Abstract
There is controversy about the effectiveness of branched chain amino acids for treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Searching in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple databases, we identified seven systematic reviews including 32 randomized controlled trials, of which 30 address the question of this article. We extracted results, combined the evidence using meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings following the GRADE approach. We concluded branched chain amino acids might improve hepatic encephalopathy, but they probably lead to little or no effect on mortality.
Problem
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain dysfunction associated to the presence of portal-systemic shunting, generally as consequence of liver insufficiency. The pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy is not completely understood, but it is accepted hyperammonaemia plays a central role, so most interventions for this condition are directed to a reduction of ammonia.
It is postulated the plasma ratio of aromatic and branched chain amino acids is altered in this condition, leading to an imbalance in neurotransmitter synthesis and accumulation of false neurotransmitters, which would contribute to hepatic encephalopathy.
Therefore, supplementation with branched chain amino acids could improve hepatic encephalopathy. However, it is unclear whether this is an effective intervention.
Methods
We used Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening more than 30 databases, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. With this information, we generated a structured summary using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found seven systematic reviews [1],[2],[3],[4],[5], |
|
What types of patients were included |
In 27 trials, all of the participants had cirrhosis |
|
What types of interventions were included |
Nine trials administered intravenous branched chain amino acids [8],[13],[30],[31],[32],[36],[46],[50],[56], 18 trials used oral branched chain amino acids [16],[20],[21],[24], |
|
What types of outcomes |
The main outcomes addressed by the different systematic reviews were the following:
Other outcomes evaluated were: development of ascites, resolution of ascites, gastrointestinal bleeding, resolution of encephalopathy, infections, bilirubin level, length of hospital stay, stay in intensive care unit, postoperative complications, intra-abdominal complications, postoperative pneumonia, operative wound infection, nitrogen balance, re-hospitalisation post liver transplantation,infections, changes in grade of hepatic encephalopathy, side effects (vomiting, diarrhoea), and time on mechanical ventilation. |
Summary of findings
The information on the effects of branched chain amino acids in patients with hepatic encephalopathy is based on 23 randomized trials [8], [13],[16],[20],[21],[24],[26],[27],[30],[31],[32],[36],[39],[44],[46],[48],[50],[56],[58],[59],[60],[61],[62] including 1040 patients. The remaining trials did not provide data about relevant outcomes, or these were not suitable for meta-analysis. All of the trials measure the outcome hepatic encephalopathy and 19 trials (936 patients) measured mortality [8],[13],[16],[20],[21],[26],[27],[30],[32],[36],[39],[44],[46],[48],[50],[56],[58],[61],[62]. The summary of findings is the following:
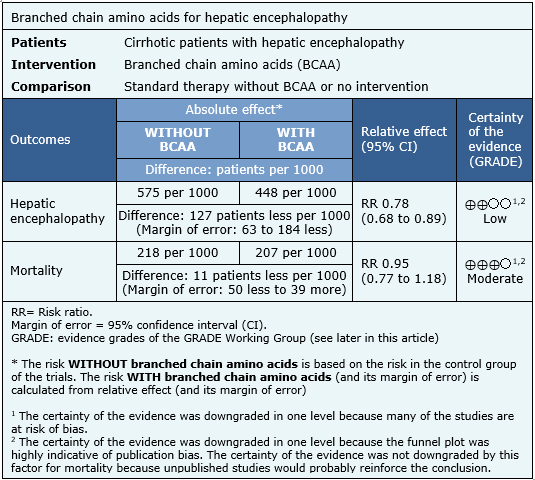
- Branched chain amino acids probably lead to little or no effect on mortality in hepatic encephalopathy. The certainty of the evidence is moderate.
- Branched chain amino acids might decrease hepatic encephalopathy, but the certainty of this evidence is low.

Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
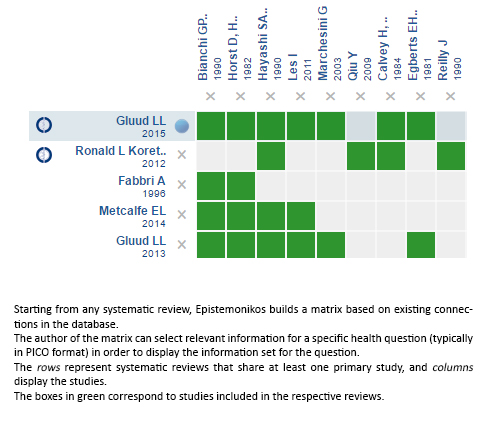
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Branched-chain amino acids for treatment of hepatic encephalopathy
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier. After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
The details about the methods used to produce these summaries are described here http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
These summaries follow a rigorous process of internal peer review.
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

Existe controversia sobre si los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada son efectivos para el tratamiento de la encefalopatía hepática. Utilizando la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, identificamos siete revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 32 estudios aleatorizados, de los cuales 30 responden la pregunta de este resumen. Extrajimos los resultados, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada podrían llevar a una mejoría sintomática en la encefalopatía hepática, pero probablemente tienen poco o nulo efecto sobre la mortalidad.
 Authors:
Maximiliano Vergara[1,2], Victoria Castro-Gutiérrez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]
Authors:
Maximiliano Vergara[1,2], Victoria Castro-Gutiérrez[1,2], Gabriel Rada[2,3,4,5,6]
Affiliation:
[1] Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[2] Proyecto Epistemonikos, Santiago, Chile
[3] Programa de Salud Basada en Evidencia, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[4] Departamento de Medicina Interna, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[5] GRADE working group
[6] The Cochrane Collaboration
E-mail: radagabriel@epistemonikos.org
Author address:
[1] Facultad de Medicina Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Lira 63 Santiago Centro Chile

Citation: Vergara M, Castro-Gutiérrez V, Rada G. Do branched chain amino acids improve hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis?. Medwave 2016;16(Suppl5):e6795 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.6795
Publication date: 14/12/2016

Comments (0)
We are pleased to have your comment on one of our articles. Your comment will be published as soon as it is posted. However, Medwave reserves the right to remove it later if the editors consider your comment to be: offensive in some sense, irrelevant, trivial, contains grammatical mistakes, contains political harangues, appears to be advertising, contains data from a particular person or suggests the need for changes in practice in terms of diagnostic, preventive or therapeutic interventions, if that evidence has not previously been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
No comments on this article.
To comment please log in
 Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics.
Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics. There may be a 48-hour delay for most recent metrics to be posted.

- Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed |
- Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link |
- Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed |
- Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link |
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed |
- Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link |
- Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed |
- Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link |
- Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link |
- Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed |
- Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link |
- Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed |
- Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed |
- Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed |
- Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed |
- Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link |
- Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link |
- Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed |
- Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed |
- Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link |
- Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link |
- Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link |
- Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link |
- Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed |
- Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link |
- Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed |
- Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link |
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed |
- Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link |
- Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link |
- Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef |
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed |
- Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed |
- Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link |
- Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed |
- Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed |
- Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link |
- Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link |
- Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link |
- Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed |
- Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed |
- Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link |
- Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link |
- Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link |
- Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed |
- Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed |
- Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link |
- Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link |
- Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link |
- Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link |
- Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link |
- Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed |
- Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link |
- McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed |
- Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link |
- Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link |
- Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed |
- Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link |
- Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link |
- Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link |
- Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |
 Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Koretz RL, Avenell A, Lipman TO. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008344 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Córdoba J, Marchesini G, Borre M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 17;(9):CD001939 | CrossRef | PubMed | Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Metcalfe EL, Avenell A, Fraser A. Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in adults with cirrhosis and porto-systemic encephalopathy: systematic review. Clin Nutr. 2014 Dec;33(6):958-65 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gluud LL, Dam G, Borre M, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. Oral branched-chain amino acids have a beneficial effect on manifestations of hepatic encephalopathy in a systematic review with meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J Nutr. 2013 Aug;143(8):1263-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Zhu GQ, Shi KQ, Huang S, Wang LR, Lin YQ, Huang GQ, et al. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: the comparative effectiveness and safety of interventions in patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Apr;41(7):624-35 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed |
Fabbri A, Magrini N, Bianchi G, Zoli M, Marchesini G. Overview of randomized clinical trials of oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1996 Mar-Apr;20(2):159-64 | PubMed | Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Langer G, Großmann K, Fleischer S, Berg A, Grothues D, Wienke A, et al. Nutritional interventions for liver-transplanted patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD007605 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. Italian Journal of Gastroenterology 1985;17:5–10. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Mancia D. Mental state course and biochemical findings in HE treated by BCAA-enriched mixtures. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and Nutrition in Liver Disease Freiburg 1984: Proceedings of the 41st Falk Symposium. Lancaster: MTP Press, 1985:281–5. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pedretti G, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Zeneroli ML, et al. Branched chain amino acid enriched solutions in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:323–33. | Link | Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed |
Fiaccadori F, Ghinelli F, Pelosi G, Sacchini D, Vaona GL, Zeneroli ML, et al. Selective amono acid solutions in hepatic encephalopathy treatment (a preliminary report). Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Apr-Jun;10(2):411-22 | PubMed | Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link |
Fiaccadori F, Elia GF, Lehndorff H, Merli M, Pedretti G, Riggio O, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) versus casein in patients with chronic recurrent portal systemic encephalopathy: a controlled trial. In: Soeters P, Wilson J, et al., editors. Advances in ammonia metabolism and hepatic encephalopathy. Oxford: Excerpta Medica; 1988. pp. 489e97. | Link | Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed |
Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. Disease-specific amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):288-95 | PubMed | Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link |
Cerra FB, Cheung NK, Fischer JE, Kaplowitz N, Schiff ER, Dienstag JL, et al. A multicenter trial of branched chain enriched amino acid infusion (F080) in hepatic encephalopathy (HE). Hepatology 1982;2:699. | Link | Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed |
Cerra FB, McMillen M, Angelico R, Cline B, Lyons J, Faulkenbach L, Paysinger, J. Cirrhosis, encephalopathy, and improved results with metabolic support. Surgery. 1983 Oct;94(4):612-9 | PubMed | Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link |
Plauth M, Egberts E-H, Hamster W, Török M, Müller P, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment with branchedchain amino acids (BCA) improves the portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) in ambulant patients Results of a double blind, placebo controlled crossover study. Klinische Wochenschrift 1992;69:126. | Link | Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link |
Plauth M, Egberts EH, Hamster W, Török M, Müller PH, Brand O, et al. Long-term treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy with branched-chain amino acids. A double-blind placebo-crossover study. Journal of Hepatology 1993;17:308–14. | Link | Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed |
Reilly J, Mehta R, Teperman L, Cemaj S, Tzakis A, Yanaga K, Ritter P, Rezak A, Makowka L. Nutritional support after liver transplantation: a randomized prospective study. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):386-91. | PubMed | Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link |
Reilly J, Yanaga K, Tzakis A, Teperman L, Mehta R, Rezak A, et al. A randomized prospective study of nutritional support after liver transplant (Abstract). Journal Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1989;13:8S. | Link | Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed |
Marchesini G, Bianchi G, Merli M, Amodio P, Panella C, Loguercio C, et al. Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: a double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1792-801 | PubMed | Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed |
Bianchi GP, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Abbiati R, Ferrario E, Fabbri A, et al. Oral BCAA supplementation in cirrhosis with chronic encephalopathy: effects on prolactin and estradiol levels. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Oct;39(5):443-6. | PubMed | Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed |
Charlton M. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease: Rasputin lives. Gastroenterology. 2003 Jun;124(7):1980-2 | PubMed | Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed |
Marchesini G, Dioguardi FS, Bianchi GP, Zoli M, Bellati G, Roffi L, et al. Long-term oral branched-chain amino acid treatment in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. A randomized double-blind casein-controlled trial. The Italian Multicenter Study Group. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):92-101 | PubMed | Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link |
Hayashi S, Aoyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Oka H, Oda T. A randomized controlled trial of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)-enriched elemental diet (ED-H) for hepatic encephalopathy. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hematology 1991;6:191. | Link | Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link |
Hayashi, S. A randomized controlled study of an elementary diet (ED-H) in cirrhotic with hepatic encephalopathy. JJPEN 1990 | Link | Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Les I, Doval E, García-Martínez R, Planas M, Cárdenas G, Gómez P, et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Jun;106(6):1081-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed |
Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation, with and without branched chain amino acid enrichment, in treatment of acute alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1985;1(2):141-51 | PubMed | Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed |
Calvey H, Davis M, Williams R. Prospective study of nasogastric feeding via East Grinstead or Viomedex tubes compared with oral dietary supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Nutr. 1984 Jul;3(2):63-6 | PubMed | Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link |
Williams R, Calvey H, Davis M. Controlled trial of nutritional supplementation in acute alcoholic hepatitis. In: Holm E, Kasper H editor(s). Metabolism and nutrition in liver disease. Lancaster, England: MTP Press, Ltd., 1985: 361–8. | Link | Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link |
Hwang SJ, Chan CY, Wu JC, Lee SD, Huan YS, Tsai YT, et al. A randomized controlled trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of branched chain amino acid-enriched amino acid solution in the treatment of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 1988;5: 185–92. | Link | Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link |
Hasse J, Crippin J, Blue L, Huang K, DiCecco S, Francisco-Ziller N, et al. Does nutrition supplementation benefit liver transplant candidates with a history of encephalopathy? (Abstract). J Parenter Enter Nutr 1997;21(1). S16(91). | Link | Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link |
Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Stortoni M, Rossi-Fanelli F, et al. Long term dietary supplement with branched chain amino acids: a new approach in the prevention of hepatic encephalopathy: results of a controlled study in cirrhotics with porto-caval anastomosis. In: Associazione Italiana per Lo Studio del Fegato. Congress, editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:183–92. | Link | Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed |
Rossi Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Capocaccia L, Cascino A, Ceci F, Muscaritoli M, et al. Use of branched chain amino acids for treating hepatic encephalopathy: clinical experiences. Gut. 1986 Nov;27 Suppl 1:111-5 | PubMed | Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link |
Rossi-Fanelli F, Cangiano C, Cascino A, Merli M, Riggio O, Stortoni M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:335–44 | Link | Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed |
Rossi-Fanelli F, Riggio O, Cangiano C, Cascino A, De Conciliis D, Merli M, et al. Branched-chain amino acids vs lactulose in the treatment of hepatic coma: a controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Oct;27(10):929-35 | PubMed | Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link |
Gluud C, Dejgaard A, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Preliminary treatment results with balanced amino acid infusion to patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1983;18:19. | Link | Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed |
Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Køhler O, Melgaard B, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid versus glucose treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. A double-blind study of 65 patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1990 May;10(3):291-6 | PubMed | Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link |
