Resumen
Existe controversia sobre si los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada son efectivos para el tratamiento de la encefalopatía hepática. Utilizando la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, identificamos siete revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 32 estudios aleatorizados, de los cuales 30 responden la pregunta de este resumen. Extrajimos los resultados, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada podrían llevar a una mejoría sintomática en la encefalopatía hepática, pero probablemente tienen poco o nulo efecto sobre la mortalidad.
Problema
La encefalopatía hepática es una disfunción cerebral asociada a la presencia de un cortocircuito portosistémico, generalmente secundario a insuficiencia hepática. El mecanismo subyacente no es completamente claro, pero se acepta que la hiperamonemia juega un rol central, por lo que la mayoría de las intervenciones para esta condición intentan reducir el amonio.
Existiría también una alteración en la relación entre aminoácidos aromáticos y aminoácidos ramificados, que llevaría a un desbalance en la síntesis de neurotransmisores y a la acumulación de falsos neurotransmisores, lo cual contribuiría a la encefalopatía hepática.
De esta forma, la suplementación con aminoácidos ramificados podría producir una mejoría en la encefalopatía hepática. Sin embargo, no está claro si se trata de una intervención realmente efectiva.
Métodos
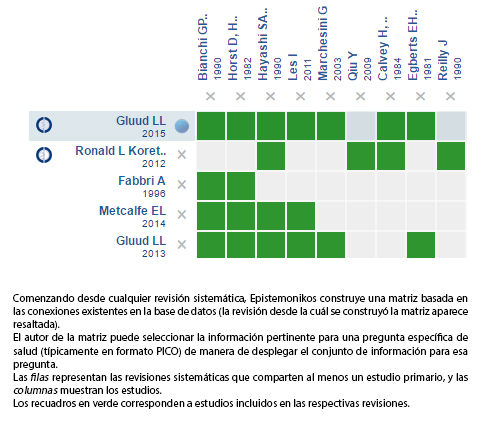
Utilizamos la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, para identificar revisiones sistemáticas y sus estudios primarios incluidos. Con esta información generamos un resumen estructurado, siguiendo un formato preestablecido, que incluye mensajes clave, un resumen del conjunto de evidencia (presentado como matriz de evidencia en Epistemonikos), metanálisis del total de los estudios, tablas de resumen de resultados con el método GRADE, y tabla de otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión.
|
Mensajes clave
|
Acerca del conjunto de evidencia para esta pregunta
|
Cuál es la evidencia. |
Encontramos siete revisiones sistemáticas [1],[2],[3],[4],[5],[6],[7] que incluyen 32 estudios controlados aleatorizados reportados en 61 referencias [8],[9],[10], |
|
Qué tipo de pacientes incluyeron los estudios |
En 27 estudios la totalidad de los pacientes presentaron cirrosis [8],[13],[16],[20],[21],[24],[26],[30],[31],[32], [36],[39],[44],[46],[48],[50],[54],[55],[58],[59],[60],[61] |
|
Qué tipo de intervenciones incluyeron los estudios |
En nueve estudios se utilizaron aminoácidos ramificados intravenosos [8],[13],[30],[31],[32],[36],[46],[50],[56], en 18 estudios aminoácidos ramificados orales [16], [20],[21],[24],[26],[39],[44],[48],[54],[55],[58],[59],[61], [62],[64],[65],[66],[67], un estudio utilizó aminoácidos orales o intravenosos según la condición del paciente [27] y un estudio no especificó la vía de administración [60]. Para un estudio no fue posible extraer este dato desde ninguna de las revisiones [12]. Un estudio incluyó caseína como cointervención [54]. Todos los estudios compararon contra placebo o tratamiento estándar. |
|
Qué tipo de desenlaces midieron |
Las distintas revisiones sistemáticas evaluaron los siguientes desenlaces principales:
