 Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Para Descargar PDF debe Abrir sesión.
Dear editor:
In the context of the World Health Assembly in May 2013 and the roadmap designed by the advisory group Neglected Tropical Diseases of the World Health Organization [1], it should be noted the epidemiological importance that echinococcosis and cysticercosis acquire in Chile.
Echinococcosis or hydatidosis is a zoonotic disease often associated with poverty. It is caused by tapeworms of the genus Echinococcus, being the organism most frequently involved the Echinococcus granulosus especially in the hydatid cyst. The human being is an accidental intermediate host in the cycle of this organism, often manifesting liver and / or lung cystic tumors. Cysticercosis is also related to the socioeconomic status of the country and is caused by tapeworms of the genus Taenia, highlighting T. solium and T. saginata [2].
To appreciate the trend in mortality from this zoonosis in Chile, an analysis of mortality caused by echinococcosis and cysticercosis between 2009 and 2013 from the data in the Yearbooks of Vital Statistics of the National Institute of Statistics was performed (Table 1).
While these diseases are not major causes of mortality compared with others such as acute myocardial infarction or different types of cancers, they convey a significant socio-economic burden in years of potential life lost. A recent study noted that deaths from echinococcosis are preventable and therefore wrongful [3], an idea that is totally acceptable considering that in sectors such as Maule, Ñuble and Araucania farming is the economic livelihood of many families. Considering the results of our analysis, 139 people died during 2009 and 2013 from preventable and treatable infectious diseases.
It is necessary that the relevant ministerial authorities consider this matter with more emphasis so that in conjunction with the national medical community, achieve reductions in the incidence, prevalence, and mortality from these diseases, and many others that are preventable in the rural sectors of our country. Conducting environmental sanitation measures, having greater control of breeding cattle and for instance, adding cysticercosis to the list of notifiable diseases, an improvement in this topic could be achieved and thus comply with the internationally established agreements.
From the editor
The authors originally submitted this article in Spanish and English. The Journal has not copyedited this English version.
Declaration of conflicts of interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Financing
The authors declare not having received any funding whatsoever for writing this letter.

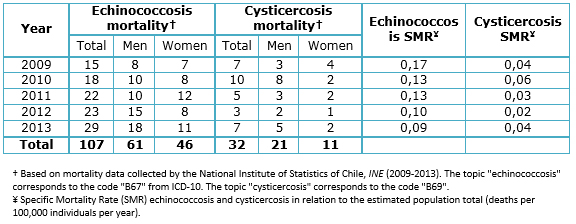 Table 1. Echinococcosis and cysticercosis mortality. Specific mortality rates by echinococcosis and cysticercosis in Chile, 2009-2013.
Table 1. Echinococcosis and cysticercosis mortality. Specific mortality rates by echinococcosis and cysticercosis in Chile, 2009-2013.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

 Autores:
Esteban Parra-Valencia[1], Andrea Urra-Canales[2]
Autores:
Esteban Parra-Valencia[1], Andrea Urra-Canales[2]

Citación: Parra-Valencia E, Urra-Canales A. Echinococcosis and cysticercosis: neglected diseases in Chile. Medwave 2016 Oct;16(9):e6566 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.09.6566
Fecha de publicación: 5/10/2016

Nos complace que usted tenga interés en comentar uno de nuestros artículos. Su comentario será publicado inmediatamente. No obstante, Medwave se reserva el derecho a eliminarlo posteriormente si la dirección editorial considera que su comentario es: ofensivo en algún sentido, irrelevante, trivial, contiene errores de lenguaje, contiene arengas políticas, obedece a fines comerciales, contiene datos de alguna persona en particular, o sugiere cambios en el manejo de pacientes que no hayan sido publicados previamente en alguna revista con revisión por pares.
Aún no hay comentarios en este artículo.
Para comentar debe iniciar sesión
 Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
Medwave publica las vistas HTML y descargas PDF por artículo, junto con otras métricas de redes sociales.
 Organización Mundial de la Salud. La OMS insta a los gobiernos a que aumenten la inversión para hacer frente a las enfermedades tropicales desatendidas. WHO; 2015 [on line]. | Link |
Organización Mundial de la Salud. La OMS insta a los gobiernos a que aumenten la inversión para hacer frente a las enfermedades tropicales desatendidas. WHO; 2015 [on line]. | Link | Murray ,Rosenthal K, Pfaller M. Microbiologia Médica. 6 ed. Ed. Elsevier; 2009.
Murray ,Rosenthal K, Pfaller M. Microbiologia Médica. 6 ed. Ed. Elsevier; 2009.