerdling T, Dothage J. Meningiomas in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002 Mar-Apr;24(3):199-204 | PubMed |
Zwerdling T, Dothage J. Meningiomas in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2002 Mar-Apr;24(3):199-204 | PubMed | Wagner GL, Wilms EB, Van Donselaar CA, Vecht ChJ. Levetiracetam: preliminary experience in patients with primary brain tumours. Seizure. 2003 Dec;12(8):585-6 | PubMed |
Wagner GL, Wilms EB, Van Donselaar CA, Vecht ChJ. Levetiracetam: preliminary experience in patients with primary brain tumours. Seizure. 2003 Dec;12(8):585-6 | PubMed | Rothoerl RD, Bernreuther D, Woertgen C, Brawanski A. The value of routine electroencephalographic recordings in predicting postoperative seizures associated with meningioma surgery. Neurosurg Rev. 2003 May;26(2):108-12 | PubMed |
Rothoerl RD, Bernreuther D, Woertgen C, Brawanski A. The value of routine electroencephalographic recordings in predicting postoperative seizures associated with meningioma surgery. Neurosurg Rev. 2003 May;26(2):108-12 | PubMed | Tucha O, Smely C, Preier M, Becker G, Paul GM, Lange KW. Preoperative and postoperative cognitive functioning in patients with frontal meningiomas. JNeurosurg. 2003 Jan;98(1):21-31 | PubMed |
Tucha O, Smely C, Preier M, Becker G, Paul GM, Lange KW. Preoperative and postoperative cognitive functioning in patients with frontal meningiomas. JNeurosurg. 2003 Jan;98(1):21-31 | PubMed | Rushing EJ, Olsen C, Mena H, Rueda ME, Lee YS, Keating RF, et al. Central nervous system meningiomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathological analysis of 87 patients. J Neurosurg. 2005 Dec;103(6 Suppl):489-95 | PubMed |
Rushing EJ, Olsen C, Mena H, Rueda ME, Lee YS, Keating RF, et al. Central nervous system meningiomas in the first two decades of life: a clinicopathological analysis of 87 patients. J Neurosurg. 2005 Dec;103(6 Suppl):489-95 | PubMed | Maschio M, Albani F, Baruzzi A, Zarabla A, Dinapoli L, Pace A, et al. Levetiracetam therapy in patients with brain tumour and epilepsy. J Neurooncol. 2006 Oct;80(1):97-100 | PubMed |
Maschio M, Albani F, Baruzzi A, Zarabla A, Dinapoli L, Pace A, et al. Levetiracetam therapy in patients with brain tumour and epilepsy. J Neurooncol. 2006 Oct;80(1):97-100 | PubMed | Newton HB, Goldlust SA, Pearl D. Retrospective analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam in brain tumor patients. J Neurooncol. 2006 May;78(1):99-102 | PubMed |
Newton HB, Goldlust SA, Pearl D. Retrospective analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam in brain tumor patients. J Neurooncol. 2006 May;78(1):99-102 | PubMed | Otani N, Muroi C, Yano H, Khan N, Pangalu A, Yonekawa Y. Surgical management of tuberculum sellae meningioma: role of selective extradural anterior clinoidectomy. Br J Neurosurg. 2006 Jun;20(3):129-38 | PubMed |
Otani N, Muroi C, Yano H, Khan N, Pangalu A, Yonekawa Y. Surgical management of tuberculum sellae meningioma: role of selective extradural anterior clinoidectomy. Br J Neurosurg. 2006 Jun;20(3):129-38 | PubMed | Newton HB, Dalton J, Goldlust S, Pearl D. Retrospective analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam in patients with metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 2007 Sep;84(3):293-6 | PubMed |
Newton HB, Dalton J, Goldlust S, Pearl D. Retrospective analysis of the efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam in patients with metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 2007 Sep;84(3):293-6 | PubMed | Gelabert-González M, García-Allut A, Bandín-Diéguez J, Serramito-García R, Martínez-Rumbo R. Meningiomas of the lateral ventricles. A review of 10 cases. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2008 Oct;19(5):427-33 | PubMed |
Gelabert-González M, García-Allut A, Bandín-Diéguez J, Serramito-García R, Martínez-Rumbo R. Meningiomas of the lateral ventricles. A review of 10 cases. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2008 Oct;19(5):427-33 | PubMed | Behari S, Giri PJ, Shukla D, Jain VK, Banerji D. Surgical strategies for giant medial sphenoid wing meningiomas: a new scoring system for predicting extent of resection. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008 Sep;150(9):865-77; discussion 877 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Behari S, Giri PJ, Shukla D, Jain VK, Banerji D. Surgical strategies for giant medial sphenoid wing meningiomas: a new scoring system for predicting extent of resection. