Resumen
La clozapina constituye el tratamiento de elección en los pacientes con esquizofrenia que no presentan remisión de los síntomas pese al manejo con antipsicóticos por periodos de tiempo y en dosis adecuados. Sin embargo, un porcentaje importante persiste sintomático pese al tratamiento con dosis óptimas de clozapina, por lo que se ha planteado que agregar un segundo antipsicótico podría mejorar la respuesta clínica. Utilizando la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, identificamos 17 revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 62 estudios, entre ellos 26 estudios aleatorizados pertinentes. Realizamos un metanálisis y tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina en pacientes con esquizofrenia resistente probablemente resulta en poca o nula diferencia en la respuesta clínica, y aumenta los efectos adversos.
Problema
Existe entre un 20% a un 30% de los pacientes con esquizofrenia que se consideran resistentes al tratamiento, es decir, no presentan remisión de los síntomas pese al manejo con antipsicóticos por periodos de tiempo y en dosis adecuados [1]. Para este tipo de pacientes la clozapina es el tratamiento de elección [2], [3], [4]. Sin embargo, existe una proporción importante de los pacientes que persiste sintomático pese al tratamiento con dosis óptimas de clozapina [5]. Es por esto que se ha planteado que agregar un segundo antipsicótico podría mejorar la respuesta clínica, sin embargo, existe controversia sobre la real efectividad de esta medida. Por otra parte, se asocia a efectos adversos importantes, y a costos.
Métodos
Utilizamos la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en 30 bases de datos, para identificar revisiones sistemáticas y sus estudios primarios incluidos. Con esta información generamos un resumen estructurado, siguiendo un formato preestablecido, que incluye mensajes clave, un resumen del conjunto de evidencia (presentado como matriz de evidencia en Epistemonikos), metanálisis del total de los estudios, tablas de resumen de resultados con el método GRADE, y tabla de otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión.
|
Mensajes clave
|
Acerca del conjunto de evidencia para esta pregunta
|
Cuál es la evidencia. |
Encontramos 17 revisiones sistemáticas [5],[6],[7], |
|
Qué tipo de pacientes incluyeron los estudios |
Todos los estudios incluyeron pacientes adultos, con diagnóstico de esquizofrenia (seis estudios según DSM IV o CIE 10 [31], [39], [44], [62], [63], [64]), con persistencia de síntomas psicóticos pese al tratamiento con clozapina, en dosis y duración adecuados. Diecinueve estudios incluyeron también trastornos relacionados a esquizofrenia [22], [23], [24], [25], [31], [35], [39], [40], [41], [44], [48], [58], [62], [63], [64], [66], [70], [79], [84]. Los estudios incluyeron pacientes tanto ambulatorios como hospitalizados, sin comorbilidades mayores médicas o psiquiátricas. Con respecto a la severidad del cuadro al inicio del estudio, 11 estudios reportaron PANSS >= a 60 [23], [24], [36], [41], [43], [44], [48], [52], [58], [64], [70], 11 estudios BPRS >= a 25 [22], [25], [31], [34], [35], [40], [63], [66], [78], [79], [84], dos estudios CGI >=4 [62], [75] y en el resto no se describió la severidad. |
|
Qué tipo de intervenciones incluyeron los estudios |
Todos los estudios compararon la adición de algún antipsicótico a clozapina contra clozapina sola o clozapina + placebo. Once estudios agregaron risperidona [23], [24], [39], [40], [43], [44], [48], [58], [62], [63], |
|
Qué tipo de desenlaces midieron |
Los estudios midieron múltiples desenlaces, sin embargo, las diferentes revisiones sistemáticas los agruparon de la siguiente manera:
|
Resumen de los resultados
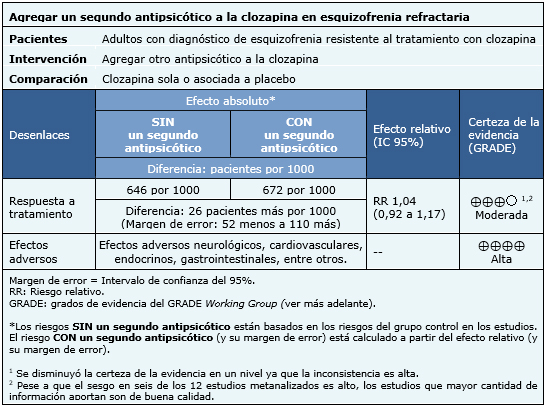
La información sobre los efectos de agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina está basada en 12 estudios aleatorizados [22], [25], [31], [39], [40], [44], [48], [58], [62], [63], [64], [79], los cuales incluyen a 771 pacientes. El resto de los estudios no midieron los desenlaces de interés o no entregaron datos que pudieran ser incorporados al metanálisis. El resumen de los resultados es el siguiente:
- Agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina en pacientes con esquizofrenia refractaria probablemente resulta en poca o nula diferencia en la respuesta clínica. La certeza de la evidencia es moderada.
- Agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina aumenta los efectos adversos. La certeza de la evidencia es alta.

Otras consideraciones para la toma de decisión
|
A quién se aplica y a quién no se aplica esta evidencia |
|
| Sobre los desenlaces incluidos en este resumen |
|
| Balance riesgo/beneficio y certeza de la evidencia |
|
| Qué piensan los pacientes y sus tratantes |
|
| Consideraciones de recursos |
|
| Diferencias entre este resumen y otras fuentes |
|
| ¿Puede que cambie esta información en el futuro? |
|
Cómo realizamos este resumen
Mediante métodos automatizados y colaborativos recopilamos toda la evidencia relevante para la pregunta de interés y la presentamos en una matriz de evidencia.
Siga el enlace para acceder a la versión interactiva: Agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina en esquizofrenia resistente
Notas
Si con posterioridad a la publicación de este resumen se publican nuevas revisiones sistemáticas sobre este tema, en la parte superior de la matriz se mostrará un aviso de “nueva evidencia”. Si bien el proyecto contempla la actualización periódica de estos resúmenes, los usuarios están invitados a comentar en Medwave o contactar a los autores mediante correo electrónico si creen que hay evidencia que motive una actualización más rápida.
Luego de crear una cuenta en Epistemonikos, al guardar las matrices recibirá notificaciones automáticas cada vez que exista nueva evidencia que potencialmente responda a esta pregunta. El detalle de los métodos para elaborar este resumen están descritos aquí: http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
La Fundación Epistemonikos es una organización que busca acercar la información a quienes toman decisiones en salud, mediante el uso de tecnologías. Su principal desarrollo es la base de datos Epistemonikos (www.epistemonikos.org).
Los resúmenes de evidencia siguen un riguroso proceso de revisión por pares interno.
