Abstract
UPDATE
This Living FRISBEE (Living FRIendly Summary of the Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) is an update of the summary published in January 2016.
INTRODUCTION
Appendicitis is a typical cause of acute abdominal pain and the most frequent cause of emergency abdominal surgery. In the last two decades, increasing evidence has been published about the use of antibiotics as an exclusive treatment for acute appendicitis.
METHODS
To answer this question, we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained through searches from multiple sources of information, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted the data from the identified reviews, reanalyzed the data from the primary studies, performed a meta-analysis and prepared a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
We identified 23 systematic reviews including 28 primary studies, of which eight were randomized trials. We concluded the exclusive use of antibiotics for the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis could be less effective than appendectomy, but it might be associated with a lower rate of complications.
About this update
This Living FRISBEE (Living Friendly Summary of the Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) is an update of the summary published in January 2016 (doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.6375), based on 14 new systematic reviews including two new randomized trials not included in previous reviews. In addition, we added a trial that had not been previously incorporated into the analysis, and a trial previously incorporated was removed because it was retracted due to plagiarism. Finally, the outcome ‘major complications’ was replaced by ‘complications’, since most identified systematic reviews analyzed this variable as the outcome of choice. The incorporation of this new evidence leads to a change in the direction of the effect on complications, and therefore to changes in the key messages and considerations for decision-making.
Problem
Acute appendicitis is a common cause of acute abdominal pain and the most frequent cause of emergency abdominal surgery, with an estimated life incidence between 7 and 14% [1],[2]. Since the 1890s, when McBurney described early appendectomy as the therapy of choice for acute appendicitis [3],[4], surgery has become the mainstay for the treatment of this condition, drastically decreasing its mortality rate [5].
The treatment of acute appendicitis with antibiotics as an initial strategy was historically reserved for patients with several days of evolution of the inflammatory process, who presented a plastron or appendicular abscess, to avoid major surgery [2]. In 1953, Harrison reported 42 out of 47 cases of acute appendicitis successfully treated with antibiotics only. Coldrey published in 1959 an article with 471 cases of acute appendicitis treated conservatively, with only one death, nine patients requiring abscess drainage and only 48 patients requiring appendectomy [6]. In the last two decades, the production of research on the use of antibiotics as an exclusive treatment for acute appendicitis has steadily increased, so it is important to synthesize the existing evidence.
Methods
To answer the question, we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found 23 systematic reviews [5],[6],[7],[8],[9],[10],[11],[12], This table and the summary in general are based on seven randomized trials [28],[29],[30],[31],[32],[33],[38], since the observational studies did not increase the certainty of the existing evidence, nor did they provide relevant additional information. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
All trials included patients with suspected acute appendicitis. Six trials [28],[29],[30],[31],[32],[33] excluded children and one trial also excluded women [32]. One trial only included pediatric patients between 5 and 15 years old [38]. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
Six trials used intravenous antibiotics as the initial treatment, of which one did so for 24 hours [29], three for 48 hours [28],[32],[38] and two for 72 hours [31],[33]. Of these, two trials used cefotaxime associated with tinidazole [28,32], one used cefotaxime associated with metronidazole [29], one used ampicillin associated with gentamicin and metronidazole [31], one used meropenem associated with metronidazole [38] and one used ertapenem [33]. The remaining trial [30] used intravenous amoxicillin with clavulanic acid only if the patient presented nausea or vomiting and for a time that was not specified. All trials continued the treatment using oral antibiotics. One trial completed eight days [30] and six completed ten days [28],[29],[31],[32],[33],[38]. During the oral phase, two trials used the combination of ofloxacin with tinidazole [28],[32], two used ciprofloxacin with metronidazole [29],[38], one used levofloxacin with metronidazole [33], one used amoxicillin with clavulanic acid [30] and one trial did not specify the antibiotic used orally [31]. All trials compared antibiotic treatment against surgery. Two trials performed open appendectomy [28],[33], one performed only laparoscopic appendectomy [38] and the remaining four trials performed the procedure open or laparoscopic according to surgeon's preference [29],[30],[31],[32]. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The trials measured multiple outcomes, which were pooled by the systematic reviews as follows:
All trials followed their patients up to 12 months. |
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
Summary of findings
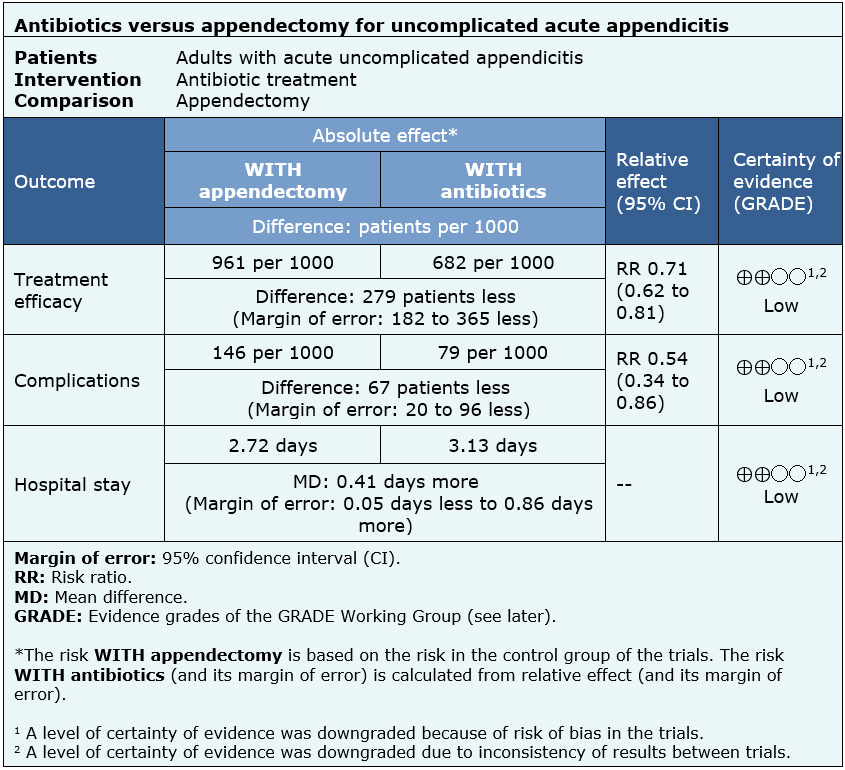
The information on the effects of antibiotics or surgical treatment for uncomplicated acute appendicitis is based on seven randomized trials [28],[29],[30],[31],[32],[33],[38] that included 1770 participants, of whom 858 were initially treated with antibiotics and 912 with appendectomy. All trials reported treatment efficacy, complications and hospital stay.