Otros desenlaces evaluados: aparición de ascitis, resolución de ascitis, sangrado gastrointestinal, resolución de la encefalopatía, infecciones, nivel de bilirrubina, duración de la hospitalización, estadía en unidad de cuidados intensivos, complicaciones postoperatorias, complicaciones intraabdominales, neumonía postoperatoria, infección de herida operatoria, balance nitrogenado, efectos adversos, cambio en encefalopatía hepática, tiempo en ventilación mecánica. |
Resumen de los resultados
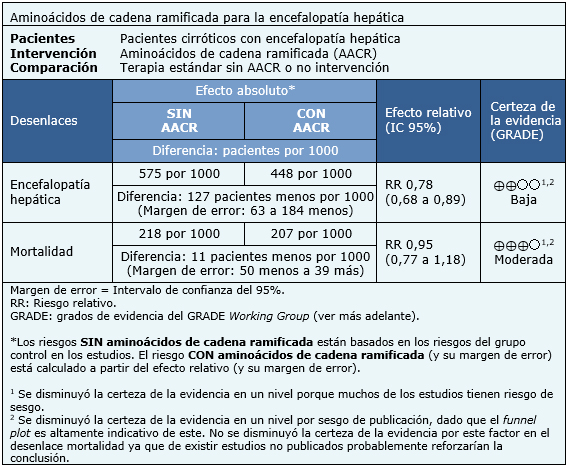
La información sobre el efecto de los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada en pacientes con encefalopatía hepática está basada en 23 estudios aleatorizados [8], [13],[16],[20],[21],[24],[26],[27],[30],[31],[32],[36],[39],[44],[46],[48],[50],[56],[58],[59],[60],[61],[62] que incluyen 1040 pacientes. El resto de los estudios no entregó datos sobre los desenlaces relevantes, o estos no pudieron ser incorporados al metanálisis. Todos los estudios midieron el desenlace encefalopatía hepática y 19 estudios (936 pacientes) midieron el desenlace mortalidad [8],[13],[16],[20],[21],[26],[27],[30],[32],[36],[39],[44],[46],[48],[50],[56],[58],[61],[62]. El resumen de los resultados es el siguiente:
- Los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada probablemente tienen poco o nulo efecto sobre la mortalidad en la encefalopatía hepática. La certeza de esta evidencia es moderada.
- Los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada podrían acelerar la recuperación en la encefalopatía hepática, aunque la certeza de esta evidencia es baja.

Otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión
|
A quién se aplica y a quién no se aplica esta evidencia |
|
| Sobre los desenlaces incluidos en este resumen |
|
| Balance riesgo/beneficio y certeza de la evidencia |
|
| Qué piensan los pacientes y sus tratantes |
|
| Consideraciones de recursos |
|
| Diferencias entre este resumen y otras fuentes |
|
| ¿Puede que cambie esta información en el futuro? |
Cómo realizamos este resumen
Mediante métodos automatizados y colaborativos recopilamos toda la evidencia relevante para la pregunta de interés y la presentamos en una matriz de evidencia.
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva: Aminoácidos ramificados para el tratamiento de la encefalopatía hepática
Notas
Si con posterioridad a la publicación de este resumen se publican nuevas revisiones sistemáticas sobre este tema, en la parte superior de la matriz se mostrará un aviso de “nueva evidencia”. Si bien el proyecto contempla la actualización periódica de estos resúmenes, los usuarios están invitados a comentar en Medwave o contactar a los autores mediante correo electrónico si creen que hay evidencia que motive una actualización más rápida.
Luego de crear una cuenta en Epistemonikos, al guardar las matrices recibirá notificaciones automáticas cada vez que exista nueva evidencia que potencialmente responda a esta pregunta. El detalle de los métodos para elaborar este resumen están descritos aquí: http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
La Fundación Epistemonikos es una organización que busca acercar la información a quienes toman decisiones en salud, mediante el uso de tecnologías. Su principal desarrollo es la base de datos Epistemonikos (www.epistemonikos.org).
Los resúmenes de evidencia siguen un riguroso proceso de revisión por pares interno.