Declaración de conflictos de intereses
Los autores declaran no tener conflictos de intereses con la materia de este artículo.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

La clozapina constituye el tratamiento de elección en los pacientes con esquizofrenia que no presentan remisión de los síntomas pese al manejo con antipsicóticos por periodos de tiempo y en dosis adecuados. Sin embargo, un porcentaje importante persiste sintomático pese al tratamiento con dosis óptimas de clozapina, por lo que se ha planteado que agregar un segundo antipsicótico podría mejorar la respuesta clínica. Utilizando la base de datos Epistemonikos, la cual es mantenida mediante búsquedas en múltiples bases de datos, identificamos 17 revisiones sistemáticas que en conjunto incluyen 62 estudios, entre ellos 26 estudios aleatorizados pertinentes. Realizamos un metanálisis y tablas de resumen de los resultados utilizando el método GRADE. Concluimos que agregar un segundo antipsicótico a la clozapina en pacientes con esquizofrenia resistente probablemente resulta en poca o nula diferencia en la respuesta clínica, y aumenta los efectos adversos.
 Authors:
Magdalena Jiménez-Cornejo[1,2], Gonzalo Munizaga[1,2], David Aceituno[2,3]
Authors:
Magdalena Jiménez-Cornejo[1,2], Gonzalo Munizaga[1,2], David Aceituno[2,3]
Affiliation:
[1] Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
[2] Proyecto Epistemonikos, Santiago, Chile
[3] Departamento de Medicina Interna, Facultad de Medicina, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
E-mail: daceituno@med.puc.cl
Author address:
[1] Facultad de Medicina Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Diagonal Paraguay 476 Santiago Centro Chile

Citation: Jiménez-Cornejo M, Munizaga G, Aceituno D. Does adding a second antipsychotic to clozapine improve clinical response in resistant schizophrenia?. Medwave 2016;16(Suppl 5):e6614 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2016.6614
Publication date: 2/12/2016

Comments (0)
We are pleased to have your comment on one of our articles. Your comment will be published as soon as it is posted. However, Medwave reserves the right to remove it later if the editors consider your comment to be: offensive in some sense, irrelevant, trivial, contains grammatical mistakes, contains political harangues, appears to be advertising, contains data from a particular person or suggests the need for changes in practice in terms of diagnostic, preventive or therapeutic interventions, if that evidence has not previously been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
No comments on this article.
To comment please log in
 Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics.
Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics. There may be a 48-hour delay for most recent metrics to be posted.

- Conley RR, Kelly DL. Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Dec 1;50(11):898-911 | PubMed |
- Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Sep;45(9):789-96 | PubMed |
- Rosenheck R1, Cramer J, Xu W, Thomas J, Henderson W, Frisman L, et al. A comparison of clozapine and haloperidol in hospitalized patients with refractory schizophrenia. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Clozapine in Refractory Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:809–815. 4. Wahlbeck K, Cheine M, Essali A, Adams C. Evidence of clozapine’s effectiveness in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156:990–999. | CrossRef |
- Chakos M, Lieberman J, Hoffman E, Bradford D, Sheitman B. Effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2001 Apr;158(4):518-26 | PubMed |
- Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Paplos KG, Pappa DA, Christodoulou GN. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine: a critical review. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006 Sep;256(6):350-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Wang J, Omori IM, Fenton M, Soares B. Sulpiride augmentation for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD008125 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Roukas DK. Randomized controlled augmentation trials in clozapine-resistant schizophrenic patients: a critical review. Eur Psychiatry. 2005 Aug;20(5-6):409-15 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Srisurapanont M, Suttajit S, Maneeton N, Maneeton B. Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2015 Mar;62:38-47 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Veerman SR, Schulte PF, Begemann MJ, de Haan L. Non-glutamatergic clozapine augmentation strategies: a review and meta-analysis. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2014 Nov;47(7):231-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Porcelli S, Balzarro B, Serretti A. Clozapine resistance: augmentation strategies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Mar;22(3):165-82 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Paton C, Whittington C, Barnes TR. Augmentation with a second antipsychotic in patients with schizophrenia who partially respond to clozapine: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2007 Apr;27(2):198-204 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Muscatello MR, Bruno A, De Fazio P, Segura-Garcia C, Pandolfo G, Zoccali R. Augmentation strategies in partial responder and/or treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014 Nov;15(16):2329-45 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Sommer IE, Begemann MJ, Temmerman A, Leucht S. Pharmacological augmentation strategies for schizophrenia patients with insufficient response to clozapine: a quantitative literature review. Schizophr Bull. 2012 Sep;38(5):1003-11 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Taylor DM, Smith L, Gee SH, Nielsen J. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic - a meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2012 Jan;125(1):15-24 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Taylor DM, Smith L. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic--a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2009 Jun;119(6):419-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Barbui C, Signoretti A, Mulè S, Boso M, Cipriani A. Does the addition of a second antipsychotic drug improve clozapine treatment? Schizophr Bull. 2009 Mar;35(2):458-68 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Chong SA, Remington G. Clozapine augmentation: safety and efficacy. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26(2):421-40 | PubMed |
- Vayısoğlu S, Anıl Yağcıoğlu E. [Augmentation strategies in patients with schizophrenia who show partial response to clozapine treatment]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2014 Fall;25(3):201-11 | PubMed |
- Freudenreich O, Goff DC. Antipsychotic combination therapy in schizophrenia. A review of efficacy and risks of current combinations. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2002 Nov;106(5):323-30 | PubMed |
- Mouaffak F, Tranulis C, Gourevitch R, Poirier MF, Douki S, Olié JP, et al. Augmentation strategies of clozapine with antipsychotics in the treatment of ultraresistant schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006 Jan-Feb;29(1):28-33 | PubMed |
- Sobów T, Magierski R, Kloszewska I.[Risperidone as adjunctive therapy in clozapine treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials]. Postêpy Psychiatrii i Neurologii. 2009;18(4):333-337 | Link |
- Zou G, Huang Y, Zou S, & Yang Y. A comparative trial of the beneficial effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. J Yichun Univ(2003) 25, 94–96 | Link |
- Wu L. A control study of risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Health Psychol J.(2002), 10, 135–137 | Link |
- Yue H, Song L, & Xu Y. A comparative trial of risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia over two years. Shangai Arch Psychiatry, (2004)16, 165–167. | Link |
- Liu Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Jin S, Li Z, Wang N,et al. A control study of clozapine in combination with sulpiride in alleviating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry, (1996) 29(2), 87–90. | Link |
- Raju, Kumar R, Khanna S. Clozapine-risperidone combination in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2001 Aug;35(4):543. | PubMed |
