Key Words: Ralstonia, Bacterial Infections, Bacteremia, Catheter-Related Infections
Abstract
The first report of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in Peru is presented. The patient was a pediatric cancer patient with a long-term central venous access device. For the diagnosis, the MicroScan Walk Away 96 automated system was used. 16S rDNA was amplified by conventional PCR, and the bacterial genus and species were identified by genetic sequencing. In addition, the bacterial resistance profile to major antimicrobials was determined. The article discusses the need to actively monitor Ralstonia mannitolilytica, especially in hospital areas of immunocompromised patients.
Main messages
|
Introduction
Ralstonia spp are described as a genus of non-fermenting gram-negative bacilli that are associated with nosocomial infections. Infection by this microorganism is associated with contaminated solutions (e.g., water for injection and saline) or disinfectants (contaminated chlorhexidine) [1]. Ralstonia mannitolilytica is one of the three species of the genus Ralstonia mainly described as etiological agents of bacteremia in hospital outbreaks, with particular importance in hospital services of onco-hematologic patients [2],[3],[4]. Automated laboratory methods may misidentify this genus as Burkholderia cepacia complex or Pseudomonas fluorescens, so confirmation by molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is necessary [5].
We present the case of an immunocompromised pediatric patient with long-standing catheter-related bacteremia, in whom infection by this bacterium was determined by amplification and subsequent genetic sequencing of recombinant DNA, 16S rDNA.
Case report
A 5-year-old male patient presented with a diagnosis of acute B-lymphoid leukemia undergoing chemotherapy and long-term port catheterization. He has a history of presenting bacteremia due to carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa during previous courses of treatment of the underlying disease.
In the current course of the disease, the patient is hospitalized for consolidation chemotherapy in the onco-hematology ward. On physical examination, the patient was hemodynamically stable, with adequate nutrition and hydration. In the examination by apparatus and systems, he presented in the thorax and lung: vesicular murmur passes in both hemithorax; cardiovascular system: rhythmic heart sounds of good intensity, no murmurs were auscultated, no S3, no jugular ingurgitation; skin: warm and hydrated, signs of inflammation around the catheter, no signs suggestive of endocarditis were appreciated. The rest of the physical examination did not provide any new data. After opening the port catheter, she presented fever and chills, so peripheral blood and central venous catheter cultures were requested. Empirical treatment with piperacillin-tazobactam was then started. Laboratory tests showed a hemogram with leukocytosis and neutrophils with elevated differential count and an increase in acute-phase reactants (C-reactive protein [CRP]: 88 mg/L). At 48 hours, growth of non-pigmented gram-negative bacilli, oxidase, and catalase-positive in both culture samples was reported. With these results, removal of the port catheter was ordered.
The final result of the automated MicroScan Walk Away 96® kit identified Ralstonia pickettii with a susceptibility profile sensitive to piperacillin-tazobactam (Table 1).
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility test.
with fever. Due to this, a second series of blood cultures were performed, which resulted in the isolation and growth of the same microorganism. With the information from the susceptibility profile, it was decided to continue with the initial antimicrobial coverage, completing a total of 17 days. After that time, the catheter was removed with favorable clinical evolution, remission of fever, and a drop of acute-phase reactants. Follow-up blood cultures were negative. The patient continued with his chemotherapy treatment without intercurrence.
Microbiological isolation and initial identification of the Ralstonia strain were performed using the MicroScan Walk Away 96 automatic system in the Guillermo Almenara Irigoyen National Hospital microbiology laboratory (Ralstonia pickettii). For confirmation, this strain was sent to the Molecular Biology Laboratory of the Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas/Instituto de Investigación Nutricional, Lima, Peru. At this facility, the 16S rDNA gene was amplified by conventional PCR, and the amplified PCR products were observed by agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). These products were purified for direct sequencing by the Sanger method (Macrogen® Korea). The sequences obtained were compared with the reference sequence from the BLAST® platform, National Library of Medicine, USA. The isolate was identified as Ralstonia mannitolilytica (99.51% identity in the Blast report). The molecular profile of the isolate was registered in GenBank with the accession code MW020025.1.
Figure 1. Bands in agarose gel electrophoresis after polymerase chain reaction.
As part of the microbiological surveillance program at the hospital, there were no previous reports of Ralstonia mannitolilytica, and no isolation of this microorganism was achieved in the environmental cultures obtained.