The summary of findings is the following:
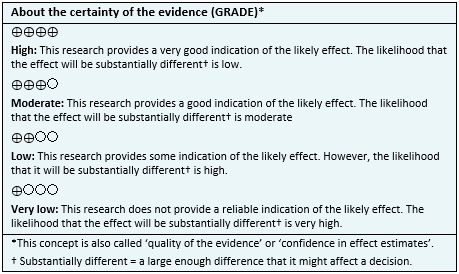
- The use of antibiotics for the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis might be less effective than appendectomy, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
- The use of antibiotics for the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis might be associated with fewer complications than appendectomy, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
- The use of antibiotics for the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis might be associated with a longer hospital stay than appendectomy, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
| Following the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF) |
Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
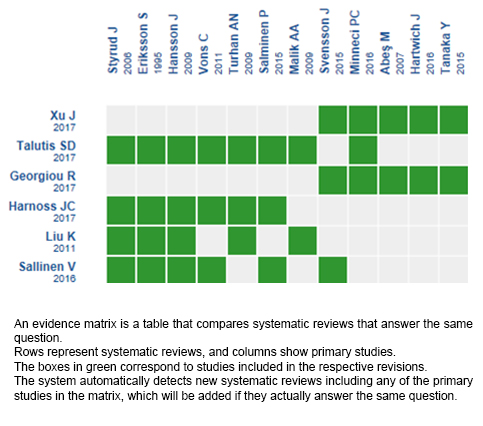
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Antibiotics versus appendectomy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis.
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

ACTUALIZACIÓN
Este resumen Epistemonikos (Living FRISBEE: Living FRIendly Summary of the Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) es una actualización del resumen publicado en enero de 2016.
INTRODUCCIÓN
La apendicitis es una causa típica de dolor abdominal agudo y la causa más frecuente de cirugía abdominal de urgencia. En las últimas dos décadas se ha publicado creciente evidencia sobre el uso de antibióticos como tratamiento exclusivo de la apendicitis aguda.
MÉTODOS
Para responder esta pregunta utilizamos Epistemonikos, la mayor base de datos de revisiones sistemáticas en salud, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples fuentes de información, incluyendo MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, entre otras. Extrajimos los datos desde las revisiones identificadas, reanalizamos los datos de los estudios primarios, realizamos un metanálisis y preparamos una tabla de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE.
RESULTADOS Y CONCLUSIONES
Identificamos 23 revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyeron 28 estudios primarios, de los cuales ocho corresponden a ensayos aleatorizados. Concluimos que el uso exclusivo de antibióticos para el tratamiento de la apendicitis aguda no complicada podría ser menos efectivo que la apendicectomía y asociarse a una mayor estadía hospitalaria, pero por otro lado podría asociarse a una menor tasa de complicaciones.
 Authors:
Rubén Allende[1,2], Rodrigo Muñoz[2,3]
Authors:
Rubén Allende[1,2], Rodrigo Muñoz[2,3]
Affiliation:
[1] Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[2] Proyecto Epistemonikos, Santiago, Chile
[3] Departamento de Cirugía Digestiva, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
E-mail: rmunozc@med.puc.cl
Author address:
[1] Centro Evidencia UC Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Diagonal Paraguay 476 Santiago Chile

Citation: Allende R, Muñoz R. Are antibiotics a safe and effective treatment for acute uncomplicated appendicitis?- First update. Medwave 2018 Jul-Ago;18(4):e7229 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2018.04.7229
Submission date: 26/12/2017
Acceptance date: 23/4/2018
Publication date: 11/7/2018
Origin: This article is a product of the Evidence Synthesis Project of Epistemonikos Fundation, in collaboration with Medwave for its publication.
Type of review: Non-blinded peer review by members of the methodological team of Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis Project.

Comments (0)
We are pleased to have your comment on one of our articles. Your comment will be published as soon as it is posted. However, Medwave reserves the right to remove it later if the editors consider your comment to be: offensive in some sense, irrelevant, trivial, contains grammatical mistakes, contains political harangues, appears to be advertising, contains data from a particular person or suggests the need for changes in practice in terms of diagnostic, preventive or therapeutic interventions, if that evidence has not previously been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
No comments on this article.
To comment please log in
 Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics.
Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics. There may be a 48-hour delay for most recent metrics to be posted.

- D’Souza N, Nugent K. Appendicitis. BMJ Clin Evid. 2014 Dec;2014.
- Flum DR. Clinical practice. Acute appendicitis--appendectomy or the “antibiotics first” strategy. N Engl J Med. 2015 May;372(20:1937–43.
- McBurney C. II. The Indications for Early Laparotomy in Appendicitis. Ann Surg. 1891 Apr;13(4):233–54.
- McBurney C. IV. The Incision Made in the Abdominal Wall in Cases of Appendicitis, with a Description of a New Method of Operating. Ann Surg. 1894 Jul;20(1):38–43.
- Wilms IMHA, de Hoog DENM, de Visser DC, Janzing HMJ. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment for acute appendicitis. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov;(11):CD008359.
- Ansaloni L, Catena F, Coccolini F, Ercolani G, Gazzotti F, Pasqualini E, et al. Surgery versus conservative antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Surg. 2011;28(3):210–21.
- Fitzmaurice GJ, McWilliams B, Hurreiz H, Epanomeritakis E. Antibiotics versus appendectomy in the management of acute appendicitis: a review of the current evidence. Can J Surg. 2011 Oct;54(5):307–14.
- Harnoss JC, Zelienka I, Probst P, Grummich K, Muller-Lantzsch C, Harnoss JM, et al. Antibiotics Versus Surgical Therapy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials (PROSPERO 2015: CRD42015016882). Ann Surg. 2017 May;265(5):889–900.
- Liu K, Fogg L. Use of antibiotics alone for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgery. 2011 Oct;150(4):673–83.
- Liu Z-H, Li C, Zhang X-W, Kang L, Wang J-P. Meta-analysis of the therapeutic effects of antibiotic versus appendicectomy for the treatment of acute appendicitis. Exp Ther Med. 2014 May;7(5):1181–6.