Declaración de conflictos de intereses
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses con la materia de este artículo.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Existe controversia sobre si los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada son efectivos para el tratamiento de la encefalopatía hepática. Utilizando la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, identificamos siete revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 32 estudios aleatorizados, de los cuales 30 responden la pregunta de este resumen. Extrajimos los resultados, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada podrían llevar a una mejoría sintomática en la encefalopatía hepática, pero probablemente tienen poco o nulo efecto sobre la mortalidad.
 Authors:
Maximiliano Vergara[1,2], Victoria Castro-Gutiérrez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]
Authors:
Maximiliano Vergara[1,2], Victoria Castro-Gutiérrez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]
Affiliation:
[1] Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[2] Proyecto Epistemonikos, Santiago, Chile
[3] Programa de Salud Basada en Evidencia, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[4] Departamento de Medicina Interna, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[5] GRADE working group
[6] The Cochrane Collaboration
E-mail: radagabriel@epistemonikos.org
Author address:
[1] Facultad de Medicina Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Lira 63 Santiago Centro Chile

Citation: Vergara M, Castro-Gutiérrez V, Rada G. Do branched chain amino acids improve hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis?. Medwave 2016;16(Suppl5):e6795 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.6795
Publication date: 14/12/2016

Comments (0)
We are pleased to have your comment on one of our articles. Your comment will be published as soon as it is posted. However, Medwave reserves the right to remove it later if the editors consider your comment to be: offensive in some sense, irrelevant, trivial, contains grammatical mistakes, contains political harangues, appears to be advertising, contains data from a particular person or suggests the need for changes in practice in terms of diagnostic, preventive or therapeutic interventions, if that evidence has not previously been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
No comments on this article.
To comment please log in
 Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics.
Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics. There may be a 48-hour delay for most recent metrics to be posted.

- Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed |
- Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed |
- Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link |
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed |
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link |
- Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed |
- Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link |
- Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link |
- Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed |
- Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link |
- Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed |
- Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed |
- Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed |
- Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed |
- Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link |
- Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link |
- Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed |
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed |
- Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link |
- Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link |
- Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link |
- Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link |
- Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed |
- Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link |
- Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed |
- Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link |
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed |
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link |
- Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link |
- Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef |
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed |
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed |
- Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link |
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed |
- Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed |
- Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link |
- Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link |
- Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link |
- Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed |
- Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed |
- Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link |
- Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link |
- Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link |
- Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed |
- Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed |
- Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link |
- Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link |
- Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link |
- Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link |
- Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link |
- Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed |
- Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link |
- McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed |
- Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link |
- Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link |
- Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed |
- Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link |
- Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link |
- Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link |
- Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |
 Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed | Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed |
Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed | Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed | Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link | Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed |
Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed | Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link |
Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link | Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed |
Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed | Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link |
Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link | Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link |
Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link | Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed |
Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed | Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link |
Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link | Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed |
Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed | Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed |
Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed | Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed |
Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed | Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed |
Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed | Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link |
Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link | Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link |
Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link | Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed |
Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed | Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed |
Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed | Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link |
Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link | Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link |
Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link | Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link |
Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link | Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link |
Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link | Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed |
Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed | Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link |
Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link | Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed |
Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed | Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link |
Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link | Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed |
Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed | Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link |
Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link | Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link |
Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link | Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef |
Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef | Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed |
Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed | Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed |
Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed | Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link |
Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link | Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed |
Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed | Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed |
Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed | Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link |
Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link | Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link |
Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link | Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link |
Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link | Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed |
Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed | Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed |
Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed | Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link |
Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link | Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link |
Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link | Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link |
Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link | Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed |
Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed | Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed |
Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed | Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link |
Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link | Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link |
Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link | Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link |
Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link | Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link |
Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link | Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link |
Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link | Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed |
Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed | Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link |
Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link | McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed |
McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed | Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link |
Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link | Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link |
Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link | Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed |
Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed | Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed | Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link |
Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link | Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link |
Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link | Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link |
Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link | Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |
Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |Systematization of initiatives in sexual and reproductive health about good practices criteria in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in primary health care in Chile
Clinical, psychological, social, and family characterization of suicidal behavior in Chilean adolescents: a multiple correspondence analysis