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008 Sep;150(9):865-77; discussion 877 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Gazzeri G. Giant olfactory groove meningioma: ophthalmological and cognitive outcome after bifrontal microsurgical approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008 Nov;150(11):1117-25; discussion 1126 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Gazzeri G. Giant olfactory groove meningioma: ophthalmological and cognitive outcome after bifrontal microsurgical approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008 Nov;150(11):1117-25; discussion 1126 | CrossRef | PubMed | Milligan TA, Hurwitz S, Bromfield EB. Efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam versus phenytoin after supratentorial neurosurgery. Neurology. 2008 Aug 26;71(9):665-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Milligan TA, Hurwitz S, Bromfield EB. Efficacy and tolerability of levetiracetam versus phenytoin after supratentorial neurosurgery. Neurology. 2008 Aug 26;71(9):665-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chang EF, Potts MB, Keles GE, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Barbaro NM, et al. Seizure characteristics and control following resection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg. 2008 Feb;108(2):227-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Chang EF, Potts MB, Keles GE, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Barbaro NM, et al. Seizure characteristics and control following resection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg. 2008 Feb;108(2):227-35 | CrossRef | PubMed | Menon G, Nair S, Sudhir J, Rao BR, Mathew A, Bahuleyan B. Childhood and adolescent meningiomas: a report of 38 cases and review of literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009 Mar;151(3):239-44; discussion 244 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Menon G, Nair S, Sudhir J, Rao BR, Mathew A, Bahuleyan B. Childhood and adolescent meningiomas: a report of 38 cases and review of literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009 Mar;151(3):239-44; discussion 244 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chaichana KL, Parker SL, Olivi A, Quiñones-Hinojosa A. Long-term seizure outcomes in adult patients undergoing primary resection of malignant brain astrocytomas. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2009 Aug;111(2):282-92 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Chaichana KL, Parker SL, Olivi A, Quiñones-Hinojosa A. Long-term seizure outcomes in adult patients undergoing primary resection of malignant brain astrocytomas. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2009 Aug;111(2):282-92 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dinapoli L, Maschio M, Jandolo B, Fabi A, Pace A, Sperati F, et al. Quality of life and seizure control in patients with brain tumor-related epilepsy treated with levetiracetam monotherapy: preliminary data of an open-label study. Neurol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(4):353-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dinapoli L, Maschio M, Jandolo B, Fabi A, Pace A, Sperati F, et al. Quality of life and seizure control in patients with brain tumor-related epilepsy treated with levetiracetam monotherapy: preliminary data of an open-label study. Neurol Sci. 2009 Aug;30(4):353-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Dijkstra M, van Nieuwenhuizen D, Stalpers LJ, Wumkes M, Waagemans M, Vandertop WP, et al. Late neurocognitive sequelae in patients with WHO grade I meningioma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009 Aug;80(8):910-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Dijkstra M, van Nieuwenhuizen D, Stalpers LJ, Wumkes M, Waagemans M, Vandertop WP, et al. Late neurocognitive sequelae in patients with WHO grade I meningioma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009 Aug;80(8):910-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Li X, Zhao J. Intracranial meningiomas of childhood and adolescence: report of 34 cases with follow-up. Childs Nerv Syst. 2009 Nov;25(11):1411-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Li X, Zhao J. Intracranial meningiomas of childhood and adolescence: report of 34 cases with follow-up. Childs Nerv Syst. 2009 Nov;25(11):1411-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Tsai MC, Huang TL. Generalized anxiety disorder in a patient prior to the diagnosis of left temporal lobe meningioma: a case report. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Aug 31;33(6):1082-3 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tsai MC, Huang TL. Generalized anxiety disorder in a patient prior to the diagnosis of left temporal lobe meningioma: a case report. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Aug 31;33(6):1082-3 | CrossRef | PubMed | Tellez-Zenteno JF, Sadanand V, Riesberry M, Robinson CA, Ogieglo L, Masiowski P, et al. Epilepsy surgery in the elderly: an unusual case of a 75-year-old man with recurrent status epilepticus. Epileptic Disord. 2009 Jun;11(2):144-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Tellez-Zenteno JF, Sadanand V, Riesberry M, Robinson CA, Ogieglo L, Masiowski P, et al. Epilepsy surgery in the elderly: an unusual case of a 75-year-old man with recurrent status epilepticus. Epileptic Disord. 2009 Jun;11(2):144-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | van Breemen MS, Rijsman RM, Taphoorn MJ, Walchenbach R, Zwinkels H, Vecht CJ. Efficacy of anti-epileptic drugs in patients with gliomas and seizures. J Neurol. 2009 Sep;256(9):1519-26 | CrossRef | PubMed |
van Breemen MS, Rijsman RM, Taphoorn MJ, Walchenbach R, Zwinkels H, Vecht CJ. Efficacy of anti-epileptic drugs in patients with gliomas and seizures. J Neurol. 2009 Sep;256(9):1519-26 | CrossRef | PubMed | Lim DA, Tarapore P, Chang E, Burt M, Chakalian L, Barbaro N, et al. Safety and feasibility of switching from phenytoin to levetiracetam monotherapy for glioma-related seizure control following craniotomy: a randomized phase II pilot study. J Neurooncol. 2009 Jul;93(3):349-54 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lim DA, Tarapore P, Chang E, Burt M, Chakalian L, Barbaro N, et al. Safety and feasibility of switching from phenytoin to levetiracetam monotherapy for glioma-related seizure control following craniotomy: a randomized phase II pilot study. J Neurooncol. 2009 Jul;93(3):349-54 | CrossRef | PubMed | Rosati A, Tomassini A, Pollo B, Ambrosi C, Schwarz A, Padovani A, et al. Epilepsy in cerebral glioma: timing of appearance and histological correlations. J Neurooncol. 2009 Jul;93(3):395-400 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Rosati A, Tomassini A, Pollo B, Ambrosi C, Schwarz A, Padovani A, et al. Epilepsy in cerebral glioma: timing of appearance and histological correlations. J Neurooncol. 2009 Jul;93(3):395-400 | CrossRef | PubMed | Merrell RT, Anderson SK, Meyer FB, Lachance DH. Seizures in patients with glioma treated with phenytoin and levetiracetam. J Neurosurg. 2010 Dec;113(6):1176-81 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Merrell RT, Anderson SK, Meyer FB, Lachance DH. Seizures in patients with glioma treated with phenytoin and levetiracetam. J Neurosurg. 2010 Dec;113(6):1176-81 | CrossRef | PubMed | Usery JB, Michael LM 2nd, Sills AK, Finch CK. A prospective evaluation and literature review of levetiracetam use in patients with brain tumors and seizures. J Neurooncol. 2010 Sep;99(2):251-60 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Usery JB, Michael LM 2nd, Sills AK, Finch CK. A prospective evaluation and literature review of levetiracetam use in patients with brain tumors and seizures. J Neurooncol. 2010 Sep;99(2):251-60 | CrossRef | PubMed | Maschio M, Dinapoli L, Gomellini S, Ferraresi V, Sperati F, Vidiri A, et al. Antiepileptics in brain metastases: safety, efficacy and impact on life expectancy. J Neurooncol. 2010 May;98(1):109-16 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Maschio M, Dinapoli L, Gomellini S, Ferraresi V, Sperati F, Vidiri A, et al. Antiepileptics in brain metastases: safety, efficacy and impact on life expectancy. J Neurooncol. 2010 May;98(1):109-16 | CrossRef | PubMed | Rosati A, Buttolo L, Stefini R, Todeschini A, Cenzato M, Padovani A. Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam in patients with glioma: a clinical prospective study. Arch Neurol. 2010 Mar;67(3):343-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Rosati A, Buttolo L, Stefini R, Todeschini A, Cenzato M, Padovani A. Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam in patients with glioma: a clinical prospective study. Arch Neurol. 