- Mason RJ, Moazzez A, Sohn H, Katkhouda N. Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing antibiotic therapy with appendectomy for acute uncomplicated (no abscess or phlegmon) appendicitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2012 Apr;13(2):74–84.
- Podda M, Cillara N, Di Saverio S, Lai A, Feroci F, Luridiana G, et al. Antibiotics-first strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults is associated with increased rates of peritonitis at surgery. A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing appendectomy and non-operative managem. Surgeon. 2017 Oct;15(5):303–14.
- Poon SHT, Lee JWY, Ng KM, Chiu GWY, Wong BYK, Foo CC, et al. The current management of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: should there be a change in paradigm? A systematic review of the literatures and analysis of treatment performance. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:46.
- Rollins KE, Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotics Versus Appendicectomy for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. World J Surg. 2016 Oct;40(10):2305–18.
- Sakran J V, Mylonas KS, Gryparis A, Stawicki SP, Burns CJ, Matar MM, et al. Operation versus antibiotics--The “appendicitis conundrum” continues: A meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jun;82(6):1129–37.
- Sallinen V, Akl EA, You JJ, Agarwal A, Shoucair S, Vandvik PO, et al. Meta-analysis of antibiotics versus appendicectomy for non-perforated acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2016 May;103(6):656–67.
- Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2012 Apr;344:e2156.
- Varadhan KK, Humes DJ, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotic therapy versus appendectomy for acute appendicitis: a meta-analysis. World J Surg. 2010 Feb;34(2):199–209.
- Huang L, Yin Y, Yang L, Wang C, Li Y, Zhou Z. Comparison of Antibiotic Therapy and Appendectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Children: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May;171(5):426–34.
- Talutis SD, Drake FT. Comparative effectiveness of surgery versus antibiotics in acute appendicitis: a systematic review. J Comp Eff Res. 2017 Jul;6(5):471–82.
- Kessler U, Mosbahi S, Walker B, Hau EM, Cotton M, Peiry B, et al. Conservative treatment versus surgery for uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. 2017 Dec;102(12):1118–24.
- Ehlers AP, Talan DA, Moran GJ, Flum DR, Davidson GH. Evidence for an Antibiotics-First Strategy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Gap Analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Mar;222(3):309–14.
- Kirby A, Hobson RP, Burke D, Cleveland V, Ford G, West RM. Appendicectomy for suspected uncomplicated appendicitis is associated with fewer complications than conservative antibiotic management: a meta-analysis of post-intervention complications. J Infect. 2015 Feb;70(2):105–10.
- Horst JA, Trehan I, Warner BW, Cohn BG. Can Children With Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis Be Treated With Antibiotics Instead of an Appendectomy? Ann Emerg Med. 2015 Aug;66(2):119–22.
- Xu J, Adams S, Liu YC, Karpelowsky J. Nonoperative management in children with early acute appendicitis: A systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Sep;52(9):1409–15.
- Findlay JM, Kafsi J El, Hammer C, Gilmour J, Gillies RS, Maynard ND. Nonoperative Management of Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Dec;223(6):814–824.e2.
- Georgiou R, Eaton S, Stanton MP, Pierro A, Hall NJ. Efficacy and Safety of Nonoperative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2017 Mar;139(3).
- Eriksson S, Granstrom L. Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 1995 Feb;82(2):166–9.
- Hansson J, Korner U, Khorram-Manesh A, Solberg A, Lundholm K. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy versus appendicectomy as primary treatment of acute appendicitis in unselected patients. Br J Surg. 2009 May;96(5):473–81.
- Vons C, Barry C, Maitre S, Pautrat K, Leconte M, Costaglioli B, et al. Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2011 May;377(9777):1573–9.
- Turhan AN, Kapan S, Kutukcu E, Yigitbas H, Hatipoglu S, Aygun E. Comparison of operative and non operative management of acute appendicitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2009 Sep;15(5):459–62.
- Styrud J, Eriksson S, Nilsson I, Ahlberg G, Haapaniemi S, Neovius G, et al. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis. a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J Surg. 2006 Jun;30(6):1033–7.
- Salminen P, Paajanen H, Rautio T, Nordstrom P, Aarnio M, Rantanen T, et al. Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: The APPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015 Jun;313(23):2340–8.
- Liu K, Ahanchi S, Pisaneschi M, Lin I, Walter R. Can acute appendicitis be treated by antibiotics alone? Am Surg. 2007 Nov;73(11):1161–5.
- Abes M, Petik B, Kazil S. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2007 Aug;42(8):1439–42.
- Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. The outcome of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis with diameters ≤ 10 mm. Int J Surg. 2014;12(9):897–900.
- Hansson J, Korner U, Ludwigs K, Johnsson E, Jonsson C, Lundholm K. Antibiotics as first-line therapy for acute appendicitis: evidence for a change in clinical practice. World J Surg. 2012 Sep;36(9):2028–36.
- Svensson JF, Patkova B, Almstrom M, Naji H, Hall NJ, Eaton S, et al. Nonoperative treatment with antibiotics versus surgery for acute nonperforated appendicitis in children: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2015 Jan;261(1):67–71.
- Mudri M, Coriolano K, Butter A. Cost analysis of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 May;52(5):791–4.
- Hartwich J, Luks FI, Watson-Smith D, Kurkchubasche AG, Muratore CS, Wills HE, et al. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children: A feasibility study. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jan;51(1):111–6.
- Minneci PC, Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Cooper JN, et al. Effectiveness of Patient Choice in Nonoperative vs Surgical Management of Pediatric Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis. JAMA Surg. 2016 May;151(5):408–15.
- Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Feasibility of a nonoperative management strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in children. J Am Coll Surg. 2014 Aug;219(2):272–9.
- Tanaka Y, Uchida H, Kawashima H, Fujiogi M, Takazawa S, Deie K, et al. Long-term outcomes of operative versus nonoperative treatment for uncomplicated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Nov;50(11):1893–7.
- Di Saverio S, Sibilio A, Giorgini E, Biscardi A, Villani S, Coccolini F, et al. The NOTA Study (Non Operative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis): prospective study on the efficacy and safety of antibiotics (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) for treating patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain and long-term follow-up of conser. Ann Surg. 2014 Jul;260(1):109–17.
- Armstrong J, Merritt N, Jones S, Scott L, Butter A. Non-operative management of early, acute appendicitis in children: is it safe and effective? J Pediatr Surg. 2014 May;49(5):782–5.
- Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Nacion KM, Sulkowski JP, Leonhart KL, Cooper JN, et al. High failure rate of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis with an appendicolith in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jun;51(6):908–11.
- Malik AA, Bari S. Conservative management of acute appendicitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 May;13(5):966–70.
- Gorter RR, van der Lee JH, Cense HA, Kneepkens CMF, Wijnen MHWA, In ’t Hof KH, et al. Initial antibiotic treatment for acute simple appendicitis in children is safe: Short-term results from a multicenter, prospective cohort study. Surgery. 2015 May;157(5):916–23.
- Kaneko K, Tsuda M. Ultrasound-based decision making in the treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2004 Sep;39(9):1316–20.
- Steiner Z, Buklan G, Stackievicz R, Gutermacher M, Erez I. A role for conservative antibiotic treatment in early appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1566–8.
- Caruso AM, Pane A, Garau R, Atzori P, Podda M, Casuccio A, et al. Acute appendicitis in children: not only surgical treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Mar;52(3):444–8.
- Park H-C, Kim B-S, Lee BH. Efficacy of short-term antibiotic therapy for consecutive patients with mild appendicitis. Am Surg. 2011 Jun;77(6):752–5.
- Koike Y, Uchida K, Matsushita K, Otake K, Nakazawa M, Inoue M, et al. Intraluminal appendiceal fluid is a predictive factor for recurrent appendicitis after initial successful non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jul;49(7):1116–21.
- Paudel GR, Agrawal CS, Regmi R, Agrawal S. Conservative treatment in acute appendicitis. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2010;50(180):295–9.
- Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Antibiotics alone as an alternative therapy for uncomplicated pediatric appendicitis. J Am Coll Surg [Internet]. 2014;219(4):Supplement, Page e27. | Link |
- Rocha LL, Rossi FMB, Pessoa CMS, Campos FND, Pires CEF, Steinman M. Antibiotics alone versus appendectomy to treat uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults: what do meta-analyses say? World J Emerg Surg. 2015;10:51.
- Wu JX, Dawes AJ, Sacks GD, Brunicardi FC, Keeler EB. Cost effectiveness of nonoperative management versus laparoscopic appendectomy for acute uncomplicated appendicitis. Surgery. 2015 Sep;158(3):712–21.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Databases. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) [Internet]. 2012. | Link |
- Kelly ME, Khan A, Ur Rehman J, Waldron RM, Khan W, Barry K, et al. A National Evaluation of the Conservative Management of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: How Common Is This and What Are the Issues. Dig Surg. 2015;32(5):325–30.
- Sartelli M, Chichom-Mefire A, Labricciosa FM, Hardcastle T, Abu-Zidan FM, Adesunkanmi AK, et al. The management of intra-abdominal infections from a global perspective: 2017 WSES guidelines for management of intra-abdominal infections. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:29.
- Talan DA, Saltzman DJ, Mower WR, Krishnadasan A, Jude CM, Amii R, et al. Antibiotics-First Versus Surgery for Appendicitis: A US Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial Allowing Outpatient Antibiotic Management. Ann Emerg Med. 2017 Jul;70(1):1–11.e9.
- Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2017 Dec;104(13):1785–90.
- Olive View-UCLA Education & Research Institute. Pilot Trial of Antibiotics Versus Surgery for Treating Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02447224. | Link |
- Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Hospital. Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Appendicitis Treatment Without Operation [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03169114. | Link |
- Turku University Hospital. Antibiotics vs. Placebo in Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPACIII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03234296. | Link |
- Turku University Hospital. Appendicectomy Versus Antibiotics in the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPAC) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01022567. | Link |
- Turku University Hospital. Optimizing the Antibiotic Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis (APPACII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03236961. | Link |
- University of Washington. The Comparison of Outcomes of Antibiotic Drugs and Appendectomy (CODA) Trial (CODA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02800785. | Link |
- Knaapen M, van der Lee JH, Bakx R, The S-ML, van Heurn EWE, Heij HA, et al. Initial non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (APAC trial). BMJ Open. 2017 Nov;7(11):e018145.
- Minneci PC. Randomized Controlled Trial of a Patient Activation Tool in Pediatric Appendicitis (Antibiotics Alone vs. Appendectomy) (Appy-PAT) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02110485. | Link |
- First Affiliated Hospital Xi’an Jiaotong University. Clinical Trial Comparing ERAT vs Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02789865. | Link |
- A.O. Ospedale Papa Giovanni XXIII. Antibiotics Versus Surgery in Acute Appendicitis (ASAA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01421901. | Link |
- Porporm N, Wilasrusmee C, Rattanasiri S, Thakkinstian A. The efficacy of antibiotic treatment versus surgical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial.
- Chong M, Krishnan R, Martin J, Cheng D. Antibiotics vs. appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42017078467. | Link |
- Gorter RR, Gorter-Stam M, Eker H, Bakx R, van der lee H, Heij HA, et al. Systematic review of non-operative versus operative management of acute uncomplicated (simple) appendicitis in children [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42015022061. | Link |
 D’Souza N, Nugent K. Appendicitis. BMJ Clin Evid. 2014 Dec;2014.
D’Souza N, Nugent K. Appendicitis. BMJ Clin Evid. 2014 Dec;2014.  Flum DR. Clinical practice. Acute appendicitis--appendectomy or the “antibiotics first” strategy. N Engl J Med. 2015 May;372(20:1937–43.
Flum DR. Clinical practice. Acute appendicitis--appendectomy or the “antibiotics first” strategy. N Engl J Med. 2015 May;372(20:1937–43.  McBurney C. II. The Indications for Early Laparotomy in Appendicitis. Ann Surg. 1891 Apr;13(4):233–54.
McBurney C. II. The Indications for Early Laparotomy in Appendicitis. Ann Surg. 1891 Apr;13(4):233–54.  McBurney C. IV. The Incision Made in the Abdominal Wall in Cases of Appendicitis, with a Description of a New Method of Operating. Ann Surg. 1894 Jul;20(1):38–43.
McBurney C. IV. The Incision Made in the Abdominal Wall in Cases of Appendicitis, with a Description of a New Method of Operating. Ann Surg. 1894 Jul;20(1):38–43.  Wilms IMHA, de Hoog DENM, de Visser DC, Janzing HMJ. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment for acute appendicitis. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov;(11):CD008359.