Discussion
Ralstonia mannitolilytica, previously called Pseudomonas thomasii and Ralstonia picketti biovar3/thomasii [6], is an emerging pathogen in South America and has been previously described as a causative agent of catheter-related bacteremia in Argentina [7]. This microorganism has also been described as a cause of bacteremia in newborns in Brazil [8]. We present the first case of catheter-related bacteremia due to this pathogen in Peru.
The isolation of this bacterium in a unit of onco-hematologic patients compels us to investigate a possible outbreak. However, no previous or subsequent cases (up to six months later) were identified during surveillance cultures in the hospital. Environmental microbiological cultures were also negative. The study of previous nosocomial outbreaks caused by other bacterial pathogens suggests the possibility of other sources of contamination that were not analyzed in the study of this case, such as saline solutions and infusion systems (filters) [2],[3]. For this reason, the source of infection could not be defined.
It is known that over 80% of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia reported in the literature is related to a central venous catheter. In general, this condition has a good medical prognosis, even in patients with hematological malignancies [4]. Removal of the catheter and using a single parenteral antimicrobial agent are recommended in managing these patients, as was performed in this case [3].
Antimicrobial susceptibility is variable; however, we highlight that this germ is intrinsically resistant to colistin. The automated team reported susceptibilities based on Ralstonia picketti, and clinical response to treatment with piperacillin/tazobactam, which has shown susceptibility in most cases previously reported in the medical literature, was observed. Other agents with a lower resistance rate are ampicillin-sulbactam and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole [9]. In the series of Boattini et al., a 100% susceptibility to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is described. However, the present case showed resistance to this drug [4]. It is necessary to consider a specific minimum inhibitory concentration for this pathogenic microorganism.
Ralstonia mannitolilytica is considered a rare pathogen, so it may not be considered in routine microbiological diagnosis [10]. This limits the epidemiological characterization of in-hospital microorganisms. The implementation of molecular diagnostic techniques offers the possibility to characterize these pathogens and describe their clinical significance.
Conclusion
As learning points, this report demonstrates the need to actively monitor for the presence of Ralstonia mannitolilytica, especially in immunocompromised areas.
Although only one case was identified, it is necessary to routinely implement saline or water for injection cultures that could condition the appearance of microorganisms that could infect high-risk patient groups.
It is important to consider the molecular epidemiology of nosocomial infections to have an overview of the microorganisms capable of causing disease. With this, it is possible to optimize infection control programs and rational use of antimicrobials based on the information obtained.
Notes
Authorship contributions
GPL: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, research, resources, data curation, preparation of original draft, review and editing. AMM: conceptualization, research, data curation, preparation of original draft, review and editing. FSF: formal analysis, research, data curation, preparation of original draft, review and editing. LMC, HJQ: methodology, research, data curation, preparation of original draft, review and editing. JDVM: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, research, resources, preparation of original draft, review and editing. MAL: methodology, formal analysis, research, resources, preparation of original draft, review and editing. RAO: methodology, research, resources, preparation of original draft, review and editing. WSC: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, research, resources, data curation, preparation of original draft, review and editing.
Competing interests
The authors completed the ICMJE conflict of interest statement and declared that they received no funds for the realization of this article; they have no financial relationships with organizations that may have an interest in the published article in the last three years and have no other relationships or activities that may influence the publication of the article. Forms can be requested by contacting the responsible author or the Editorial Committee of the Journal.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors.
Ethics
Written authorization and informed consent were obtained from the mother as the legal representative of the minor patient for publication of this clinical case and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal upon request.
This case report did not require the approval of the ethics committee of the hospital where it was performed. This is because the case was described as part of the hospital epidemiological surveillance program for multidrug-resistant microorganisms.
Availability of data
Not applicable.
Language of submission
Spanish.