- Bachmann CJ, Lehr D, Theisen FM, Preiss M. Aripiprazole as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia: a retrospective chart review. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2009 Jul;42(4):153-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Agelink MW, Kavuk I, Ak I. Clozapine with amisulpride for refractory schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004 May;161(5):924-5 | PubMed |
- Godleski LS, Sernyak MJ. Agranulocytosis after addition of risperidone to clozapine treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1996 May;153(5):735-6 | PubMed |
- Kämpf P, Agelink MW, Naber D. Augmentation of clozapine with amisulpride: a promising therapeutic approach to refractory schizophrenic symptoms. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2005 Jan;38(1):39-40 | PubMed |
- Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Radwan M, Schwartz B, Dorfman-Etrog P, et al. Sulpiride augmentation in people with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry. 1997 Dec;171:569-73 | PubMed |
- Ziegenbein M, Wittmann G, Kropp S. Aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical observation. Clin Drug Investig. 2006;26(3):117-24 | PubMed |
- Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Weizman A. Sulpiride adjunction to clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients: a preliminary case series study. Eur Psychiatry. 1997;12(3):152-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Muscatello MR, Bruno A, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Scimeca G, Di Nardo F, et al. Effect of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2011 Apr;127(1-3):93-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gunduz-Bruce H, Oliver S, Gueorguieva R, Forselius-Bielen K, D'Souza DC, Zimolo Z, et al. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial responders with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2013 Feb;143(2-3):344-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Nielsen J, Emborg C, Gydesen S, Dybbro J, Aagaard J, Haderup K, et al. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Apr;32(2):173-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on body weight and clinical efficacy in schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010 Sep;13(8):1115-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Henderson DC, Kunkel L, Nguyen DD, Borba CP, Daley TB, Louie PM, et al. An exploratory open-label trial of aripiprazole as an adjuvant to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006 Feb;113(2):142-7 | PubMed |
- Peng H, Kuang Y, & Huang X. A control study of risperidone in combination with clozapine in treating refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Modern Clinical Medical Bioengineering, 2001.7(2), 100–102. | Link |
- Liu QH, Li XL. A comparative study on the efficacy of combining risperidone and clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Mental Medical Journal, (2001). 14(1), 28–30 | Link |
- Friedman JI, Lindenmayer JP, Alcantara F, Bowler S, Parak M, et al. Pimozide augmentation of clozapine inpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder unresponsive to clozapine monotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 May;36(6):1289-95. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Sénéchal A, Landry P, Deschamps R, Lessard M. [Neutropenia in a patient treated with clozapine in combination with other psychotropic drugs]. Encephale. 2002 Nov-Dec;28(6 Pt 1):567-9 | PubMed |
- Honer W, MacEwan GW, Williams R, Falkai P, McKenna PJ, Pomarol-Clotet E, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of augmentation of clozapine with risperidone. SCHIZOPHRENIA BULLETIN, (2005). 31(2), 487 | Link |
- Akdede BB, Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Alptekin K, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, et al. A double-blind study of combination of clozapine with risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: effects on cognition. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;67(12):1912-9 | PubMed |
- Patel JK, Salzman C, Green AI, Tsuang MT. Chronic schizophrenia: response to clozapine, risperidone, and paroxetine. Am J Psychiatry. 1997 Apr;154(4):543-6. | PubMed |
- Adesanya A, Pantelis C. Adjunctive risperidone treatment in patients with 'clozapine-resistant schizophrenia'. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2000 Jun;34(3):533-4 | PubMed |
- Lim S, Pralea C, Schnitt J, Bowers MB Jr, Cooper C. Possible increased efficacy of low-dose clozapine when combined with aripiprazole. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;65(9):1284-5 | PubMed |
- Honer WG, Thornton AE, Chen EY, Chan RC, Wong JO, Bergmann A, et al. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone with refractory schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2006 Feb 2;354(5):472-82 | PubMed |
- de Groot IW, Heck AH, van Harten PN. Addition of risperidone to clozapine therapy in chronically psychotic inpatients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001 Feb;62(2):129-30 | PubMed |
- Beauchemin MA, Millaud F, Nguyen KA. A case of neuroleptic malignant syndrome with clozapine and risperidone. Can J Psychiatry. 2002 Nov;47(9):886 | PubMed |
- Benedetti A, Di Paolo A, Lastella M, Casamassima F, Candiracci C, Litta A, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with aripiprazole in severe psychotic bipolar and schizoaffective disorders: a pilot study. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2010 Jun 4;6:30-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Mossaheb N, Sacher J, Wiesegger G, Klein N, CJ, Asenbaum S, Kasper S. Haloperidol in combination with clozapine in treatment-refractory patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology, (2006).16, 416. | Link |
- Munro J, Matthiasson P, Osborne S, Travis M, Purcell S, Cobb AM, et al. Amisulpride augmentation of clozapine: an open non-randomized study in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2004 Oct;110(4):292-8 | PubMed |
- Rhoads E. Polypharmacy of 2 atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000 Sep;61(9):678-80 | PubMed |
- Koreen AR, Lieberman JA, Kronig M, Cooper TB. Cross-tapering clozapine and risperidone. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Nov;152(11):1690 | PubMed |
- Kaye NS. Ziprasidone augmentation of clozapine in 11 patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003 Feb;64(2):215-6 | PubMed |
- Friedman J, Ault K, Powchik P. Pimozide augmentation for the treatment of schizophrenic patients who are partial responders to clozapine. Biol Psychiatry. 1997 Sep 15;42(6):522-3 | PubMed |
- Ni J, Jang L, & Hong X. Therapeutic effects of clozapine, risperidone and their combination in the treatment of schizophrenia. Health Psychol J,(2001). 3, 181–182. | Link |
- Stubbs JH, Haw CM, Staley CJ, Mountjoy CQ. Augmentation with sulpiride for a schizophrenic patient partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Nov;102(5):390-3; discussion 393-4 | PubMed |
- Rajarethinam R, Gilani S, Tancer M, DeQuardo J. Augmentation of clozapine partial responders with conventional antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2003 Mar 1;60(1):97-8 | PubMed |
- Mitsonis CI, Dimopoulos NP, Mitropoulos PA, Kararizou EG, Katsa AN, Tsakiris FE, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in the management of residual symptoms in clozapine-treated outpatients with chronic schizophrenia: An open-label pilot study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Mar 30;31(2):373-7 | PubMed |
- Weiner E, Conley RR, Ball MP, Feldman S, Gold JM, Kelly DL, et al. Adjunctive risperidone for partially responsive people with schizophrenia treated with clozapine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Oct;35(11):2274-83 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, et al. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;162(1):130-6 | PubMed |
- Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Walsh JP, Culhane MA, Goff DC. Risperidone augmentation for schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Res. 2007 May;92(1-3):90-4 | PubMed |
- McCarthy RH, Terkelsen KG. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1995 Mar;28(2):61-3 | PubMed |
- Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine-treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 May;69(5):720-31 | PubMed |
- Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade R, et al. Weight change on aripiprazole-clozapine combination in schizophrenic patients with weight gain and suboptimal response on clozapine: 16-week double-blind study. European Psychiatry, (2008). 23, S114–S115. | CrossRef |
- Raskin S, Katz G, Zislin Z, Knobler HY, Durst R. Clozapine and risperidone: combination/augmentation treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a preliminary observation. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Apr;101(4):334-6 | PubMed |
- Tyson SC, Devane CL, Risch SC. Pharmacokinetic interaction between risperidone and clozapine. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;152(9):1401-2 | PubMed |
- Xao H. A double-blind comparative study of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Sichuan Ment Health, (1999).12, 250–251 | Link |
- Kontaxakis VP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Stamouli SS, Christodoulou GN. Toxic interaction between risperidone and clozapine: a case report. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;26(2):407-9 | PubMed |
- Mowerman S, Siris SG. Adjunctive loxapine in a clozapine-resistant cohort of schizophrenic patients. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Dec;8(4):193-7 | PubMed |
- Lerner V, Bergman J, Borokhov A, Loewenthal U, Miodownik C. Augmentation with amisulpride for schizophrenic patients nonresponsive to antipsychotic monotherapy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005 Mar-Apr;28(2):66-71 | PubMed |
- Morera AL, Barreiro P, Cano-Muñoz JL. Risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1999 Apr;99(4):305-6; discussion 306-7 | PubMed |
- Assion HJ, Reinbold H, Lemanski S, Basilowski M, Juckel G. Amisulpride augmentation in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive or unresponsive to clozapine. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2008 Jan;41(1):24-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-993209 | PubMed |
- Henderson DC, Goff DC. Risperidone as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenics. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Sep;57(9):395-7 | PubMed |
- Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Kivircik Akdede BB, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double-blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;66(1):63-72 | PubMed |
- Muscatello MR, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Lamberti Castronuovo E, Abenavoli E, Scimeca G, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with ziprasidone in refractory schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Feb;34(1):129-33. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Si S, Yuan C. A comparative trial of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Arch Psychiatry, (1999).12, 17–20 | Link |
- Chong SA, Tan CH, Lee HS. Atrial ectopics with clozapine-risperidone combination. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1997 Apr;17(2):130-1 | PubMed |
- Taylor CG, Flynn SW, Altman S, Ehmann T, MacEwan GW, Honer WG. An open trial of risperidone augmentation of partial response to clozapine. Schizophr Res. 2001 Mar 1;48(1):155-8 | PubMed |
- Gupta S, Sonnenberg SJ, Frank B. Olanzapine augmentation of clozapine. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1998 Sep;10(3):113-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Zink M, Knopf U, Henn FA, Thome J. Combination of clozapine and amisulpride in treatment-resistant schizophrenia--case reports and review of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004 Jan;37(1):26-31 | PubMed |
- Haibing Z, Guohang Y, Deqing D. A study of clozapine combined with or without pipotiazine palmitate in refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine, (2002). 12(1), 15–17 | Link |
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: prevention and management 2014. | Link |
- American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia Second Edition,2010. | Link |
- Sheng-Chang Wang, MD ,M Sc, Amisulpride Augmentation Therapy for Clozapine-resistant Schizophrenic Patients: A 14-week Randomized, Double-blind and Placebo-controlled Trial | Link |
- Aalborg Psychiatric Hospital, Research Unit. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole - A double-blinded randomized placebo study (SERCLOZ) - SERCLOZ | Link |
 Conley RR, Kelly DL. Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Dec 1;50(11):898-911 | PubMed |
Conley RR, Kelly DL. Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Dec 1;50(11):898-911 | PubMed | Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Sep;45(9):789-96 | PubMed |
Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Sep;45(9):789-96 | PubMed | Rosenheck R1, Cramer J, Xu W, Thomas J, Henderson W, Frisman L, et al. A comparison of clozapine and haloperidol in hospitalized patients with refractory schizophrenia. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Clozapine in Refractory Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:809–815. 4. Wahlbeck K, Cheine M, Essali A, Adams C. Evidence of clozapine’s effectiveness in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156:990–999. | CrossRef |
Rosenheck R1, Cramer J, Xu W, Thomas J, Henderson W, Frisman L, et al. A comparison of clozapine and haloperidol in hospitalized patients with refractory schizophrenia. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Clozapine in Refractory Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:809–815. 4. Wahlbeck K, Cheine M, Essali A, Adams C. Evidence of clozapine’s effectiveness in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156:990–999. | CrossRef | Chakos M, Lieberman J, Hoffman E, Bradford D, Sheitman B. Effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2001 Apr;158(4):518-26 | PubMed |
Chakos M, Lieberman J, Hoffman E, Bradford D, Sheitman B. Effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2001 Apr;158(4):518-26 | PubMed | Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Paplos KG, Pappa DA, Christodoulou GN. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine: a critical review. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006 Sep;256(6):350-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Paplos KG, Pappa DA, Christodoulou GN. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine: a critical review. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006 Sep;256(6):350-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Wang J, Omori IM, Fenton M, Soares B. Sulpiride augmentation for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD008125 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Wang J, Omori IM, Fenton M, Soares B. Sulpiride augmentation for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Jan 20;(1):CD008125 | CrossRef | PubMed | Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Roukas DK. Randomized controlled augmentation trials in clozapine-resistant schizophrenic patients: a critical review. Eur Psychiatry. 2005 Aug;20(5-6):409-15 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Kontaxakis VP, Ferentinos PP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Roukas DK. Randomized controlled augmentation trials in clozapine-resistant schizophrenic patients: a critical review. Eur Psychiatry. 2005 Aug;20(5-6):409-15 | CrossRef | PubMed | Srisurapanont M, Suttajit S, Maneeton N, Maneeton B. Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2015 Mar;62:38-47 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Srisurapanont M, Suttajit S, Maneeton N, Maneeton B. Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. J Psychiatr Res. 2015 Mar;62:38-47 | CrossRef | PubMed | Veerman SR, Schulte PF, Begemann MJ, de Haan L. Non-glutamatergic clozapine augmentation strategies: a review and meta-analysis. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2014 Nov;47(7):231-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Veerman SR, Schulte PF, Begemann MJ, de Haan L. Non-glutamatergic clozapine augmentation strategies: a review and meta-analysis. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2014 Nov;47(7):231-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Porcelli S, Balzarro B, Serretti A. Clozapine resistance: augmentation strategies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Mar;22(3):165-82 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Porcelli S, Balzarro B, Serretti A. Clozapine resistance: augmentation strategies. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Mar;22(3):165-82 | CrossRef | PubMed | Paton C, Whittington C, Barnes TR. Augmentation with a second antipsychotic in patients with schizophrenia who partially respond to clozapine: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2007 Apr;27(2):198-204 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Paton C, Whittington C, Barnes TR. Augmentation with a second antipsychotic in patients with schizophrenia who partially respond to clozapine: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2007 Apr;27(2):198-204 | CrossRef | PubMed | Muscatello MR, Bruno A, De Fazio P, Segura-Garcia C, Pandolfo G, Zoccali R. Augmentation strategies in partial responder and/or treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014 Nov;15(16):2329-45 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Muscatello MR, Bruno A, De Fazio P, Segura-Garcia C, Pandolfo G, Zoccali R. Augmentation strategies in partial responder and/or treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014 Nov;15(16):2329-45 | CrossRef | PubMed | Sommer IE, Begemann MJ, Temmerman A, Leucht S. Pharmacological augmentation strategies for schizophrenia patients with insufficient response to clozapine: a quantitative literature review. Schizophr Bull. 2012 Sep;38(5):1003-11 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Sommer IE, Begemann MJ, Temmerman A, Leucht S. Pharmacological augmentation strategies for schizophrenia patients with insufficient response to clozapine: a quantitative literature review. Schizophr Bull. 2012 Sep;38(5):1003-11 | CrossRef | PubMed | Taylor DM, Smith L, Gee SH, Nielsen J. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic - a meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2012 Jan;125(1):15-24 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Taylor DM, Smith L, Gee SH, Nielsen J. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic - a meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2012 Jan;125(1):15-24 | CrossRef | PubMed | Taylor DM, Smith L. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic--a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2009 Jun;119(6):419-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Taylor DM, Smith L. Augmentation of clozapine with a second antipsychotic--a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2009 Jun;119(6):419-25 | CrossRef | PubMed | Barbui C, Signoretti A, Mulè S, Boso M, Cipriani A. Does the addition of a second antipsychotic drug improve clozapine treatment? Schizophr Bull. 2009 Mar;35(2):458-68 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Barbui C, Signoretti A, Mulè S, Boso M, Cipriani A. Does the addition of a second antipsychotic drug improve clozapine treatment? Schizophr Bull. 2009 Mar;35(2):458-68 | CrossRef | PubMed | Chong SA, Remington G. Clozapine augmentation: safety and efficacy. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26(2):421-40 | PubMed |
Chong SA, Remington G. Clozapine augmentation: safety and efficacy. Schizophr Bull. 2000;26(2):421-40 | PubMed | Vayısoğlu S, Anıl Yağcıoğlu E. [Augmentation strategies in patients with schizophrenia who show partial response to clozapine treatment]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2014 Fall;25(3):201-11 | PubMed |
Vayısoğlu S, Anıl Yağcıoğlu E. [Augmentation strategies in patients with schizophrenia who show partial response to clozapine treatment]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg. 2014 Fall;25(3):201-11 | PubMed | Freudenreich O, Goff DC. Antipsychotic combination therapy in schizophrenia. A review of efficacy and risks of current combinations. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2002 Nov;106(5):323-30 | PubMed |
Freudenreich O, Goff DC. Antipsychotic combination therapy in schizophrenia. A review of efficacy and risks of current combinations. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2002 Nov;106(5):323-30 | PubMed | Mouaffak F, Tranulis C, Gourevitch R, Poirier MF, Douki S, Olié JP, et al. Augmentation strategies of clozapine with antipsychotics in the treatment of ultraresistant schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006 Jan-Feb;29(1):28-33 | PubMed |
Mouaffak F, Tranulis C, Gourevitch R, Poirier MF, Douki S, Olié JP, et al. Augmentation strategies of clozapine with antipsychotics in the treatment of ultraresistant schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2006 Jan-Feb;29(1):28-33 | PubMed | Sobów T, Magierski R, Kloszewska I.[Risperidone as adjunctive therapy in clozapine treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials]. Postêpy Psychiatrii i Neurologii. 2009;18(4):333-337 | Link |
Sobów T, Magierski R, Kloszewska I.[Risperidone as adjunctive therapy in clozapine treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials]. Postêpy Psychiatrii i Neurologii. 2009;18(4):333-337 | Link | Zou G, Huang Y, Zou S, & Yang Y. A comparative trial of the beneficial effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. J Yichun Univ(2003) 25, 94–96 | Link |
Zou G, Huang Y, Zou S, & Yang Y. A comparative trial of the beneficial effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. J Yichun Univ(2003) 25, 94–96 | Link | Wu L. A control study of risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Health Psychol J.(2002), 10, 135–137 | Link |
Wu L. A control study of risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Health Psychol J.(2002), 10, 135–137 | Link | Yue H, Song L, & Xu Y. A comparative trial of risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia over two years. Shangai Arch Psychiatry, (2004)16, 165–167. | Link |
Yue H, Song L, & Xu Y. A comparative trial of risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia over two years. Shangai Arch Psychiatry, (2004)16, 165–167. | Link | Liu Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Jin S, Li Z, Wang N,et al. A control study of clozapine in combination with sulpiride in alleviating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry, (1996) 29(2), 87–90. | Link |
Liu Q, Li X, Zhang Y, Jin S, Li Z, Wang N,et al. A control study of clozapine in combination with sulpiride in alleviating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry, (1996) 29(2), 87–90. | Link | Raju, Kumar R, Khanna S. Clozapine-risperidone combination in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2001 Aug;35(4):543. | PubMed |
Raju, Kumar R, Khanna S. Clozapine-risperidone combination in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2001 Aug;35(4):543. | PubMed | Bachmann CJ, Lehr D, Theisen FM, Preiss M. Aripiprazole as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia: a retrospective chart review. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2009 Jul;42(4):153-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Bachmann CJ, Lehr D, Theisen FM, Preiss M. Aripiprazole as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in adolescents with early-onset schizophrenia: a retrospective chart review. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2009 Jul;42(4):153-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Agelink MW, Kavuk I, Ak I. Clozapine with amisulpride for refractory schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004 May;161(5):924-5 | PubMed |
Agelink MW, Kavuk I, Ak I. Clozapine with amisulpride for refractory schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004 May;161(5):924-5 | PubMed | Godleski LS, Sernyak MJ. Agranulocytosis after addition of risperidone to clozapine treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1996 May;153(5):735-6 | PubMed |
Godleski LS, Sernyak MJ. Agranulocytosis after addition of risperidone to clozapine treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1996 May;153(5):735-6 | PubMed | Kämpf P, Agelink MW, Naber D. Augmentation of clozapine with amisulpride: a promising therapeutic approach to refractory schizophrenic symptoms. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2005 Jan;38(1):39-40 | PubMed |