Wilms IMHA, de Hoog DENM, de Visser DC, Janzing HMJ. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment for acute appendicitis. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov;(11):CD008359.  Ansaloni L, Catena F, Coccolini F, Ercolani G, Gazzotti F, Pasqualini E, et al. Surgery versus conservative antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Surg. 2011;28(3):210–21.
Ansaloni L, Catena F, Coccolini F, Ercolani G, Gazzotti F, Pasqualini E, et al. Surgery versus conservative antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Surg. 2011;28(3):210–21.  Fitzmaurice GJ, McWilliams B, Hurreiz H, Epanomeritakis E. Antibiotics versus appendectomy in the management of acute appendicitis: a review of the current evidence. Can J Surg. 2011 Oct;54(5):307–14.
Fitzmaurice GJ, McWilliams B, Hurreiz H, Epanomeritakis E. Antibiotics versus appendectomy in the management of acute appendicitis: a review of the current evidence. Can J Surg. 2011 Oct;54(5):307–14.  Harnoss JC, Zelienka I, Probst P, Grummich K, Muller-Lantzsch C, Harnoss JM, et al. Antibiotics Versus Surgical Therapy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials (PROSPERO 2015: CRD42015016882). Ann Surg. 2017 May;265(5):889–900.
Harnoss JC, Zelienka I, Probst P, Grummich K, Muller-Lantzsch C, Harnoss JM, et al. Antibiotics Versus Surgical Therapy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials (PROSPERO 2015: CRD42015016882). Ann Surg. 2017 May;265(5):889–900.  Liu K, Fogg L. Use of antibiotics alone for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgery. 2011 Oct;150(4):673–83.
Liu K, Fogg L. Use of antibiotics alone for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgery. 2011 Oct;150(4):673–83.  Liu Z-H, Li C, Zhang X-W, Kang L, Wang J-P. Meta-analysis of the therapeutic effects of antibiotic versus appendicectomy for the treatment of acute appendicitis. Exp Ther Med. 2014 May;7(5):1181–6.
Liu Z-H, Li C, Zhang X-W, Kang L, Wang J-P. Meta-analysis of the therapeutic effects of antibiotic versus appendicectomy for the treatment of acute appendicitis. Exp Ther Med. 2014 May;7(5):1181–6.  Mason RJ, Moazzez A, Sohn H, Katkhouda N. Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing antibiotic therapy with appendectomy for acute uncomplicated (no abscess or phlegmon) appendicitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2012 Apr;13(2):74–84.
Mason RJ, Moazzez A, Sohn H, Katkhouda N. Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing antibiotic therapy with appendectomy for acute uncomplicated (no abscess or phlegmon) appendicitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2012 Apr;13(2):74–84.  Podda M, Cillara N, Di Saverio S, Lai A, Feroci F, Luridiana G, et al. Antibiotics-first strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults is associated with increased rates of peritonitis at surgery. A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing appendectomy and non-operative managem. Surgeon. 2017 Oct;15(5):303–14.
Podda M, Cillara N, Di Saverio S, Lai A, Feroci F, Luridiana G, et al. Antibiotics-first strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults is associated with increased rates of peritonitis at surgery. A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing appendectomy and non-operative managem. Surgeon. 2017 Oct;15(5):303–14.  Poon SHT, Lee JWY, Ng KM, Chiu GWY, Wong BYK, Foo CC, et al. The current management of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: should there be a change in paradigm? A systematic review of the literatures and analysis of treatment performance. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:46.
Poon SHT, Lee JWY, Ng KM, Chiu GWY, Wong BYK, Foo CC, et al. The current management of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: should there be a change in paradigm? A systematic review of the literatures and analysis of treatment performance. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:46.  Rollins KE, Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotics Versus Appendicectomy for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. World J Surg. 2016 Oct;40(10):2305–18.
Rollins KE, Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotics Versus Appendicectomy for the Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. World J Surg. 2016 Oct;40(10):2305–18.  Sakran J V, Mylonas KS, Gryparis A, Stawicki SP, Burns CJ, Matar MM, et al. Operation versus antibiotics--The “appendicitis conundrum” continues: A meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jun;82(6):1129–37.
Sakran J V, Mylonas KS, Gryparis A, Stawicki SP, Burns CJ, Matar MM, et al. Operation versus antibiotics--The “appendicitis conundrum” continues: A meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jun;82(6):1129–37.  Sallinen V, Akl EA, You JJ, Agarwal A, Shoucair S, Vandvik PO, et al. Meta-analysis of antibiotics versus appendicectomy for non-perforated acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2016 May;103(6):656–67.
Sallinen V, Akl EA, You JJ, Agarwal A, Shoucair S, Vandvik PO, et al. Meta-analysis of antibiotics versus appendicectomy for non-perforated acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2016 May;103(6):656–67.  Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2012 Apr;344:e2156.
Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2012 Apr;344:e2156.  Varadhan KK, Humes DJ, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotic therapy versus appendectomy for acute appendicitis: a meta-analysis. World J Surg. 2010 Feb;34(2):199–209.
Varadhan KK, Humes DJ, Neal KR, Lobo DN. Antibiotic therapy versus appendectomy for acute appendicitis: a meta-analysis. World J Surg. 2010 Feb;34(2):199–209.  Huang L, Yin Y, Yang L, Wang C, Li Y, Zhou Z. Comparison of Antibiotic Therapy and Appendectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Children: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May;171(5):426–34.
Huang L, Yin Y, Yang L, Wang C, Li Y, Zhou Z. Comparison of Antibiotic Therapy and Appendectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Children: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May;171(5):426–34.  Talutis SD, Drake FT. Comparative effectiveness of surgery versus antibiotics in acute appendicitis: a systematic review. J Comp Eff Res. 2017 Jul;6(5):471–82.
Talutis SD, Drake FT. Comparative effectiveness of surgery versus antibiotics in acute appendicitis: a systematic review. J Comp Eff Res. 2017 Jul;6(5):471–82.  Kessler U, Mosbahi S, Walker B, Hau EM, Cotton M, Peiry B, et al. Conservative treatment versus surgery for uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. 2017 Dec;102(12):1118–24.
Kessler U, Mosbahi S, Walker B, Hau EM, Cotton M, Peiry B, et al. Conservative treatment versus surgery for uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child. 2017 Dec;102(12):1118–24.  Ehlers AP, Talan DA, Moran GJ, Flum DR, Davidson GH. Evidence for an Antibiotics-First Strategy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Gap Analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Mar;222(3):309–14.