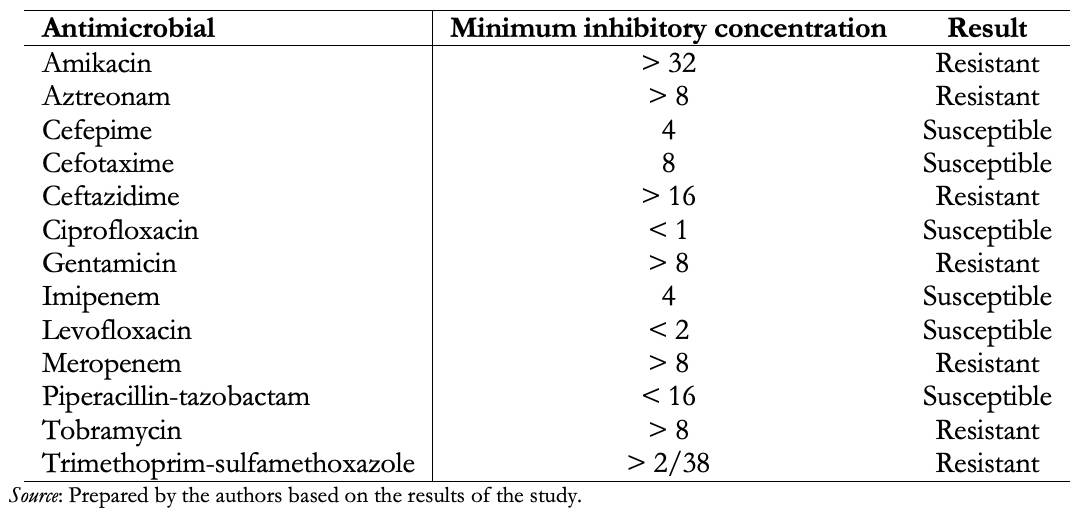 Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility test.
Table 1. Antimicrobial susceptibility test.

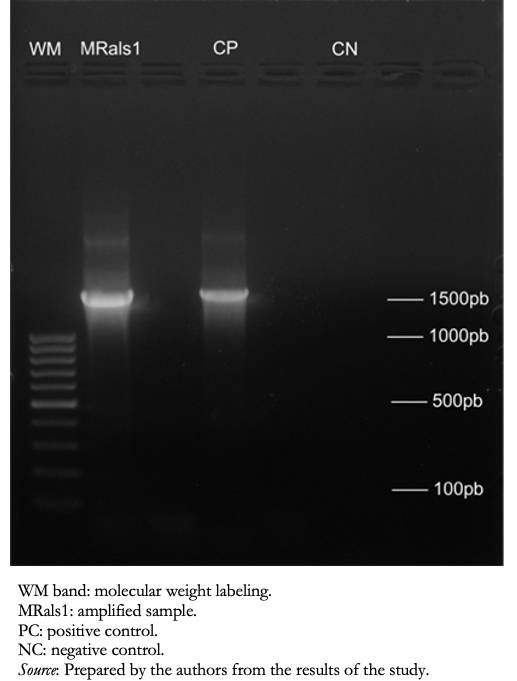 Figure 1. Bands in agarose gel electrophoresis after polymerase chain reaction.
Figure 1. Bands in agarose gel electrophoresis after polymerase chain reaction.

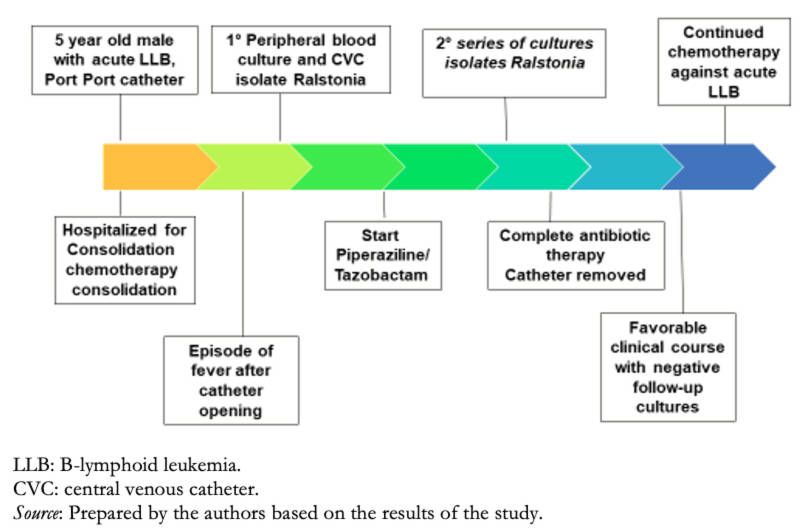 Figure 2. Timeline.
Figure 2. Timeline.
 Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.
Esta obra de Medwave está bajo una licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 3.0 Unported. Esta licencia permite el uso, distribución y reproducción del artículo en cualquier medio, siempre y cuando se otorgue el crédito correspondiente al autor del artículo y al medio en que se publica, en este caso, Medwave.

The first report of Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in Peru is presented. The patient was a pediatric cancer patient with a long-term central venous access device. For the diagnosis, the MicroScan Walk Away 96 automated system was used. 16S rDNA was amplified by conventional PCR, and the bacterial genus and species were identified by genetic sequencing. In addition, the bacterial resistance profile to major antimicrobials was determined. The article discusses the need to actively monitor Ralstonia mannitolilytica, especially in hospital areas of immunocompromised patients.