Kämpf P, Agelink MW, Naber D. Augmentation of clozapine with amisulpride: a promising therapeutic approach to refractory schizophrenic symptoms. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2005 Jan;38(1):39-40 | PubMed | Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Radwan M, Schwartz B, Dorfman-Etrog P, et al. Sulpiride augmentation in people with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry. 1997 Dec;171:569-73 | PubMed |
Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Radwan M, Schwartz B, Dorfman-Etrog P, et al. Sulpiride augmentation in people with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Psychiatry. 1997 Dec;171:569-73 | PubMed | Ziegenbein M, Wittmann G, Kropp S. Aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical observation. Clin Drug Investig. 2006;26(3):117-24 | PubMed |
Ziegenbein M, Wittmann G, Kropp S. Aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical observation. Clin Drug Investig. 2006;26(3):117-24 | PubMed | Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Weizman A. Sulpiride adjunction to clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients: a preliminary case series study. Eur Psychiatry. 1997;12(3):152-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Shiloh R, Zemishlany Z, Aizenberg D, Weizman A. Sulpiride adjunction to clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients: a preliminary case series study. Eur Psychiatry. 1997;12(3):152-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Muscatello MR, Bruno A, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Scimeca G, Di Nardo F, et al. Effect of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2011 Apr;127(1-3):93-9 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Muscatello MR, Bruno A, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Scimeca G, Di Nardo F, et al. Effect of aripiprazole augmentation of clozapine in schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2011 Apr;127(1-3):93-9 | CrossRef | PubMed | Gunduz-Bruce H, Oliver S, Gueorguieva R, Forselius-Bielen K, D'Souza DC, Zimolo Z, et al. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial responders with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2013 Feb;143(2-3):344-7 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gunduz-Bruce H, Oliver S, Gueorguieva R, Forselius-Bielen K, D'Souza DC, Zimolo Z, et al. Efficacy of pimozide augmentation for clozapine partial responders with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2013 Feb;143(2-3):344-7 | CrossRef | PubMed | Nielsen J, Emborg C, Gydesen S, Dybbro J, Aagaard J, Haderup K, et al. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Apr;32(2):173-8 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Nielsen J, Emborg C, Gydesen S, Dybbro J, Aagaard J, Haderup K, et al. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2012 Apr;32(2):173-8 | CrossRef | PubMed | Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on body weight and clinical efficacy in schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010 Sep;13(8):1115-25 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade RD, et al. Effects of adjunctive treatment with aripiprazole on body weight and clinical efficacy in schizophrenia patients treated with clozapine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010 Sep;13(8):1115-25 | CrossRef | PubMed | Henderson DC, Kunkel L, Nguyen DD, Borba CP, Daley TB, Louie PM, et al. An exploratory open-label trial of aripiprazole as an adjuvant to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006 Feb;113(2):142-7 | PubMed |
Henderson DC, Kunkel L, Nguyen DD, Borba CP, Daley TB, Louie PM, et al. An exploratory open-label trial of aripiprazole as an adjuvant to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2006 Feb;113(2):142-7 | PubMed | Peng H, Kuang Y, & Huang X. A control study of risperidone in combination with clozapine in treating refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Modern Clinical Medical Bioengineering, 2001.7(2), 100–102. | Link |
Peng H, Kuang Y, & Huang X. A control study of risperidone in combination with clozapine in treating refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Modern Clinical Medical Bioengineering, 2001.7(2), 100–102. | Link | Liu QH, Li XL. A comparative study on the efficacy of combining risperidone and clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Mental Medical Journal, (2001). 14(1), 28–30 | Link |
Liu QH, Li XL. A comparative study on the efficacy of combining risperidone and clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Mental Medical Journal, (2001). 14(1), 28–30 | Link | Friedman JI, Lindenmayer JP, Alcantara F, Bowler S, Parak M, et al. Pimozide augmentation of clozapine inpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder unresponsive to clozapine monotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 May;36(6):1289-95. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Friedman JI, Lindenmayer JP, Alcantara F, Bowler S, Parak M, et al. Pimozide augmentation of clozapine inpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder unresponsive to clozapine monotherapy. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 May;36(6):1289-95. | CrossRef | PubMed | Sénéchal A, Landry P, Deschamps R, Lessard M. [Neutropenia in a patient treated with clozapine in combination with other psychotropic drugs]. Encephale. 2002 Nov-Dec;28(6 Pt 1):567-9 | PubMed |
Sénéchal A, Landry P, Deschamps R, Lessard M. [Neutropenia in a patient treated with clozapine in combination with other psychotropic drugs]. Encephale. 2002 Nov-Dec;28(6 Pt 1):567-9 | PubMed | Honer W, MacEwan GW, Williams R, Falkai P, McKenna PJ, Pomarol-Clotet E, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of augmentation of clozapine with risperidone. SCHIZOPHRENIA BULLETIN, (2005). 31(2), 487 | Link |
Honer W, MacEwan GW, Williams R, Falkai P, McKenna PJ, Pomarol-Clotet E, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of augmentation of clozapine with risperidone. SCHIZOPHRENIA BULLETIN, (2005). 31(2), 487 | Link | Akdede BB, Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Alptekin K, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, et al. A double-blind study of combination of clozapine with risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: effects on cognition. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;67(12):1912-9 | PubMed |
Akdede BB, Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Alptekin K, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, et al. A double-blind study of combination of clozapine with risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: effects on cognition. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006 Dec;67(12):1912-9 | PubMed | Patel JK, Salzman C, Green AI, Tsuang MT. Chronic schizophrenia: response to clozapine, risperidone, and paroxetine. Am J Psychiatry. 1997 Apr;154(4):543-6. | PubMed |
Patel JK, Salzman C, Green AI, Tsuang MT. Chronic schizophrenia: response to clozapine, risperidone, and paroxetine. Am J Psychiatry. 1997 Apr;154(4):543-6. | PubMed | Adesanya A, Pantelis C. Adjunctive risperidone treatment in patients with 'clozapine-resistant schizophrenia'. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2000 Jun;34(3):533-4 | PubMed |
Adesanya A, Pantelis C. Adjunctive risperidone treatment in patients with 'clozapine-resistant schizophrenia'. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2000 Jun;34(3):533-4 | PubMed | Lim S, Pralea C, Schnitt J, Bowers MB Jr, Cooper C. Possible increased efficacy of low-dose clozapine when combined with aripiprazole. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;65(9):1284-5 | PubMed |
Lim S, Pralea C, Schnitt J, Bowers MB Jr, Cooper C. Possible increased efficacy of low-dose clozapine when combined with aripiprazole. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;65(9):1284-5 | PubMed | Honer WG, Thornton AE, Chen EY, Chan RC, Wong JO, Bergmann A, et al. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone with refractory schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2006 Feb 2;354(5):472-82 | PubMed |