Ehlers AP, Talan DA, Moran GJ, Flum DR, Davidson GH. Evidence for an Antibiotics-First Strategy for Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Gap Analysis. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Mar;222(3):309–14.  Kirby A, Hobson RP, Burke D, Cleveland V, Ford G, West RM. Appendicectomy for suspected uncomplicated appendicitis is associated with fewer complications than conservative antibiotic management: a meta-analysis of post-intervention complications. J Infect. 2015 Feb;70(2):105–10.
Kirby A, Hobson RP, Burke D, Cleveland V, Ford G, West RM. Appendicectomy for suspected uncomplicated appendicitis is associated with fewer complications than conservative antibiotic management: a meta-analysis of post-intervention complications. J Infect. 2015 Feb;70(2):105–10.  Horst JA, Trehan I, Warner BW, Cohn BG. Can Children With Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis Be Treated With Antibiotics Instead of an Appendectomy? Ann Emerg Med. 2015 Aug;66(2):119–22.
Horst JA, Trehan I, Warner BW, Cohn BG. Can Children With Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis Be Treated With Antibiotics Instead of an Appendectomy? Ann Emerg Med. 2015 Aug;66(2):119–22.  Xu J, Adams S, Liu YC, Karpelowsky J. Nonoperative management in children with early acute appendicitis: A systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Sep;52(9):1409–15.
Xu J, Adams S, Liu YC, Karpelowsky J. Nonoperative management in children with early acute appendicitis: A systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Sep;52(9):1409–15.  Findlay JM, Kafsi J El, Hammer C, Gilmour J, Gillies RS, Maynard ND. Nonoperative Management of Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Dec;223(6):814–824.e2.
Findlay JM, Kafsi J El, Hammer C, Gilmour J, Gillies RS, Maynard ND. Nonoperative Management of Appendicitis in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Dec;223(6):814–824.e2.  Georgiou R, Eaton S, Stanton MP, Pierro A, Hall NJ. Efficacy and Safety of Nonoperative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2017 Mar;139(3).
Georgiou R, Eaton S, Stanton MP, Pierro A, Hall NJ. Efficacy and Safety of Nonoperative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2017 Mar;139(3).  Eriksson S, Granstrom L. Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 1995 Feb;82(2):166–9.
Eriksson S, Granstrom L. Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg. 1995 Feb;82(2):166–9.  Hansson J, Korner U, Khorram-Manesh A, Solberg A, Lundholm K. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy versus appendicectomy as primary treatment of acute appendicitis in unselected patients. Br J Surg. 2009 May;96(5):473–81.
Hansson J, Korner U, Khorram-Manesh A, Solberg A, Lundholm K. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy versus appendicectomy as primary treatment of acute appendicitis in unselected patients. Br J Surg. 2009 May;96(5):473–81.  Vons C, Barry C, Maitre S, Pautrat K, Leconte M, Costaglioli B, et al. Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2011 May;377(9777):1573–9.
Vons C, Barry C, Maitre S, Pautrat K, Leconte M, Costaglioli B, et al. Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2011 May;377(9777):1573–9.  Turhan AN, Kapan S, Kutukcu E, Yigitbas H, Hatipoglu S, Aygun E. Comparison of operative and non operative management of acute appendicitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2009 Sep;15(5):459–62.
Turhan AN, Kapan S, Kutukcu E, Yigitbas H, Hatipoglu S, Aygun E. Comparison of operative and non operative management of acute appendicitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2009 Sep;15(5):459–62.  Styrud J, Eriksson S, Nilsson I, Ahlberg G, Haapaniemi S, Neovius G, et al. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis. a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J Surg. 2006 Jun;30(6):1033–7.
Styrud J, Eriksson S, Nilsson I, Ahlberg G, Haapaniemi S, Neovius G, et al. Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis. a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J Surg. 2006 Jun;30(6):1033–7.  Salminen P, Paajanen H, Rautio T, Nordstrom P, Aarnio M, Rantanen T, et al. Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: The APPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015 Jun;313(23):2340–8.
Salminen P, Paajanen H, Rautio T, Nordstrom P, Aarnio M, Rantanen T, et al. Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: The APPAC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015 Jun;313(23):2340–8.  Liu K, Ahanchi S, Pisaneschi M, Lin I, Walter R. Can acute appendicitis be treated by antibiotics alone? Am Surg. 2007 Nov;73(11):1161–5.
Liu K, Ahanchi S, Pisaneschi M, Lin I, Walter R. Can acute appendicitis be treated by antibiotics alone? Am Surg. 2007 Nov;73(11):1161–5.  Abes M, Petik B, Kazil S. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2007 Aug;42(8):1439–42.
Abes M, Petik B, Kazil S. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2007 Aug;42(8):1439–42.  Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. The outcome of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis with diameters ≤ 10 mm. Int J Surg. 2014;12(9):897–900.
Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. The outcome of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis with diameters ≤ 10 mm. Int J Surg. 2014;12(9):897–900.  Hansson J, Korner U, Ludwigs K, Johnsson E, Jonsson C, Lundholm K. Antibiotics as first-line therapy for acute appendicitis: evidence for a change in clinical practice. World J Surg. 2012 Sep;36(9):2028–36.
Hansson J, Korner U, Ludwigs K, Johnsson E, Jonsson C, Lundholm K. Antibiotics as first-line therapy for acute appendicitis: evidence for a change in clinical practice. World J Surg. 2012 Sep;36(9):2028–36.  Svensson JF, Patkova B, Almstrom M, Naji H, Hall NJ, Eaton S, et al. Nonoperative treatment with antibiotics versus surgery for acute nonperforated appendicitis in children: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2015 Jan;261(1):67–71.
Svensson JF, Patkova B, Almstrom M, Naji H, Hall NJ, Eaton S, et al. Nonoperative treatment with antibiotics versus surgery for acute nonperforated appendicitis in children: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2015 Jan;261(1):67–71.  Mudri M, Coriolano K, Butter A. Cost analysis of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 May;52(5):791–4.
Mudri M, Coriolano K, Butter A. Cost analysis of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 May;52(5):791–4.  Hartwich J, Luks FI, Watson-Smith D, Kurkchubasche AG, Muratore CS, Wills HE, et al. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children: A feasibility study. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jan;51(1):111–6.