 Authors:
Giancarlo Pérez Lazo[1], Wilmer Silva Caso[2], Adriana Morales Moreno[1], Fernando Soto Febres[1], Liliana Morales Castillo[3], Hugo Jove Químper[3], Juana Del Valle Mendoza[2,4], Miguel Angel Aguilar Luis[2,4], Ronald Aquino Ortega[4]
Authors:
Giancarlo Pérez Lazo[1], Wilmer Silva Caso[2], Adriana Morales Moreno[1], Fernando Soto Febres[1], Liliana Morales Castillo[3], Hugo Jove Químper[3], Juana Del Valle Mendoza[2,4], Miguel Angel Aguilar Luis[2,4], Ronald Aquino Ortega[4]
Affiliation:
[1] Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Nacional Guillermo Almenara, EsSalud, Lima, Perú
[2] Escuela de Medicina, Centro de Investigación e Innovación de la Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas, Lima, Perú
[3] Servicio de Microbiología, Hospital Nacional Guillermo Almenara, EsSalud, Lima, Perú
[4] Instituto de Investigación Nutricional, Lima, Perú
E-mail: gian_will@hotmail.com
Author address:
[1] Av. Primavera 2390
Monterrico, Lima
Perú

Citation: Pérez Lazo G, Silva Caso W, Morales Moreno A, Soto Febres F, Morales Castillo L, Jove Químper H, et al. Bacteremia due to Ralstonia mannitolilytica: A report of the first case in Peru. Medwave 2021;21(04):e8200 doi: 10.5867/medwave.2021.04.8200
Submission date: 22/12/2020
Acceptance date: 16/4/2021
Publication date: 26/5/2021
Origin: Not commissioned.
Type of review: Externally peer-reviewed by four reviewers, double-blind.

Comments (0)
We are pleased to have your comment on one of our articles. Your comment will be published as soon as it is posted. However, Medwave reserves the right to remove it later if the editors consider your comment to be: offensive in some sense, irrelevant, trivial, contains grammatical mistakes, contains political harangues, appears to be advertising, contains data from a particular person or suggests the need for changes in practice in terms of diagnostic, preventive or therapeutic interventions, if that evidence has not previously been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
No comments on this article.
To comment please log in
 Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics.
Medwave provides HTML and PDF download counts as well as other harvested interaction metrics. There may be a 48-hour delay for most recent metrics to be posted.

- Ryan MP, Adley CC. Ralstonia spp.: emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;33(3):291-304. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Gröbner S, Heeg P, Autenrieth IB, Schulte B. Monoclonal outbreak of catheter- related bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica on two haemato-oncology wards. J Infect. 2007 Dec;55(6):539-44. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Lucarelli C, Di Domenico EG, Toma L, Bracco D, Prignano G, Fortunati M, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica infections in an oncologic day ward: description of a cluster among high-risk patients. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017 Feb 7;6:20. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Boattini M, Bianco G, Biancone L, Cavallo R, Costa C. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteraemia: a case report and literature review. Infez Med. 2018 Dec 1;26(4):374-378. | PubMed |
- Daxboeck F, Stadler M, Assadian O, Marko E, Hirschl AM, Koller W. Characterization of clinically isolated Ralstonia mannitolilytica strains using random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing and antimicrobial sensitivity, and comparison of the classification efficacy of phenotypic and genotypic assays. J Med Microbiol. 2005 Jan;54(Pt 1):55-61. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- De Baere T, Steyaert S, Wauters G, Des Vos P, Goris J, Coenye T, et al. Classification of Ralstonia pickettii biovar 3/'thomasii' strains (Pickett 1994) and of new isolates related to nosocomial recurrent meningitis as Ralstonia mannitolytica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001 Mar;51(Pt 2):547-558. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Soloaga R, Carrión N, Pidone JC, Suar MB, Salinas A, Guelfand L, et al. Catheter-related bloodstream infection by Ralstonia mannitolilytica. Acta Bioquim Clin Latinoam. Jan 2011;45(1):109-112. [Internet] | Link |
- Souza DC, Palmeiro JK, Maestri AC, Cogo LL, Rauen CH, Graaf ME, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2018 Sep-Oct;51(5):709-711. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Basso M, Venditti C, Raponi G, Navazio AS, Alessandri F, Giombini E, et al. A case of persistent bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica and Ralstonia pickettii in an intensive care unit. Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Aug 2;12:2391-2395. | CrossRef | PubMed |