Vilstrup H, Gluud C, Hardt F, Kristensen M, Melgaard B, Køhler O, et al. Branched chain enriched amino acid nutrition does not change the outcome of hepatic coma in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Hepatology 1985;1:S347. | Link | Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link |
Egberts EH, Hamster W, Schomeerus H, Jürgens P. Effect of branched chain amino acids on latent porto-systemic-encephalopathy (PSE). JPEN. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1981;5:5. | Link | Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef |
Egberts EH, Schomeerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Effective treatment of latens porto-systemic encephalopathy with oral branched chain amino acids. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984: 351–7. | CrossRef | Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed |
Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. Branched chain amino acids in the treatment of latent portosystemic encephalopathy. A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Gastroenterology. 1985 Apr;88(4):887-95. | PubMed | Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed |
Egberts EH, Schomerus H, Hamster W, Jürgens P. [Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of latent porto-systemic encephalopathy. A placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study]. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1986 Mar;25(1):9-28. German. | PubMed | Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link |
Hamster W, Egberts EH, Hamster H. Treatment with branched-chain amino acids and effect on psycho-physical capacity functions in latent porto-systemic encephalopathy [Behandlung mit verzweigtkettigen aminosäuren und ihre auswirkung auf psychophysische leistungsfunktionen bei latenter portosystemischer enzephalopathie].Arzneimittelforschung 1982;32:901–2. | Link | Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed |
Muto Y, Sato S, Watanabe A, Moriwaki H, Suzuki K, Kato A, et al. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Jul;3(7):705-13 | PubMed | Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed |
Sato S, Watanabe A, Muto Y, Suzuki K, Kato A, Moriwaki H, et al. Clinical comparison of branched-chain amino acid (l-Leucine, l-Isoleucine, l-Valine) granules and oral nutrition for hepatic insufficiency in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis (LIV-EN study). Hepatol Res. 2005 Apr;31(4):232-40 | PubMed | Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link |
Strauss E, Cartapatti Da Silva E, Lacet CM, Capacci MLL, Bernardini AP. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized clinical trial comparing a branched chain enriched amino acid solution to oral neomycin. Nutritional Support Services 1986;6:18–21. | Link | Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link |
Strauss E, Santos WR, Da Silva EC, Lacet CM, Capacci LL, Bernardini AP. A randomized controlled clinical trial for the evaluation of the efficacy of an enriched branched-chain amino-acid solution compared to neomycin in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 1983;3:862. | Link | Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link |
Horst D, Grace N, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. A double-blind randomized comparison of dietary protein and an oral branched chain amino acid (BCAA) solution in cirrhotic patients with chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE) [IASL abstract]. Hepatology 1982;2: 184 | Link | Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed |
Horst D, Grace ND, Conn HO, Schiff E, Schenker S, Viteri A, et al. Comparison of dietary protein with an oral, branched chain-enriched amino acid supplement in chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):279-87 | PubMed | Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed |
Michel H, Bories P, Aubin JP, Pomier-Layrargues G, Bauret P, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics with a branched-chain amino acids enriched versus a conventional amino acids mixture. A controlled study of 70 patients. Liver. 1985 Oct;5(5):282-9 | PubMed | Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link |
Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Aubin JP, Bories P, Mirouze D, Bellet-Herman H. Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy by infusion of a modified amino acid solution: results of a controlled study in 47 cirrhotic patients. In: Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:301–10. | Link | Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link |
Michel H, Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet-Hermann H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy (controlled study, 30 patients). Gastroenterology 1980;79:1038. | Link | Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link |
Pomier-Layrargues G, Duhamel O, Lacombe B, Cuilleret G, Bellet H, Michel H. Intravenous infusion of ordinary and modified amino-acid solutions in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver 1981;1:140 | Link | Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed |
Christie ML, Sack DM, Pomposelli J, Horst D. Enriched branched-chain amino acid formula versus a casein-based supplement in the treatment of cirrhosis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1985 Nov-Dec;9(6):671-8 | PubMed | Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed |
Sieg A, Walker S, Czygan P, Gärtner U, Lanzinger-Rossnagel G, Stiehl A, et al. Branched-chain amino acid-enriched elemental diet in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. A double blind crossover trial. Z Gastroenterol. 1983 Nov;21(11):644-50 | PubMed | Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link |
Ceriati F, Cavicchioni C, Marino IR, De Luca G, Puglionisi A. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients after derivative surgery [Trattamento dell’encefalopatia epatica nei pazienti cirrotici sottoposti ad intervento chirurgico derivativo]. Acta Medica Romana 1985;23(1):69–76. | Link | Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link |
Puglionisi A, Ceriati F, Marino IR, Cavicchioni C, De Luca G, Roncone A, et al. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after porta-caval anastomosis using branched chain amino acid mixtures. In: Capacaccio L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F editor(s). Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure. New York: Plenum Press, 1984:345–50 | Link | Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ichikawa T, Naota T, Miyaaki H, Miuma S, Isomoto H, Takeshima F, Nakao K. Effect of an oral branched chain amino acid-enriched snack in cirrhotic patients with sleep disturbance. Hepatol Res. 2010 Oct;40(10):971-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link |
Simko V. Long-term tolerance of a special amino acid oral formula in patients with advanced liver disease. Nutrition Reports International 1983;27(4):765–73 | Link | Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link |
Sievert W, Gibson PR, Colman JC, Kronborg I, Crawford DH, Keogh J, et al. Energy and amino acid supplements in a malnourished patients with cirrhosis: a randomised controlled trial. 50th Annual Meeting American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (Published in: . Hepatology. 1999;30(Supp 4):434A. 1999 | Link | Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link |
Humbert P, Pintó A, Johnston S, Fábrega C, Planas R, Boix J, et al. Effect of oral administration of branched-chain amino acids for the treatment of nutrition disturbances and for the prophylaxis of encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients [Efecto de la administración oral de aminoácidos ramificados en el tratamiento de los trastornos nutricionales y en la prevención de la encefalopatía de pacientes cirróticos.]. Gastroenterología y Hepatología 1989;12(1): 9–13. | Link | Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed |
Nakaya Y, Okita K, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H, Kato A, Miwa Y, et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition. 2007 Feb;23(2):113-20 | PubMed | Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link |
Nakaya Y, Okita K, Kato A, Miwa Y, Suzuki K, Moriwaki H. Randomized trial of branched chain amino acid rich supplement against carbohydrate-rich snacks as a late evening snack in patients with liver cirrhosis (Abstract). Hepatology 2005;42 Suppl 1(4):699A–700A. | Link | McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed |
McGhee A, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Bleier JC, Vogel R, Kassouny M, et al. Comparison of the effects of Hepatic-Aid and a Casein modular diet on encephalopathy, plasma amino acids, and nitrogen balance in cirrhotic patients. Ann Surg. 1983 Mar;197(3):288-93 | PubMed | Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link |
Panella C, Guglielmi F, Laddaga L, Reale L, Polimeno L, DiLeo A. Oral branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of low portosystemic encephalopathy: a long term multicentric trial. Liver and Hormones 1992 Volume 43, Pages 97-106 | Link | Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link |
Guarnieri GF, Toigo G, Situlin R, Pozzato G, Faccini L. Muscle biopsy studies on malnutrition in patients with liver cirrhosis: Preliminary results of long-term treatment with a branched-chain amino acid enriched diet. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Chronic Liver Failure, Capocaccia L, Fischer JE, Rossi-Fanelli F (eds). Plenum Press, New York 1984 | Link | Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed |
Eriksson LS, Persson A, Wahren J. Branched-chain amino acids in the treatment of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1982 Oct;23(10):801-6 | PubMed | Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Qiu Y, Zhu X, Wang W, Xu Q, Ding Y. Nutrition support with glutamine dipeptide in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009 Dec;41(10):4232-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J, Cordoba J, Ferenci P, Mullen KD, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014 Aug;60(2):715-35 | CrossRef | PubMed | Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link |
Won Young Tak. Branched-chain Amino Acid (BCAA) on Progression of Advanced Liver Disease (BRAVE) | Link | Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link |
Keiding S. Effects of Branched-Chain Amino Acids on Muscle Ammonia Metabolism in Patients With Cirrhosis and Healthy Subjects | Link | Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link |
Torre A. Branched chain aminoacid supplementation in patients with liver cirrhosis | CrossRef | Link | Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |
Córdoba J. Effects of proteins in patients with cirrhosis and prior hepatic encephalopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00955500 | Link |Systematization of initiatives in sexual and reproductive health about good practices criteria in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in primary health care in Chile
Clinical, psychological, social, and family characterization of suicidal behavior in Chilean adolescents: a multiple correspondence analysis