2010 Mar;67(3):343-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Sughrue ME, Cage T, Shangari G, Parsa AT, McDermott MW. Clinical characteristics and surgical outcomes of patients presenting with meningiomas arising predominantly from the floor of the middle fossa. Neurosurgery. 2010 Jul;67(1):80-6; discussion 86 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sughrue ME, Cage T, Shangari G, Parsa AT, McDermott MW. Clinical characteristics and surgical outcomes of patients presenting with meningiomas arising predominantly from the floor of the middle fossa. Neurosurgery. 2010 Jul;67(1):80-6; discussion 86 | CrossRef | PubMed | Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, Chang EF, Shangari G, Kane AJ, McDermott MW, et al. Postoperative seizures following the resection of convexity meningiomas: are prophylactic anticonvulsants indicated? Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2011 Mar;114(3):705-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, Chang EF, Shangari G, Kane AJ, McDermott MW, et al. Postoperative seizures following the resection of convexity meningiomas: are prophylactic anticonvulsants indicated? Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2011 Mar;114(3):705-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zachenhofer I, Donat M, Oberndorfer S, Roessler K. Perioperative levetiracetam for prevention of seizures in supratentorial brain tumor surgery. J Neurooncol. 2011 Jan;101(1):101-67 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zachenhofer I, Donat M, Oberndorfer S, Roessler K. Perioperative levetiracetam for prevention of seizures in supratentorial brain tumor surgery. J Neurooncol. 2011 Jan;101(1):101-67 | CrossRef | PubMed | Waagemans ML, van Nieuwenhuizen D, Dijkstra M, Wumkes M, Dirven CM, Leenstra S, et al. Long-term impact of cognitive deficits and epilepsy on quality of life in patients with low-grade meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 2011 Jul;69(1):72-8; discussion 78-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Waagemans ML, van Nieuwenhuizen D, Dijkstra M, Wumkes M, Dirven CM, Leenstra S, et al. Long-term impact of cognitive deficits and epilepsy on quality of life in patients with low-grade meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 2011 Jul;69(1):72-8; discussion 78-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Maschio M, Dinapoli L, Sperati F, Pace A, Fabi A, Vidiri A, et al. Levetiracetam monotherapy in patients with brain tumor-related epilepsy: seizure control, safety, and quality of life. J Neurooncol. 2011 Aug;104(1):205-14 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Maschio M, Dinapoli L, Sperati F, Pace A, Fabi A, Vidiri A, et al. Levetiracetam monotherapy in patients with brain tumor-related epilepsy: seizure control, safety, and quality of life. J Neurooncol. 2011 Aug;104(1):205-14 | CrossRef | PubMed | You G, Sha ZY, Yan W, Zhang W, Wang YZ, Li SW, et al. Seizure characteristics and outcomes in 508 Chinese adult patients undergoing primary resection of low-grade gliomas: a clinicopathological study. Neuro Oncol. 2012 Feb;14(2):230-41. | CrossRef | PubMed |
You G, Sha ZY, Yan W, Zhang W, Wang YZ, Li SW, et al. Seizure characteristics and outcomes in 508 Chinese adult patients undergoing primary resection of low-grade gliomas: a clinicopathological study. Neuro Oncol. 2012 Feb;14(2):230-41. | CrossRef | PubMed | Musluman AM, Yilmaz A, R TC, Cavusoglu H, Kahyaoglu O, Aydin Y. Unilateral frontal interhemispheric transfalcial approaches for the removal of olfactory groove meninjiomas. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(2):174-82. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Musluman AM, Yilmaz A, R TC, Cavusoglu H, Kahyaoglu O, Aydin Y. Unilateral frontal interhemispheric transfalcial approaches for the removal of olfactory groove meninjiomas. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22(2):174-82. | CrossRef | PubMed | Bähr O, Hermisson M, Rona S, Rieger J, Nussbaum S, Körtvelyessy P, et al. Intravenous and oral levetiracetam in patients with a suspected primary brain tumor and symptomatic seizures undergoing neurosurgery: the HELLO trial. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012 Feb;154(2):229-35; discussion 23 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bähr O, Hermisson M, Rona S, Rieger J, Nussbaum S, Körtvelyessy P, et al. Intravenous and oral levetiracetam in patients with a suspected primary brain tumor and symptomatic seizures undergoing neurosurgery: the HELLO trial. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012 Feb;154(2):229-35; discussion 23 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kern K, Schebesch KM, Schlaier J, Hansen E, Feigl GC, Brawanski AT, et al. Levetiracetam compared to phenytoin for the prevention of postoperative seizures after craniotomy for intracranial tumours in patients without epilepsy. J Clin Neurosci. 2012 Jan;19(1):99-100 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kern K, Schebesch KM, Schlaier J, Hansen E, Feigl GC, Brawanski AT, et al. Levetiracetam compared to phenytoin for the prevention of postoperative seizures after craniotomy for intracranial tumours in patients without epilepsy. J Clin Neurosci. 2012 Jan;19(1):99-100 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chaichana KL, Pendleton C, Zaidi H, Olivi A, Weingart JD, Gallia GL, et al. Seizure control for patients undergoing meningioma surgery. World Neurosurg. 2013 Mar-Apr;79(3-4):515-24 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Chaichana KL, Pendleton C, Zaidi H, Olivi A, Weingart JD, Gallia GL, et al. Seizure control for patients undergoing meningioma surgery. World Neurosurg. 2013 Mar-Apr;79(3-4):515-24 | CrossRef | PubMed | Lee YJ, Kim T, Bae SH, Kim YH, Han JH, Yun CH, et al Levetiracetam compared with valproic acid for the prevention of postoperative seizures after supratentorial tumor surgery: a retrospective chart review. CNS Drugs. 2013 Sep;27(9):753-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lee YJ, Kim T, Bae SH, Kim YH, Han JH, Yun CH, et al Levetiracetam compared with valproic acid for the prevention of postoperative seizures after supratentorial tumor surgery: a retrospective chart review. CNS Drugs. 2013 Sep;27(9):753-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kerkhof M, Dielemans JC, van Breemen MS, Zwinkels H, Walchenbach R, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Effect of valproic acid on seizure control and on survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol. 2013 Jul;15(7):961-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kerkhof M, Dielemans JC, van Breemen MS, Zwinkels H, Walchenbach R, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Effect of valproic acid on seizure control and on survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol. 2013 Jul;15(7):961-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fang S, Zhan Y, Xie YF, Shi Q, Dan W. Predictive value ofelectrocorticography for postoperative epilepsy in patients with supratentorial meningioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2013 Jan;20(1):112-6 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Fang S, Zhan Y, Xie YF, Shi Q, Dan W. Predictive value ofelectrocorticography for postoperative epilepsy in patients with supratentorial meningioma. J Clin Neurosci. 2013 Jan;20(1):112-6 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wu AS, Trinh VT, Suki D, Graham S, Forman A, Weinberg JS, et al. A prospective randomized trial of perioperative seizure prophylaxis in patients with intraparenchymal brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 2013 Apr;118(4):873-83 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Wu AS, Trinh VT, Suki D, Graham S, Forman A, Weinberg JS, et al. A prospective randomized trial of perioperative seizure prophylaxis in patients with intraparenchymal brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 2013 Apr;118(4):873-83 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fuller KL, Wang YY, Cook MJ, Murphy MA, D'Souza WJ. Tolerability, safety, and side effects of levetiracetam versus phenytoin in intravenous and total prophylactic regimen among craniotomy patients: a prospective randomized study. Epilepsia. 2013 Jan;54(1):45-57 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Fuller KL, Wang YY, Cook MJ, Murphy MA, D'Souza WJ. Tolerability, safety, and side effects of levetiracetam versus phenytoin in intravenous and total prophylactic regimen among craniotomy patients: a prospective randomized study. Epilepsia. 2013 Jan;54(1):45-57 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gokhale S, Khan SA, Agrawal A, Friedman AH, McDonagh DL. Levetiracetam seizure prophylaxis in craniotomy patients at high risk for postoperative seizures. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013 Oct;8(4):169-73 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gokhale S, Khan SA, Agrawal A, Friedman AH, McDonagh DL. Levetiracetam seizure prophylaxis in craniotomy patients at high risk for postoperative seizures. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013 Oct;8(4):169-73 | CrossRef | PubMed | Ravindranath K, Vasudevan MC, Pande A, Symss N. Management of pediatric intracranial meningiomas: an analysis of 31 cases and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013 Apr;29(4):573-82 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ravindranath K, Vasudevan MC, Pande A, Symss N. Management of pediatric intracranial meningiomas: an analysis of 31 cases and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst. 2013 Apr;29(4):573-82 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zheng Z, Chen P, Fu W, Zhu J, Zhang H, Shi J, et al. Early and late postoperative seizure outcome in 97 patients with supratentorial meningioma and preoperative seizures: a retrospective study. J Neurooncol. 2013 Aug;114(1):101-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zheng Z, Chen P, Fu W, Zhu J, Zhang H, Shi J, et al. Early and late postoperative seizure outcome in 97 patients with supratentorial meningioma and preoperative seizures: a retrospective study. J Neurooncol. 2013 Aug;114(1):101-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Garbossa D, Panciani PP, Angeleri R, Battaglia L, Tartara F, Ajello M, et al. A retrospective two-center study of antiepileptic prophylaxis in patients with surgically treated high-grade gliomas. Neurol India. 2013 Mar-Apr;61(2):131-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Garbossa D, Panciani PP, Angeleri R, Battaglia L, Tartara F, Ajello M, et al. A retrospective two-center study of antiepileptic prophylaxis in patients with surgically treated high-grade gliomas. Neurol India. 2013 Mar-Apr;61(2):131-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Rossetti AO, Jeckelmann S, Novy J, Roth P, Weller M, Stupp R. Levetiracetam and pregabalin for antiepileptic monotherapy in patients with primary brain tumors. A phase II randomized study. Neuro Oncol. 2014 Apr;16(4):584-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Rossetti AO, Jeckelmann S, Novy J, Roth P, Weller M, Stupp R. Levetiracetam and pregabalin for antiepileptic monotherapy in patients with primary brain tumors. A phase II randomized study. Neuro Oncol. 2014 Apr;16(4):584-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Iuchi T, Kuwabara K, Matsumoto M, Kawasaki K, Hasegawa Y, Sakaida T. Levetiracetam versus phenytoin for seizure prophylaxis during and early after craniotomy for brain tumours: a phase II prospective, randomised study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015 Oct;86(10):1158-62 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Iuchi T, Kuwabara K, Matsumoto M, Kawasaki K, Hasegawa Y, Sakaida T. Levetiracetam versus phenytoin for seizure prophylaxis during and early after craniotomy for brain tumours: a phase II prospective, randomised study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015 Oct;86(10):1158-62 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gokhale S, McDonagh DL. Levetiracetam Is an Effective Postoperative Seizure Prophylaxis for Patients Undergoing Brain Tumor Surgery at High Risk for Seizures. Ann Neurol 2013: 74(S17): S80–S81 | CrossRef |
Gokhale S, McDonagh DL. Levetiracetam Is an Effective Postoperative Seizure Prophylaxis for Patients Undergoing Brain Tumor Surgery at High Risk for Seizures. Ann Neurol 2013: 74(S17): S80–S81 | CrossRef | Perucca P, Gilliam FG. Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol. 2012 Sep;11(9):792-802 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Perucca P, Gilliam FG. Adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Lancet Neurol. 2012 Sep;11(9):792-802 | CrossRef | PubMed | Tsimiklis C, Harding M. Brain Tumours and Prophylactic Antiepileptic Drug Prescribing Patterns by Neurosurgeons Practising in Australasia. Neurosci Med, 2015 Mar;6(1):13-19 | CrossRef |
Tsimiklis C, Harding M. Brain Tumours and Prophylactic Antiepileptic Drug Prescribing Patterns by Neurosurgeons Practising in Australasia. Neurosci Med, 2015 Mar;6(1):13-19 | CrossRef | Bower M, Waxman J. Central Nervous System Cancers. In: Lecture Notes: Oncology, 2nd Edition. Wiley; 2010. p. 96–97.
Bower M, Waxman J. Central Nervous System Cancers. In: Lecture Notes: Oncology, 2nd Edition. Wiley; 2010. p. 96–97.