- Lampropoulos P, Gkentzi D, Tzifas S, Kapnisi G, Karatza A, Kolonitsiou F, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica, an unusual pathogen in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: a case of neonatal sepsis and literature review. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2020 Mar 30. | CrossRef | PubMed |
 Ryan MP, Adley CC. Ralstonia spp.: emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;33(3):291-304. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Ryan MP, Adley CC. Ralstonia spp.: emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;33(3):291-304. | CrossRef | PubMed | Gröbner S, Heeg P, Autenrieth IB, Schulte B. Monoclonal outbreak of catheter- related bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica on two haemato-oncology wards. J Infect. 2007 Dec;55(6):539-44. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Gröbner S, Heeg P, Autenrieth IB, Schulte B. Monoclonal outbreak of catheter- related bacteraemia by Ralstonia mannitolilytica on two haemato-oncology wards. J Infect. 2007 Dec;55(6):539-44. | CrossRef | PubMed | Lucarelli C, Di Domenico EG, Toma L, Bracco D, Prignano G, Fortunati M, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica infections in an oncologic day ward: description of a cluster among high-risk patients. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017 Feb 7;6:20. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Lucarelli C, Di Domenico EG, Toma L, Bracco D, Prignano G, Fortunati M, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica infections in an oncologic day ward: description of a cluster among high-risk patients. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017 Feb 7;6:20. | CrossRef | PubMed | Boattini M, Bianco G, Biancone L, Cavallo R, Costa C. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteraemia: a case report and literature review. Infez Med. 2018 Dec 1;26(4):374-378. | PubMed |
Boattini M, Bianco G, Biancone L, Cavallo R, Costa C. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteraemia: a case report and literature review. Infez Med. 2018 Dec 1;26(4):374-378. | PubMed | Daxboeck F, Stadler M, Assadian O, Marko E, Hirschl AM, Koller W. Characterization of clinically isolated Ralstonia mannitolilytica strains using random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing and antimicrobial sensitivity, and comparison of the classification efficacy of phenotypic and genotypic assays. J Med Microbiol. 2005 Jan;54(Pt 1):55-61. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Daxboeck F, Stadler M, Assadian O, Marko E, Hirschl AM, Koller W. Characterization of clinically isolated Ralstonia mannitolilytica strains using random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) typing and antimicrobial sensitivity, and comparison of the classification efficacy of phenotypic and genotypic assays. J Med Microbiol. 2005 Jan;54(Pt 1):55-61. | CrossRef | PubMed | De Baere T, Steyaert S, Wauters G, Des Vos P, Goris J, Coenye T, et al. Classification of Ralstonia pickettii biovar 3/'thomasii' strains (Pickett 1994) and of new isolates related to nosocomial recurrent meningitis as Ralstonia mannitolytica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001 Mar;51(Pt 2):547-558. | CrossRef | PubMed |
De Baere T, Steyaert S, Wauters G, Des Vos P, Goris J, Coenye T, et al. Classification of Ralstonia pickettii biovar 3/'thomasii' strains (Pickett 1994) and of new isolates related to nosocomial recurrent meningitis as Ralstonia mannitolytica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001 Mar;51(Pt 2):547-558. | CrossRef | PubMed | Soloaga R, Carrión N, Pidone JC, Suar MB, Salinas A, Guelfand L, et al. Catheter-related bloodstream infection by Ralstonia mannitolilytica. Acta Bioquim Clin Latinoam. Jan 2011;45(1):109-112. [Internet] | Link |
Soloaga R, Carrión N, Pidone JC, Suar MB, Salinas A, Guelfand L, et al. Catheter-related bloodstream infection by Ralstonia mannitolilytica. Acta Bioquim Clin Latinoam. Jan 2011;45(1):109-112. [Internet] | Link | Souza DC, Palmeiro JK, Maestri AC, Cogo LL, Rauen CH, Graaf ME, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2018 Sep-Oct;51(5):709-711. | CrossRef | PubMed |
Souza DC, Palmeiro JK, Maestri AC, Cogo LL, Rauen CH, Graaf ME, et al. Ralstonia mannitolilytica bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2018 Sep-Oct;51(5):709-711. | CrossRef | PubMed |Systematization of initiatives in sexual and reproductive health about good practices criteria in response to the COVID-19 pandemic in primary health care in Chile
Clinical, psychological, social, and family characterization of suicidal behavior in Chilean adolescents: a multiple correspondence analysis