Hartwich J, Luks FI, Watson-Smith D, Kurkchubasche AG, Muratore CS, Wills HE, et al. Nonoperative treatment of acute appendicitis in children: A feasibility study. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jan;51(1):111–6.  Minneci PC, Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Cooper JN, et al. Effectiveness of Patient Choice in Nonoperative vs Surgical Management of Pediatric Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis. JAMA Surg. 2016 May;151(5):408–15.
Minneci PC, Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Cooper JN, et al. Effectiveness of Patient Choice in Nonoperative vs Surgical Management of Pediatric Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis. JAMA Surg. 2016 May;151(5):408–15.  Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Feasibility of a nonoperative management strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in children. J Am Coll Surg. 2014 Aug;219(2):272–9.
Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Feasibility of a nonoperative management strategy for uncomplicated acute appendicitis in children. J Am Coll Surg. 2014 Aug;219(2):272–9.  Tanaka Y, Uchida H, Kawashima H, Fujiogi M, Takazawa S, Deie K, et al. Long-term outcomes of operative versus nonoperative treatment for uncomplicated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Nov;50(11):1893–7.
Tanaka Y, Uchida H, Kawashima H, Fujiogi M, Takazawa S, Deie K, et al. Long-term outcomes of operative versus nonoperative treatment for uncomplicated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Nov;50(11):1893–7.  Di Saverio S, Sibilio A, Giorgini E, Biscardi A, Villani S, Coccolini F, et al. The NOTA Study (Non Operative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis): prospective study on the efficacy and safety of antibiotics (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) for treating patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain and long-term follow-up of conser. Ann Surg. 2014 Jul;260(1):109–17.
Di Saverio S, Sibilio A, Giorgini E, Biscardi A, Villani S, Coccolini F, et al. The NOTA Study (Non Operative Treatment for Acute Appendicitis): prospective study on the efficacy and safety of antibiotics (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) for treating patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain and long-term follow-up of conser. Ann Surg. 2014 Jul;260(1):109–17.  Armstrong J, Merritt N, Jones S, Scott L, Butter A. Non-operative management of early, acute appendicitis in children: is it safe and effective? J Pediatr Surg. 2014 May;49(5):782–5.
Armstrong J, Merritt N, Jones S, Scott L, Butter A. Non-operative management of early, acute appendicitis in children: is it safe and effective? J Pediatr Surg. 2014 May;49(5):782–5.  Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Nacion KM, Sulkowski JP, Leonhart KL, Cooper JN, et al. High failure rate of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis with an appendicolith in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jun;51(6):908–11.
Mahida JB, Lodwick DL, Nacion KM, Sulkowski JP, Leonhart KL, Cooper JN, et al. High failure rate of nonoperative management of acute appendicitis with an appendicolith in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jun;51(6):908–11.  Malik AA, Bari S. Conservative management of acute appendicitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 May;13(5):966–70.
Malik AA, Bari S. Conservative management of acute appendicitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 May;13(5):966–70.  Gorter RR, van der Lee JH, Cense HA, Kneepkens CMF, Wijnen MHWA, In ’t Hof KH, et al. Initial antibiotic treatment for acute simple appendicitis in children is safe: Short-term results from a multicenter, prospective cohort study. Surgery. 2015 May;157(5):916–23.
Gorter RR, van der Lee JH, Cense HA, Kneepkens CMF, Wijnen MHWA, In ’t Hof KH, et al. Initial antibiotic treatment for acute simple appendicitis in children is safe: Short-term results from a multicenter, prospective cohort study. Surgery. 2015 May;157(5):916–23.  Kaneko K, Tsuda M. Ultrasound-based decision making in the treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2004 Sep;39(9):1316–20.
Kaneko K, Tsuda M. Ultrasound-based decision making in the treatment of acute appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2004 Sep;39(9):1316–20.  Steiner Z, Buklan G, Stackievicz R, Gutermacher M, Erez I. A role for conservative antibiotic treatment in early appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1566–8.
Steiner Z, Buklan G, Stackievicz R, Gutermacher M, Erez I. A role for conservative antibiotic treatment in early appendicitis in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1566–8.  Caruso AM, Pane A, Garau R, Atzori P, Podda M, Casuccio A, et al. Acute appendicitis in children: not only surgical treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Mar;52(3):444–8.
Caruso AM, Pane A, Garau R, Atzori P, Podda M, Casuccio A, et al. Acute appendicitis in children: not only surgical treatment. J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Mar;52(3):444–8.  Park H-C, Kim B-S, Lee BH. Efficacy of short-term antibiotic therapy for consecutive patients with mild appendicitis. Am Surg. 2011 Jun;77(6):752–5.
Park H-C, Kim B-S, Lee BH. Efficacy of short-term antibiotic therapy for consecutive patients with mild appendicitis. Am Surg. 2011 Jun;77(6):752–5.  Koike Y, Uchida K, Matsushita K, Otake K, Nakazawa M, Inoue M, et al. Intraluminal appendiceal fluid is a predictive factor for recurrent appendicitis after initial successful non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jul;49(7):1116–21.
Koike Y, Uchida K, Matsushita K, Otake K, Nakazawa M, Inoue M, et al. Intraluminal appendiceal fluid is a predictive factor for recurrent appendicitis after initial successful non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2014 Jul;49(7):1116–21.  Paudel GR, Agrawal CS, Regmi R, Agrawal S. Conservative treatment in acute appendicitis. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2010;50(180):295–9.
Paudel GR, Agrawal CS, Regmi R, Agrawal S. Conservative treatment in acute appendicitis. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2010;50(180):295–9.  Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Antibiotics alone as an alternative therapy for uncomplicated pediatric appendicitis. J Am Coll Surg [Internet]. 2014;219(4):Supplement, Page e27. | Link |
Minneci PC, Sulkowski JP, Nacion KM, Mahida JB, Cooper JN, Moss RL, et al. Antibiotics alone as an alternative therapy for uncomplicated pediatric appendicitis. J Am Coll Surg [Internet]. 2014;219(4):Supplement, Page e27. | Link | Rocha LL, Rossi FMB, Pessoa CMS, Campos FND, Pires CEF, Steinman M. Antibiotics alone versus appendectomy to treat uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults: what do meta-analyses say? World J Emerg Surg. 2015;10:51.
Rocha LL, Rossi FMB, Pessoa CMS, Campos FND, Pires CEF, Steinman M. Antibiotics alone versus appendectomy to treat uncomplicated acute appendicitis in adults: what do meta-analyses say? World J Emerg Surg. 2015;10:51.  Wu JX, Dawes AJ, Sacks GD, Brunicardi FC, Keeler EB. Cost effectiveness of nonoperative management versus laparoscopic appendectomy for acute uncomplicated appendicitis. Surgery. 2015 Sep;158(3):712–21.