Honer WG, Thornton AE, Chen EY, Chan RC, Wong JO, Bergmann A, et al. Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone with refractory schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2006 Feb 2;354(5):472-82 | PubMed | de Groot IW, Heck AH, van Harten PN. Addition of risperidone to clozapine therapy in chronically psychotic inpatients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001 Feb;62(2):129-30 | PubMed |
de Groot IW, Heck AH, van Harten PN. Addition of risperidone to clozapine therapy in chronically psychotic inpatients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001 Feb;62(2):129-30 | PubMed | Beauchemin MA, Millaud F, Nguyen KA. A case of neuroleptic malignant syndrome with clozapine and risperidone. Can J Psychiatry. 2002 Nov;47(9):886 | PubMed |
Beauchemin MA, Millaud F, Nguyen KA. A case of neuroleptic malignant syndrome with clozapine and risperidone. Can J Psychiatry. 2002 Nov;47(9):886 | PubMed | Benedetti A, Di Paolo A, Lastella M, Casamassima F, Candiracci C, Litta A, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with aripiprazole in severe psychotic bipolar and schizoaffective disorders: a pilot study. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2010 Jun 4;6:30-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Benedetti A, Di Paolo A, Lastella M, Casamassima F, Candiracci C, Litta A, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with aripiprazole in severe psychotic bipolar and schizoaffective disorders: a pilot study. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2010 Jun 4;6:30-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Mossaheb N, Sacher J, Wiesegger G, Klein N, CJ, Asenbaum S, Kasper S. Haloperidol in combination with clozapine in treatment-refractory patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology, (2006).16, 416. | Link |
Mossaheb N, Sacher J, Wiesegger G, Klein N, CJ, Asenbaum S, Kasper S. Haloperidol in combination with clozapine in treatment-refractory patients with schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology, (2006).16, 416. | Link | Munro J, Matthiasson P, Osborne S, Travis M, Purcell S, Cobb AM, et al. Amisulpride augmentation of clozapine: an open non-randomized study in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2004 Oct;110(4):292-8 | PubMed |
Munro J, Matthiasson P, Osborne S, Travis M, Purcell S, Cobb AM, et al. Amisulpride augmentation of clozapine: an open non-randomized study in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2004 Oct;110(4):292-8 | PubMed | Rhoads E. Polypharmacy of 2 atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000 Sep;61(9):678-80 | PubMed |
Rhoads E. Polypharmacy of 2 atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000 Sep;61(9):678-80 | PubMed | Koreen AR, Lieberman JA, Kronig M, Cooper TB. Cross-tapering clozapine and risperidone. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Nov;152(11):1690 | PubMed |
Koreen AR, Lieberman JA, Kronig M, Cooper TB. Cross-tapering clozapine and risperidone. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Nov;152(11):1690 | PubMed | Kaye NS. Ziprasidone augmentation of clozapine in 11 patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003 Feb;64(2):215-6 | PubMed |
Kaye NS. Ziprasidone augmentation of clozapine in 11 patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003 Feb;64(2):215-6 | PubMed | Friedman J, Ault K, Powchik P. Pimozide augmentation for the treatment of schizophrenic patients who are partial responders to clozapine. Biol Psychiatry. 1997 Sep 15;42(6):522-3 | PubMed |
Friedman J, Ault K, Powchik P. Pimozide augmentation for the treatment of schizophrenic patients who are partial responders to clozapine. Biol Psychiatry. 1997 Sep 15;42(6):522-3 | PubMed | Ni J, Jang L, & Hong X. Therapeutic effects of clozapine, risperidone and their combination in the treatment of schizophrenia. Health Psychol J,(2001). 3, 181–182. | Link |
Ni J, Jang L, & Hong X. Therapeutic effects of clozapine, risperidone and their combination in the treatment of schizophrenia. Health Psychol J,(2001). 3, 181–182. | Link | Stubbs JH, Haw CM, Staley CJ, Mountjoy CQ. Augmentation with sulpiride for a schizophrenic patient partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Nov;102(5):390-3; discussion 393-4 | PubMed |
Stubbs JH, Haw CM, Staley CJ, Mountjoy CQ. Augmentation with sulpiride for a schizophrenic patient partially responsive to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Nov;102(5):390-3; discussion 393-4 | PubMed | Rajarethinam R, Gilani S, Tancer M, DeQuardo J. Augmentation of clozapine partial responders with conventional antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2003 Mar 1;60(1):97-8 | PubMed |
Rajarethinam R, Gilani S, Tancer M, DeQuardo J. Augmentation of clozapine partial responders with conventional antipsychotics. Schizophr Res. 2003 Mar 1;60(1):97-8 | PubMed | Mitsonis CI, Dimopoulos NP, Mitropoulos PA, Kararizou EG, Katsa AN, Tsakiris FE, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in the management of residual symptoms in clozapine-treated outpatients with chronic schizophrenia: An open-label pilot study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Mar 30;31(2):373-7 | PubMed |
Mitsonis CI, Dimopoulos NP, Mitropoulos PA, Kararizou EG, Katsa AN, Tsakiris FE, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in the management of residual symptoms in clozapine-treated outpatients with chronic schizophrenia: An open-label pilot study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Mar 30;31(2):373-7 | PubMed | Weiner E, Conley RR, Ball MP, Feldman S, Gold JM, Kelly DL, et al. Adjunctive risperidone for partially responsive people with schizophrenia treated with clozapine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Oct;35(11):2274-83 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Weiner E, Conley RR, Ball MP, Feldman S, Gold JM, Kelly DL, et al. Adjunctive risperidone for partially responsive people with schizophrenia treated with clozapine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Oct;35(11):2274-83 | CrossRef | PubMed | Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, et al. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;162(1):130-6 | PubMed |
Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, et al. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;162(1):130-6 | PubMed | Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Walsh JP, Culhane MA, Goff DC. Risperidone augmentation for schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Res. 2007 May;92(1-3):90-4 | PubMed |
Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Walsh JP, Culhane MA, Goff DC. Risperidone augmentation for schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Res. 2007 May;92(1-3):90-4 | PubMed | McCarthy RH, Terkelsen KG. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1995 Mar;28(2):61-3 | PubMed |
McCarthy RH, Terkelsen KG. Risperidone augmentation of clozapine. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1995 Mar;28(2):61-3 | PubMed | Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine-treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 May;69(5):720-31 | PubMed |
Chang JS, Ahn YM, Park HJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Kang UG, et al. Aripiprazole augmentation in clozapine-treated patients with refractory schizophrenia: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 May;69(5):720-31 | PubMed | Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade R, et al. Weight change on aripiprazole-clozapine combination in schizophrenic patients with weight gain and suboptimal response on clozapine: 16-week double-blind study. European Psychiatry, (2008). 23, S114–S115. | CrossRef |
Fleischhacker WW, Heikkinen ME, Olié JP, Landsberg W, Dewaele P, McQuade R, et al. Weight change on aripiprazole-clozapine combination in schizophrenic patients with weight gain and suboptimal response on clozapine: 16-week double-blind study. European Psychiatry, (2008). 23, S114–S115. | CrossRef | Raskin S, Katz G, Zislin Z, Knobler HY, Durst R. Clozapine and risperidone: combination/augmentation treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a preliminary observation. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Apr;101(4):334-6 | PubMed |
Raskin S, Katz G, Zislin Z, Knobler HY, Durst R. Clozapine and risperidone: combination/augmentation treatment of refractory schizophrenia: a preliminary observation. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2000 Apr;101(4):334-6 | PubMed | Tyson SC, Devane CL, Risch SC. Pharmacokinetic interaction between risperidone and clozapine. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;152(9):1401-2 | PubMed |
Tyson SC, Devane CL, Risch SC. Pharmacokinetic interaction between risperidone and clozapine. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;152(9):1401-2 | PubMed | Xao H. A double-blind comparative study of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Sichuan Ment Health, (1999).12, 250–251 | Link |
Xao H. A double-blind comparative study of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Sichuan Ment Health, (1999).12, 250–251 | Link | Kontaxakis VP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Stamouli SS, Christodoulou GN. Toxic interaction between risperidone and clozapine: a case report. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;26(2):407-9 | PubMed |
Kontaxakis VP, Havaki-Kontaxaki BJ, Stamouli SS, Christodoulou GN. Toxic interaction between risperidone and clozapine: a case report. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;26(2):407-9 | PubMed | Mowerman S, Siris SG. Adjunctive loxapine in a clozapine-resistant cohort of schizophrenic patients. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Dec;8(4):193-7 | PubMed |
Mowerman S, Siris SG. Adjunctive loxapine in a clozapine-resistant cohort of schizophrenic patients. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Dec;8(4):193-7 | PubMed | Lerner V, Bergman J, Borokhov A, Loewenthal U, Miodownik C. Augmentation with amisulpride for schizophrenic patients nonresponsive to antipsychotic monotherapy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005 Mar-Apr;28(2):66-71 | PubMed |
Lerner V, Bergman J, Borokhov A, Loewenthal U, Miodownik C. Augmentation with amisulpride for schizophrenic patients nonresponsive to antipsychotic monotherapy. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005 Mar-Apr;28(2):66-71 | PubMed | Morera AL, Barreiro P, Cano-Muñoz JL. Risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1999 Apr;99(4):305-6; discussion 306-7 | PubMed |
Morera AL, Barreiro P, Cano-Muñoz JL. Risperidone and clozapine combination for the treatment of refractory schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1999 Apr;99(4):305-6; discussion 306-7 | PubMed | Assion HJ, Reinbold H, Lemanski S, Basilowski M, Juckel G. Amisulpride augmentation in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive or unresponsive to clozapine. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2008 Jan;41(1):24-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-993209 | PubMed |
Assion HJ, Reinbold H, Lemanski S, Basilowski M, Juckel G. Amisulpride augmentation in patients with schizophrenia partially responsive or unresponsive to clozapine. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2008 Jan;41(1):24-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-993209 | PubMed | Henderson DC, Goff DC. Risperidone as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenics. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Sep;57(9):395-7 | PubMed |
Henderson DC, Goff DC. Risperidone as an adjunct to clozapine therapy in chronic schizophrenics. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Sep;57(9):395-7 | PubMed | Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Kivircik Akdede BB, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double-blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;66(1):63-72 | PubMed |
Anil Yağcioğlu AE, Kivircik Akdede BB, Turgut TI, Tümüklü M, Yazici MK, Alptekin K, et al. A double-blind controlled study of adjunctive treatment with risperidone in schizophrenic patients partially responsive to clozapine: efficacy and safety. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;66(1):63-72 | PubMed | Muscatello MR, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Lamberti Castronuovo E, Abenavoli E, Scimeca G, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with ziprasidone in refractory schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Feb;34(1):129-33. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Muscatello MR, Pandolfo G, Micò U, Lamberti Castronuovo E, Abenavoli E, Scimeca G, et al. Augmentation of clozapine with ziprasidone in refractory schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Feb;34(1):129-33. | CrossRef | PubMed | Si S, Yuan C. A comparative trial of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Arch Psychiatry, (1999).12, 17–20 | Link |
Si S, Yuan C. A comparative trial of the effects of sulpiride combined with clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Arch Psychiatry, (1999).12, 17–20 | Link | Chong SA, Tan CH, Lee HS. Atrial ectopics with clozapine-risperidone combination. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1997 Apr;17(2):130-1 | PubMed |
Chong SA, Tan CH, Lee HS. Atrial ectopics with clozapine-risperidone combination. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1997 Apr;17(2):130-1 | PubMed | Taylor CG, Flynn SW, Altman S, Ehmann T, MacEwan GW, Honer WG. An open trial of risperidone augmentation of partial response to clozapine. Schizophr Res. 2001 Mar 1;48(1):155-8 | PubMed |
Taylor CG, Flynn SW, Altman S, Ehmann T, MacEwan GW, Honer WG. An open trial of risperidone augmentation of partial response to clozapine. Schizophr Res. 2001 Mar 1;48(1):155-8 | PubMed | Gupta S, Sonnenberg SJ, Frank B. Olanzapine augmentation of clozapine. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1998 Sep;10(3):113-5 | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gupta S, Sonnenberg SJ, Frank B. Olanzapine augmentation of clozapine. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 1998 Sep;10(3):113-5 | CrossRef | PubMed | Zink M, Knopf U, Henn FA, Thome J. Combination of clozapine and amisulpride in treatment-resistant schizophrenia--case reports and review of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004 Jan;37(1):26-31 | PubMed |
Zink M, Knopf U, Henn FA, Thome J. Combination of clozapine and amisulpride in treatment-resistant schizophrenia--case reports and review of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004 Jan;37(1):26-31 | PubMed | Haibing Z, Guohang Y, Deqing D. A study of clozapine combined with or without pipotiazine palmitate in refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine, (2002). 12(1), 15–17 | Link |
Haibing Z, Guohang Y, Deqing D. A study of clozapine combined with or without pipotiazine palmitate in refractory schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine, (2002). 12(1), 15–17 | Link | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: prevention and management 2014. | Link |
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: prevention and management 2014. | Link | American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia Second Edition,2010. | Link |
American Psychiatric Association. Practice guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia Second Edition,2010. | Link | Sheng-Chang Wang, MD ,M Sc, Amisulpride Augmentation Therapy for Clozapine-resistant Schizophrenic Patients: A 14-week Randomized, Double-blind and Placebo-controlled Trial | Link |
Sheng-Chang Wang, MD ,M Sc, Amisulpride Augmentation Therapy for Clozapine-resistant Schizophrenic Patients: A 14-week Randomized, Double-blind and Placebo-controlled Trial | Link | Aalborg Psychiatric Hospital, Research Unit. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole - A double-blinded randomized placebo study (SERCLOZ) - SERCLOZ | Link |
Aalborg Psychiatric Hospital, Research Unit. Augmenting clozapine with sertindole - A double-blinded randomized placebo study (SERCLOZ) - SERCLOZ | Link |Systematization of initiatives in sexual and reproductive health about good practices criteria in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in primary health care in Chile
Clinical, psychological, social, and family characterization of suicidal behavior in Chilean adolescents: a multiple correspondence analysis