Wu JX, Dawes AJ, Sacks GD, Brunicardi FC, Keeler EB. Cost effectiveness of nonoperative management versus laparoscopic appendectomy for acute uncomplicated appendicitis. Surgery. 2015 Sep;158(3):712–21.  Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Databases. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) [Internet]. 2012. | Link |
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Databases. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) [Internet]. 2012. | Link | Kelly ME, Khan A, Ur Rehman J, Waldron RM, Khan W, Barry K, et al. A National Evaluation of the Conservative Management of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: How Common Is This and What Are the Issues. Dig Surg. 2015;32(5):325–30.
Kelly ME, Khan A, Ur Rehman J, Waldron RM, Khan W, Barry K, et al. A National Evaluation of the Conservative Management of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis: How Common Is This and What Are the Issues. Dig Surg. 2015;32(5):325–30.  Sartelli M, Chichom-Mefire A, Labricciosa FM, Hardcastle T, Abu-Zidan FM, Adesunkanmi AK, et al. The management of intra-abdominal infections from a global perspective: 2017 WSES guidelines for management of intra-abdominal infections. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:29.
Sartelli M, Chichom-Mefire A, Labricciosa FM, Hardcastle T, Abu-Zidan FM, Adesunkanmi AK, et al. The management of intra-abdominal infections from a global perspective: 2017 WSES guidelines for management of intra-abdominal infections. World J Emerg Surg. 2017;12:29.  Talan DA, Saltzman DJ, Mower WR, Krishnadasan A, Jude CM, Amii R, et al. Antibiotics-First Versus Surgery for Appendicitis: A US Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial Allowing Outpatient Antibiotic Management. Ann Emerg Med. 2017 Jul;70(1):1–11.e9.
Talan DA, Saltzman DJ, Mower WR, Krishnadasan A, Jude CM, Amii R, et al. Antibiotics-First Versus Surgery for Appendicitis: A US Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial Allowing Outpatient Antibiotic Management. Ann Emerg Med. 2017 Jul;70(1):1–11.e9.  Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2017 Dec;104(13):1785–90.
Park HC, Kim MJ, Lee BH. Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2017 Dec;104(13):1785–90.  Olive View-UCLA Education & Research Institute. Pilot Trial of Antibiotics Versus Surgery for Treating Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02447224. | Link |
Olive View-UCLA Education & Research Institute. Pilot Trial of Antibiotics Versus Surgery for Treating Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02447224. | Link | Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Hospital. Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Appendicitis Treatment Without Operation [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03169114. | Link |
Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Hospital. Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Appendicitis Treatment Without Operation [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03169114. | Link | Turku University Hospital. Antibiotics vs. Placebo in Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPACIII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03234296. | Link |
Turku University Hospital. Antibiotics vs. Placebo in Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPACIII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03234296. | Link | Turku University Hospital. Appendicectomy Versus Antibiotics in the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPAC) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01022567. | Link |
Turku University Hospital. Appendicectomy Versus Antibiotics in the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis (APPAC) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01022567. | Link | Turku University Hospital. Optimizing the Antibiotic Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis (APPACII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03236961. | Link |
Turku University Hospital. Optimizing the Antibiotic Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis (APPACII) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT03236961. | Link | University of Washington. The Comparison of Outcomes of Antibiotic Drugs and Appendectomy (CODA) Trial (CODA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02800785. | Link |
University of Washington. The Comparison of Outcomes of Antibiotic Drugs and Appendectomy (CODA) Trial (CODA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02800785. | Link | Knaapen M, van der Lee JH, Bakx R, The S-ML, van Heurn EWE, Heij HA, et al. Initial non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (APAC trial). BMJ Open. 2017 Nov;7(11):e018145.
Knaapen M, van der Lee JH, Bakx R, The S-ML, van Heurn EWE, Heij HA, et al. Initial non-operative management of uncomplicated appendicitis in children: a protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (APAC trial). BMJ Open. 2017 Nov;7(11):e018145.  Minneci PC. Randomized Controlled Trial of a Patient Activation Tool in Pediatric Appendicitis (Antibiotics Alone vs. Appendectomy) (Appy-PAT) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02110485. | Link |
Minneci PC. Randomized Controlled Trial of a Patient Activation Tool in Pediatric Appendicitis (Antibiotics Alone vs. Appendectomy) (Appy-PAT) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02110485. | Link | First Affiliated Hospital Xi’an Jiaotong University. Clinical Trial Comparing ERAT vs Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02789865. | Link |
First Affiliated Hospital Xi’an Jiaotong University. Clinical Trial Comparing ERAT vs Antibiotic Therapy vs Appendectomy for Treatment of Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis [Internet]. Report No.: NCT02789865. | Link | A.O. Ospedale Papa Giovanni XXIII. Antibiotics Versus Surgery in Acute Appendicitis (ASAA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01421901. | Link |
A.O. Ospedale Papa Giovanni XXIII. Antibiotics Versus Surgery in Acute Appendicitis (ASAA) [Internet]. Report No.: NCT01421901. | Link | Porporm N, Wilasrusmee C, Rattanasiri S, Thakkinstian A. The efficacy of antibiotic treatment versus surgical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial.
Porporm N, Wilasrusmee C, Rattanasiri S, Thakkinstian A. The efficacy of antibiotic treatment versus surgical treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial.  Chong M, Krishnan R, Martin J, Cheng D. Antibiotics vs. appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42017078467. | Link |
Chong M, Krishnan R, Martin J, Cheng D. Antibiotics vs. appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42017078467. | Link | Gorter RR, Gorter-Stam M, Eker H, Bakx R, van der lee H, Heij HA, et al. Systematic review of non-operative versus operative management of acute uncomplicated (simple) appendicitis in children [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42015022061. | Link |
Gorter RR, Gorter-Stam M, Eker H, Bakx R, van der lee H, Heij HA, et al. Systematic review of non-operative versus operative management of acute uncomplicated (simple) appendicitis in children [Internet]. Report No.: CRD42015022061. | Link |Systematization of initiatives in sexual and reproductive health about good practices criteria in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in primary health care in Chile
Clinical, psychological, social, and family characterization of suicidal behavior in Chilean adolescents: a multiple correspondence analysis








